Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) streamline material transport by navigating factory floors with precise sensor-based guidance, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing human error. Industrial robots perform complex tasks such as welding, assembly, and painting with high accuracy and repeatability, improving production quality and speed. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how each technology can optimize your manufacturing processes.
Why it is important
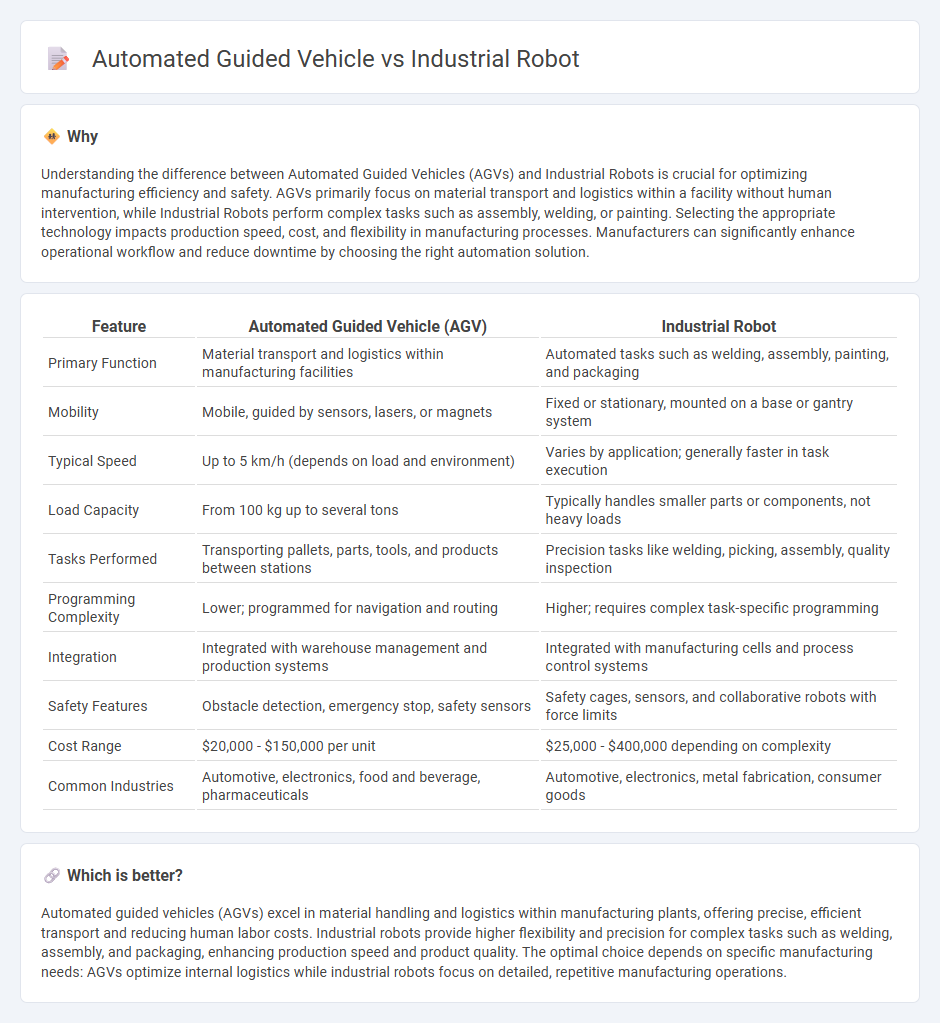
Understanding the difference between Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Industrial Robots is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and safety. AGVs primarily focus on material transport and logistics within a facility without human intervention, while Industrial Robots perform complex tasks such as assembly, welding, or painting. Selecting the appropriate technology impacts production speed, cost, and flexibility in manufacturing processes. Manufacturers can significantly enhance operational workflow and reduce downtime by choosing the right automation solution.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) | Industrial Robot |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Material transport and logistics within manufacturing facilities | Automated tasks such as welding, assembly, painting, and packaging |
| Mobility | Mobile, guided by sensors, lasers, or magnets | Fixed or stationary, mounted on a base or gantry system |
| Typical Speed | Up to 5 km/h (depends on load and environment) | Varies by application; generally faster in task execution |
| Load Capacity | From 100 kg up to several tons | Typically handles smaller parts or components, not heavy loads |
| Tasks Performed | Transporting pallets, parts, tools, and products between stations | Precision tasks like welding, picking, assembly, quality inspection |
| Programming Complexity | Lower; programmed for navigation and routing | Higher; requires complex task-specific programming |
| Integration | Integrated with warehouse management and production systems | Integrated with manufacturing cells and process control systems |
| Safety Features | Obstacle detection, emergency stop, safety sensors | Safety cages, sensors, and collaborative robots with force limits |
| Cost Range | $20,000 - $150,000 per unit | $25,000 - $400,000 depending on complexity |
| Common Industries | Automotive, electronics, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals | Automotive, electronics, metal fabrication, consumer goods |
Which is better?
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) excel in material handling and logistics within manufacturing plants, offering precise, efficient transport and reducing human labor costs. Industrial robots provide higher flexibility and precision for complex tasks such as welding, assembly, and packaging, enhancing production speed and product quality. The optimal choice depends on specific manufacturing needs: AGVs optimize internal logistics while industrial robots focus on detailed, repetitive manufacturing operations.
Connection
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and industrial robots are integrated in manufacturing to streamline material handling and assembly processes. AGVs transport raw materials and components to robotic workstations where industrial robots perform precision tasks such as welding, assembly, or inspection. This connection enhances production efficiency by reducing manual labor and minimizing errors, leading to higher throughput and consistent product quality.
Key Terms
Articulated Arm
Articulated arms in industrial robots offer high degrees of freedom, enabling complex tasks such as welding, assembly, and material handling with precision and flexibility in manufacturing environments. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) primarily focus on material transport, utilizing sensors and predefined paths but lack the intricate manipulation capabilities of articulated robotic arms. Discover the advanced applications and integration strategies of articulated arms in modern automation systems.
Navigation System
Industrial robots typically rely on fixed or guided paths using sensors and pre-programmed coordinates for precise task execution, while Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) utilize advanced navigation systems like LiDAR, GPS, and SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) to autonomously maneuver dynamic environments. AGV navigation systems enable real-time obstacle detection and path optimization, crucial for flexible industrial logistics and material handling. Explore the latest advancements in navigation technology to optimize automation strategies in manufacturing and warehousing.
End Effector
Industrial robots utilize versatile end effectors, such as grippers, welding torches, and suction cups, tailored for precise manipulation tasks in manufacturing and assembly lines. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) typically feature simplified end effectors designed for material transport and loading functions, optimizing logistical efficiency within warehouses and factories. Explore the latest advancements in end effector technology to enhance automation performance.
Source and External Links
What Are Industrial Robots? | Built In - Industrial robots are automated machines designed to perform repetitive manufacturing, assembly, and material handling tasks in factories, typically using a reprogrammable robotic arm operating on three or more axes.
What is an industrial robot? Industrial robot definition - According to international standards, an industrial robot is a multifunctional, reprogrammable, automatically controlled manipulator with three or more axes, used to automate intensive production tasks such as assembly lines and material transport.
Industrial robot - Wikipedia - Used primarily in manufacturing, industrial robots are automated, programmable systems capable of movement on three or more axes, commonly applied in welding, painting, assembly, packaging, and quality inspection.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com