Servitization transforms traditional manufacturing by shifting focus from product sales to integrated services, enhancing customer value and fostering long-term relationships. Circular economy emphasizes resource efficiency through recycling, reuse, and sustainable design, minimizing environmental impact and waste in manufacturing processes. Explore how these innovative approaches redefine industry practices and drive sustainable growth.
Why it is important
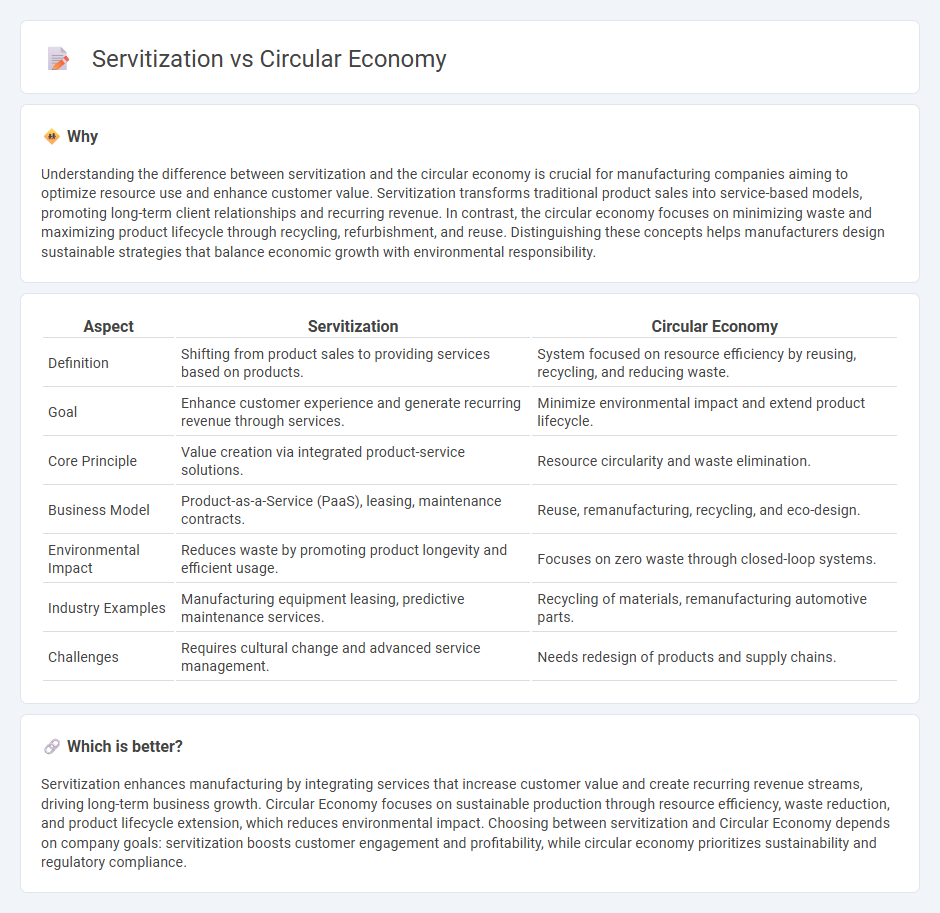
Understanding the difference between servitization and the circular economy is crucial for manufacturing companies aiming to optimize resource use and enhance customer value. Servitization transforms traditional product sales into service-based models, promoting long-term client relationships and recurring revenue. In contrast, the circular economy focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing product lifecycle through recycling, refurbishment, and reuse. Distinguishing these concepts helps manufacturers design sustainable strategies that balance economic growth with environmental responsibility.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Servitization | Circular Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shifting from product sales to providing services based on products. | System focused on resource efficiency by reusing, recycling, and reducing waste. |
| Goal | Enhance customer experience and generate recurring revenue through services. | Minimize environmental impact and extend product lifecycle. |
| Core Principle | Value creation via integrated product-service solutions. | Resource circularity and waste elimination. |
| Business Model | Product-as-a-Service (PaaS), leasing, maintenance contracts. | Reuse, remanufacturing, recycling, and eco-design. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste by promoting product longevity and efficient usage. | Focuses on zero waste through closed-loop systems. |
| Industry Examples | Manufacturing equipment leasing, predictive maintenance services. | Recycling of materials, remanufacturing automotive parts. |
| Challenges | Requires cultural change and advanced service management. | Needs redesign of products and supply chains. |
Which is better?
Servitization enhances manufacturing by integrating services that increase customer value and create recurring revenue streams, driving long-term business growth. Circular Economy focuses on sustainable production through resource efficiency, waste reduction, and product lifecycle extension, which reduces environmental impact. Choosing between servitization and Circular Economy depends on company goals: servitization boosts customer engagement and profitability, while circular economy prioritizes sustainability and regulatory compliance.
Connection
Servitization in manufacturing transforms traditional product-centric models into service-oriented offerings, enabling companies to extend product lifecycles and enhance resource efficiency. The circular economy complements servitization by promoting reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling, which reduce waste and lower environmental impact. Together, they drive sustainable manufacturing practices by integrating product services with closed-loop resource management systems.
Key Terms
Product-as-a-Service (PaaS)
Circular Economy emphasizes resource efficiency by minimizing waste through product lifecycle extension, recycling, and reuse, while Servitization shifts business models toward providing Product-as-a-Service (PaaS), enabling customers to access products as services rather than ownership. PaaS promotes sustainability by incentivizing manufacturers to design durable, easily maintainable products and fosters customer retention through subscription-based models. Explore how integrating Circular Economy principles with PaaS can revolutionize sustainable business strategies and drive innovation.
Resource Efficiency
Circular Economy and servitization both enhance resource efficiency by minimizing waste and maximizing asset utilization through product lifecycle extension and service-based models. Circular Economy emphasizes recycling, reuse, and regenerative design, while servitization shifts focus from product ownership to access, promoting longer product use and maintenance. Discover how integrating these strategies can revolutionize sustainable business practices.
Lifecycle Management
Circular economy emphasizes maximizing product lifecycle through reuse, refurbishment, and recycling to minimize environmental impact and resource consumption. Servitization shifts business models from product sales to offering lifecycle services, enhancing customer value and driving sustainable resource management. Discover how integrating circular economy principles with servitization optimizes lifecycle management for sustainable growth.
Source and External Links
Circular economy - Wikipedia - A model of production and consumption that emphasizes sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling materials and products to extend their life cycles and minimize waste and pollution.
What is a circular economy? | Ellen MacArthur Foundation - A system where materials never become waste and nature is regenerated, achieved through maintenance, reuse, refurbishment, remanufacturing, recycling, and composting, decoupling economic activity from finite resource consumption.
What is Circular Economy & How Does It Work? : Complete Guide - An industrial system designed to be restorative or regenerative, where products and materials are continuously recovered and reused, reducing the need for virgin resources and aiming for zero waste.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com