Green steel, produced using renewable energy and hydrogen instead of fossil fuels, significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to traditional brown steel, which relies heavily on coal in blast furnaces. This shift toward green steel addresses the steel industry's substantial contribution to global greenhouse gas emissions, aiming for sustainability and compliance with climate goals. Explore the transformative impact and future potential of green steel in revolutionizing manufacturing.
Why it is important
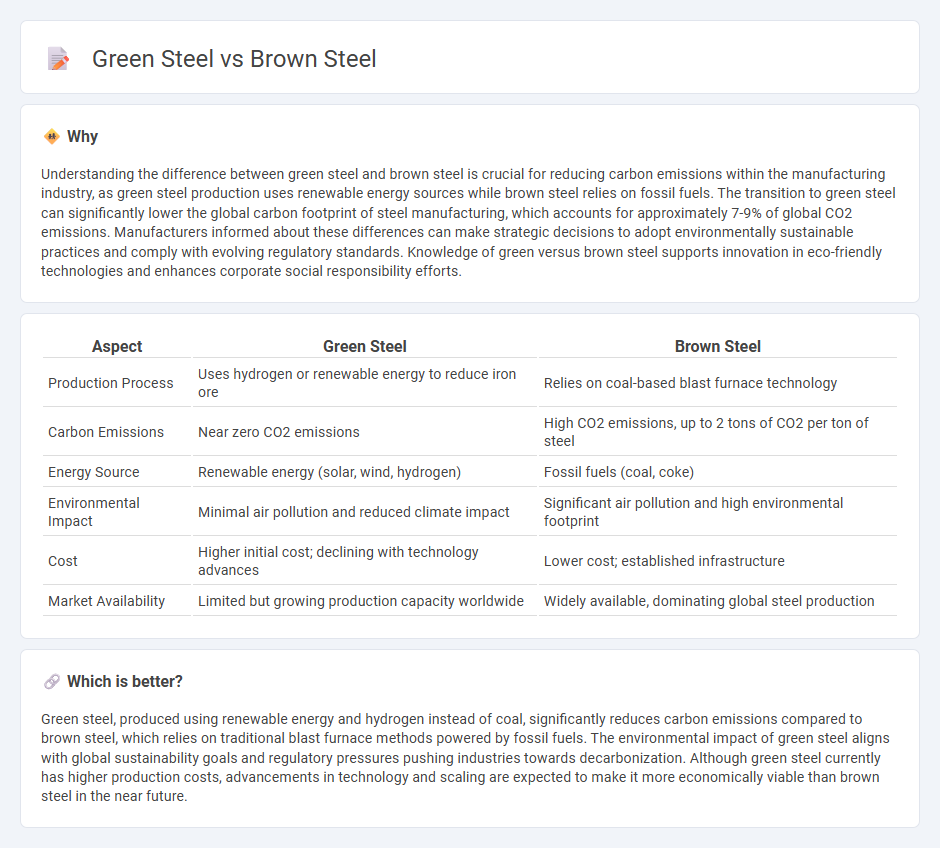
Understanding the difference between green steel and brown steel is crucial for reducing carbon emissions within the manufacturing industry, as green steel production uses renewable energy sources while brown steel relies on fossil fuels. The transition to green steel can significantly lower the global carbon footprint of steel manufacturing, which accounts for approximately 7-9% of global CO2 emissions. Manufacturers informed about these differences can make strategic decisions to adopt environmentally sustainable practices and comply with evolving regulatory standards. Knowledge of green versus brown steel supports innovation in eco-friendly technologies and enhances corporate social responsibility efforts.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Steel | Brown Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Production Process | Uses hydrogen or renewable energy to reduce iron ore | Relies on coal-based blast furnace technology |
| Carbon Emissions | Near zero CO2 emissions | High CO2 emissions, up to 2 tons of CO2 per ton of steel |
| Energy Source | Renewable energy (solar, wind, hydrogen) | Fossil fuels (coal, coke) |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal air pollution and reduced climate impact | Significant air pollution and high environmental footprint |
| Cost | Higher initial cost; declining with technology advances | Lower cost; established infrastructure |
| Market Availability | Limited but growing production capacity worldwide | Widely available, dominating global steel production |
Which is better?
Green steel, produced using renewable energy and hydrogen instead of coal, significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to brown steel, which relies on traditional blast furnace methods powered by fossil fuels. The environmental impact of green steel aligns with global sustainability goals and regulatory pressures pushing industries towards decarbonization. Although green steel currently has higher production costs, advancements in technology and scaling are expected to make it more economically viable than brown steel in the near future.
Connection
Green steel and brown steel are connected through their production processes and environmental impact, with green steel produced using renewable energy and hydrogen to reduce carbon emissions, while brown steel relies on traditional coal-based blast furnaces generating higher CO2 levels. The shift from brown steel to green steel represents a critical transition in manufacturing aimed at decarbonizing the steel industry. Innovations in green steel technology focus on replacing fossil fuels with clean energy sources, enabling sustainable manufacturing practices in steel production.
Key Terms
Carbon Emissions
Brown steel production relies heavily on coal and blast furnace methods, resulting in high carbon emissions typically exceeding 1.8 tons of CO2 per ton of steel. Green steel uses renewable energy and hydrogen-based direct reduction processes, reducing carbon emissions by up to 95% compared to conventional methods. Explore the latest technologies and policies driving the transition to low-carbon steel production for a sustainable future.
Hydrogen Reduction
Brown steel production relies on traditional blast furnace methods that emit significant CO2 due to the use of coal, while green steel employs hydrogen reduction technology which replaces coal with hydrogen, drastically lowering carbon emissions. Hydrogen reduction involves using green hydrogen derived from renewable energy sources, enabling steel manufacturing to approach carbon neutrality and supporting global decarbonization targets. Explore how hydrogen reduction is revolutionizing the steel industry and contributing to sustainable manufacturing.
Fossil Fuels
Brown steel production relies heavily on fossil fuels such as coal and natural gas, leading to significant carbon emissions and environmental degradation. Green steel utilizes renewable energy sources and hydrogen to drastically reduce reliance on fossil fuels, cutting carbon emissions by up to 95%. Learn more about how green steel innovations are transforming the future of sustainable manufacturing.
Source and External Links
Brown Strauss Steel - Premier structural steel service center in the U.S. with a vast inventory of wide flange beams, structural tubes, channels, and angles for commercial and industrial projects, serving 32 states from ten facilities.
Rustic Brown Patina - A chemical solution that imparts a deep brown finish on steel and iron, suitable for furniture, railings, architectural steel, and more, with step-by-step application and sealing instructions.
Steel Brown Roof Panels - A variety of ribbed steel roof panels in colors like chestnut, cocoa, and light brown, available in multiple sizes for residential and commercial roofing applications.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com