A lights out factory operates autonomously without human intervention, utilizing automated systems to maintain continuous production and enhance efficiency. Digital twins replicate physical manufacturing processes digitally, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimization of factory operations. Explore how integrating lights out factories with digital twin technology revolutionizes modern manufacturing strategies.
Why it is important
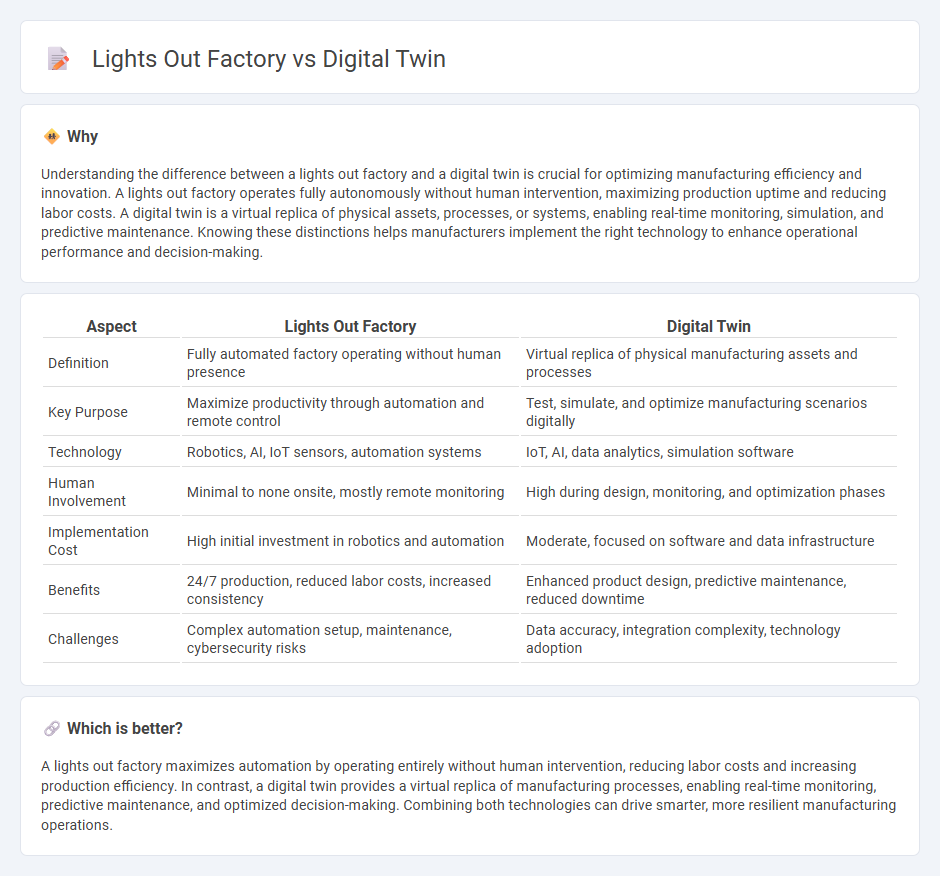
Understanding the difference between a lights out factory and a digital twin is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and innovation. A lights out factory operates fully autonomously without human intervention, maximizing production uptime and reducing labor costs. A digital twin is a virtual replica of physical assets, processes, or systems, enabling real-time monitoring, simulation, and predictive maintenance. Knowing these distinctions helps manufacturers implement the right technology to enhance operational performance and decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lights Out Factory | Digital Twin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated factory operating without human presence | Virtual replica of physical manufacturing assets and processes |
| Key Purpose | Maximize productivity through automation and remote control | Test, simulate, and optimize manufacturing scenarios digitally |
| Technology | Robotics, AI, IoT sensors, automation systems | IoT, AI, data analytics, simulation software |
| Human Involvement | Minimal to none onsite, mostly remote monitoring | High during design, monitoring, and optimization phases |
| Implementation Cost | High initial investment in robotics and automation | Moderate, focused on software and data infrastructure |
| Benefits | 24/7 production, reduced labor costs, increased consistency | Enhanced product design, predictive maintenance, reduced downtime |
| Challenges | Complex automation setup, maintenance, cybersecurity risks | Data accuracy, integration complexity, technology adoption |
Which is better?
A lights out factory maximizes automation by operating entirely without human intervention, reducing labor costs and increasing production efficiency. In contrast, a digital twin provides a virtual replica of manufacturing processes, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized decision-making. Combining both technologies can drive smarter, more resilient manufacturing operations.
Connection
Lights-out factories utilize advanced automation and AI to operate without human intervention, relying heavily on digital twin technology to simulate, monitor, and optimize production processes in real time. Digital twins create virtual replicas of physical manufacturing environments, enabling predictive maintenance, quality control, and process efficiency improvements essential for autonomous operations. Integrating digital twins with IoT sensors in lights-out factories drives continuous data feedback loops, reducing downtime and enhancing decision-making accuracy.
Key Terms
**Digital Twin:**
Digital Twin technology creates a dynamic, real-time virtual replica of a physical factory, enabling predictive maintenance, process optimization, and enhanced decision-making through continuous data integration. Unlike a lights-out factory, which operates fully autonomously without human presence, Digital Twins facilitate human-machine collaboration by providing detailed insights and simulations for improving operational efficiency. Discover how Digital Twins revolutionize manufacturing by bridging the gap between digital intelligence and physical production environments.
Simulation
Digital twin technology creates a virtual replica of physical assets, enabling real-time simulation, monitoring, and optimization of manufacturing processes. Lights out factories rely on fully automated operations with minimal human intervention, using simulations primarily for pre-deployment testing rather than continuous real-time adjustments. Explore how integrating advanced simulation capabilities in digital twins can enhance factory automation and efficiency.
Real-time Data
Digital twin technology offers a dynamic, real-time digital replica of physical assets, enabling continuous monitoring and simulation based on live data streams. Lights out factories rely heavily on automated machinery operating without human intervention, where real-time data is crucial for autonomous decision-making and immediate fault detection. Explore how integrating real-time data empowers both digital twin systems and lights out factories to optimize operational efficiency and predictive maintenance.
Source and External Links
What Is a Digital Twin? | IBM - A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical object or system updated by real-time data from sensors, used for simulations, performance analysis, and improving the original physical entity.
Definition of a Digital Twin - A digital twin is an integrated, data-driven virtual model of real-world entities and processes with synchronized interaction, built on data and physics to facilitate decision-making and continuous improvement.
Digital twin - Wikipedia - A digital twin is a digital model of a real-world product, system, or process that emulates its behavior using real-time data to support simulation, testing, monitoring, and maintenance throughout its lifecycle.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com