Circular manufacturing emphasizes resource efficiency by continuously reusing materials, reducing waste, and promoting sustainability throughout the production lifecycle. Batch production focuses on producing a set quantity of identical items in discrete runs, optimizing for volume and consistency but often generating more waste. Explore deeper insights into how circular manufacturing can revolutionize traditional batch production processes.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between circular manufacturing and batch production is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and minimizing waste in manufacturing processes. Circular manufacturing focuses on sustainability by reusing materials and reducing environmental impact, while batch production emphasizes producing goods in set quantities to meet demand. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses implement cost-effective and environmentally responsible strategies tailored to their production goals. This knowledge drives innovation and competitive advantage in the evolving global market.
Comparison Table
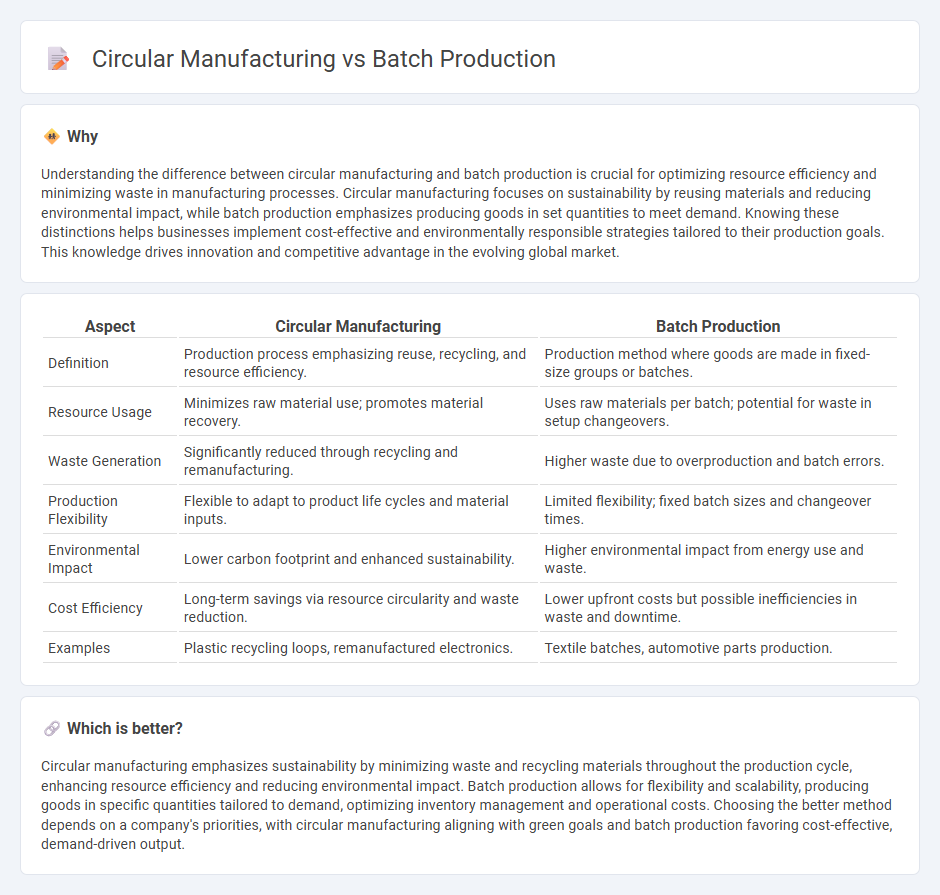
| Aspect | Circular Manufacturing | Batch Production |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Production process emphasizing reuse, recycling, and resource efficiency. | Production method where goods are made in fixed-size groups or batches. |
| Resource Usage | Minimizes raw material use; promotes material recovery. | Uses raw materials per batch; potential for waste in setup changeovers. |
| Waste Generation | Significantly reduced through recycling and remanufacturing. | Higher waste due to overproduction and batch errors. |
| Production Flexibility | Flexible to adapt to product life cycles and material inputs. | Limited flexibility; fixed batch sizes and changeover times. |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint and enhanced sustainability. | Higher environmental impact from energy use and waste. |
| Cost Efficiency | Long-term savings via resource circularity and waste reduction. | Lower upfront costs but possible inefficiencies in waste and downtime. |
| Examples | Plastic recycling loops, remanufactured electronics. | Textile batches, automotive parts production. |
Which is better?
Circular manufacturing emphasizes sustainability by minimizing waste and recycling materials throughout the production cycle, enhancing resource efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Batch production allows for flexibility and scalability, producing goods in specific quantities tailored to demand, optimizing inventory management and operational costs. Choosing the better method depends on a company's priorities, with circular manufacturing aligning with green goals and batch production favoring cost-effective, demand-driven output.
Connection
Circular manufacturing and batch production intersect through their shared emphasis on resource efficiency and waste reduction during production cycles. Batch production allows manufacturers to optimize material use by producing goods in controlled quantities, aligning with circular manufacturing principles that prioritize recycling, reuse, and sustainable resource management. The integration of batch production within circular manufacturing systems enhances closed-loop processes by minimizing leftovers and enabling easier recycling of materials.
Key Terms
Production flow
Batch production features a sequential production flow where goods are produced in specific quantities before moving to the next stage, often leading to downtime between batches. Circular manufacturing integrates continuous production flow with recycling and waste reduction, emphasizing resource efficiency and closed-loop processes. Explore how optimizing production flow in these methods can enhance sustainability and operational efficiency.
Waste management
Batch production generates significant waste due to frequent setup changes and material offcuts, leading to inefficiencies in resource utilization. Circular manufacturing minimizes waste by designing processes that enable continuous material reuse, recycling, and remanufacturing, thus promoting sustainability. Explore how these approaches impact environmental footprints and operational costs for a deeper understanding.
Scalability
Batch production offers limited scalability due to fixed production runs and changeover times, which can slow down response to market demand shifts. Circular manufacturing leverages resource efficiency and waste reduction, promoting scalability by enabling continuous product lifecycle management and closed-loop processes. Explore how integrating circular manufacturing strategies can enhance scalability in your production systems.
Source and External Links
What is batch production in manufacturing? - OneAdvanced - Batch production is a method where a group of identical products are made at the same time, with each batch moving through the production stages together before the next batch begins.
Batch Production - Benefits, Examples, and Tips - MRPeasy - In batch production, sets of identical goods go through different production steps as a group, offering flexibility and quality control, but may result in higher inventory and possible idle time.
Batch production explained simply I Everything you need to know - YAVEON - Batch production involves producing a defined quantity of goods (a batch) in one go, with products often stored between steps and the process allowing quick switches to different products or variants.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com