Decentralized manufacturing distributes production processes across multiple locations, enhancing flexibility and reducing transportation costs, while cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into compact, self-contained units to streamline workflow and improve efficiency. Both approaches aim to optimize production but differ in scalability and control mechanisms. Explore the benefits and challenges of decentralized and cellular manufacturing to identify the best fit for your supply chain strategy.
Why it is important
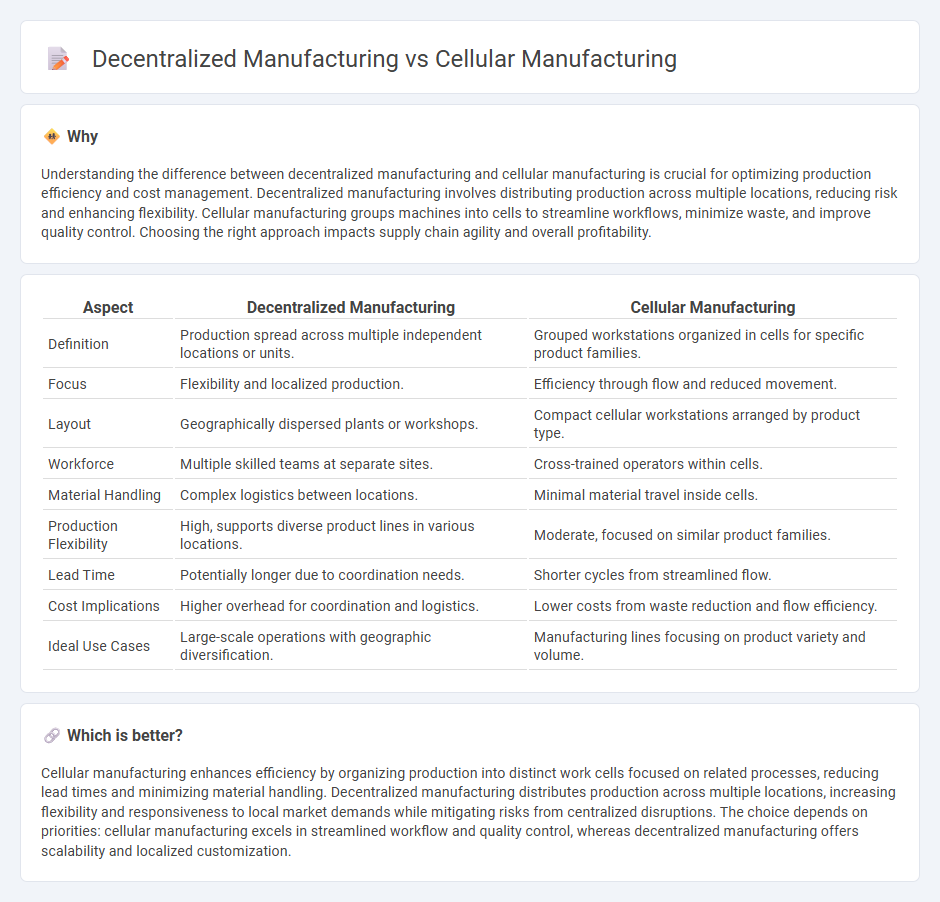
Understanding the difference between decentralized manufacturing and cellular manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and cost management. Decentralized manufacturing involves distributing production across multiple locations, reducing risk and enhancing flexibility. Cellular manufacturing groups machines into cells to streamline workflows, minimize waste, and improve quality control. Choosing the right approach impacts supply chain agility and overall profitability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Decentralized Manufacturing | Cellular Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Production spread across multiple independent locations or units. | Grouped workstations organized in cells for specific product families. |
| Focus | Flexibility and localized production. | Efficiency through flow and reduced movement. |
| Layout | Geographically dispersed plants or workshops. | Compact cellular workstations arranged by product type. |
| Workforce | Multiple skilled teams at separate sites. | Cross-trained operators within cells. |
| Material Handling | Complex logistics between locations. | Minimal material travel inside cells. |
| Production Flexibility | High, supports diverse product lines in various locations. | Moderate, focused on similar product families. |
| Lead Time | Potentially longer due to coordination needs. | Shorter cycles from streamlined flow. |
| Cost Implications | Higher overhead for coordination and logistics. | Lower costs from waste reduction and flow efficiency. |
| Ideal Use Cases | Large-scale operations with geographic diversification. | Manufacturing lines focusing on product variety and volume. |
Which is better?
Cellular manufacturing enhances efficiency by organizing production into distinct work cells focused on related processes, reducing lead times and minimizing material handling. Decentralized manufacturing distributes production across multiple locations, increasing flexibility and responsiveness to local market demands while mitigating risks from centralized disruptions. The choice depends on priorities: cellular manufacturing excels in streamlined workflow and quality control, whereas decentralized manufacturing offers scalability and localized customization.
Connection
Decentralized manufacturing distributes production processes across multiple locations, enhancing flexibility and reducing lead times. Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into self-contained units or cells focused on specific product families, streamlining workflow and minimizing waste. Integrating cellular manufacturing within decentralized systems boosts responsiveness and operational efficiency by combining localized production control with optimized process layout.
Key Terms
**Cellular Manufacturing:**
Cellular manufacturing organizes production workstations into small, self-contained units called cells, each designed to complete a specific set of tasks efficiently, reducing lead times and improving product quality. This approach minimizes work-in-progress inventory and enhances flexibility by enabling workers to handle multiple operations within the cell, fostering teamwork and faster problem-solving. Explore the advantages of cellular manufacturing and how it can transform your production efficiency.
Work Cells
Cellular manufacturing organizes work cells in a linear sequence to enhance workflow efficiency and reduce transportation waste, while decentralized manufacturing distributes work cells across multiple locations to increase flexibility and responsiveness to local demand. Work cells in cellular manufacturing are designed with standardized equipment and tasks to optimize line flow and minimize setup times, whereas decentralized manufacturing work cells prioritize adaptability and customization to local market needs. Explore further to understand how work cell design impacts operational efficiency and scalability in both manufacturing models.
Group Technology
Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into compact cells based on Group Technology principles, grouping similar parts to enhance workflow efficiency and reduce setup times. Decentralized manufacturing distributes production processes geographically or across multiple locations, focusing on flexibility and responsiveness but often sacrificing the integrated efficiency of cellular layouts. Explore deeper insights into how Group Technology drives optimized manufacturing strategies in both cellular and decentralized systems.
Source and External Links
Cellular Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide - Deskera - Cellular manufacturing is a production system that combines the processes of a production line into single manufacturing cells designed to improve efficiency by assessing environment, designing cells, developing process flow, assigning resources, and monitoring performance.
Cellular manufacturing - Wikipedia - Cellular manufacturing is a lean, just-in-time production method organizing workstations into multiple cells where each completes part of the process, improving flexibility, reducing waste, and enabling faster changeovers with a typical U-shaped layout.
Lean Thinking and Methods - Cellular Manufacturing | US EPA - Cellular manufacturing shifts from batch-and-queue production to a product-aligned one-piece flow system based on actual customer demand, reducing work-in-process inventory, lead time, and space requirements by moving products one piece at a time through the process.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com