Microfactories offer localized, flexible production capabilities with rapid prototyping and reduced lead times, ideal for customized, small-batch manufacturing. Contract manufacturing provides scalable, cost-efficient solutions for mass production by leveraging specialized facilities and expertise. Explore the benefits and differences between microfactories and contract manufacturing to optimize your production strategy.
Why it is important
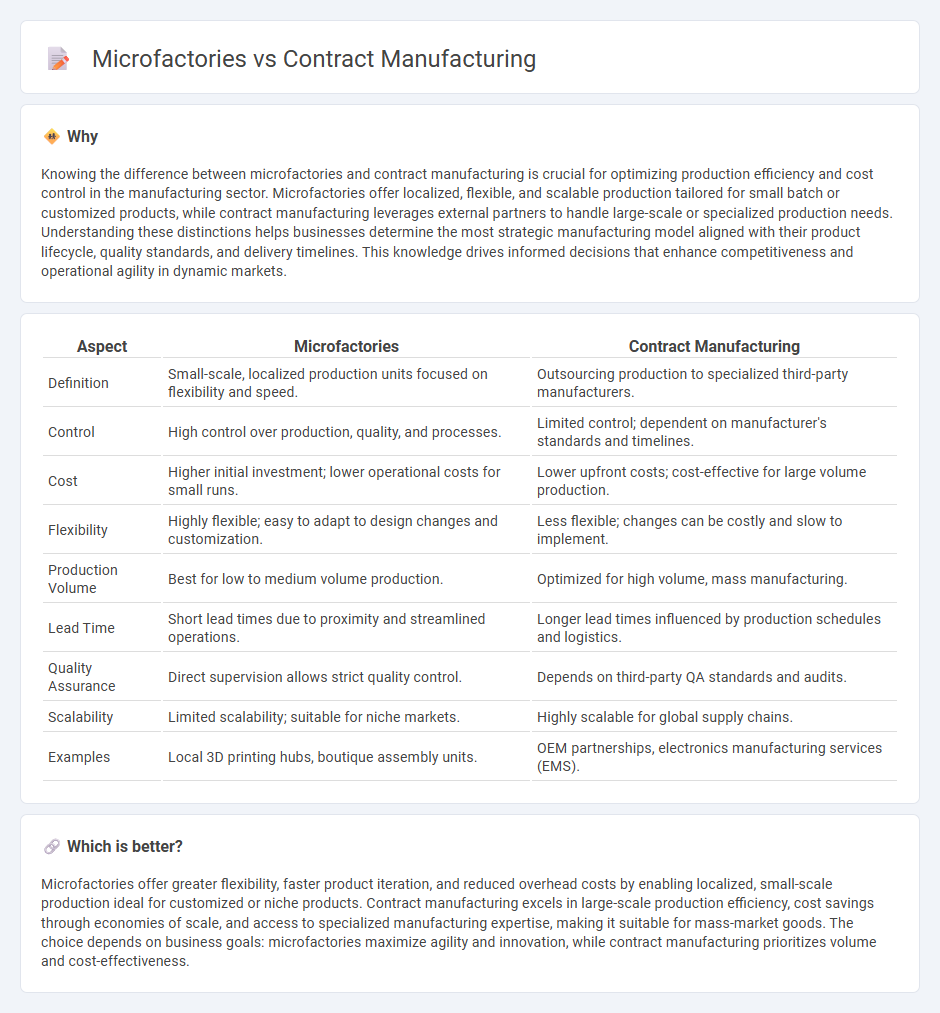
Knowing the difference between microfactories and contract manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and cost control in the manufacturing sector. Microfactories offer localized, flexible, and scalable production tailored for small batch or customized products, while contract manufacturing leverages external partners to handle large-scale or specialized production needs. Understanding these distinctions helps businesses determine the most strategic manufacturing model aligned with their product lifecycle, quality standards, and delivery timelines. This knowledge drives informed decisions that enhance competitiveness and operational agility in dynamic markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microfactories | Contract Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small-scale, localized production units focused on flexibility and speed. | Outsourcing production to specialized third-party manufacturers. |
| Control | High control over production, quality, and processes. | Limited control; dependent on manufacturer's standards and timelines. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; lower operational costs for small runs. | Lower upfront costs; cost-effective for large volume production. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible; easy to adapt to design changes and customization. | Less flexible; changes can be costly and slow to implement. |
| Production Volume | Best for low to medium volume production. | Optimized for high volume, mass manufacturing. |
| Lead Time | Short lead times due to proximity and streamlined operations. | Longer lead times influenced by production schedules and logistics. |
| Quality Assurance | Direct supervision allows strict quality control. | Depends on third-party QA standards and audits. |
| Scalability | Limited scalability; suitable for niche markets. | Highly scalable for global supply chains. |
| Examples | Local 3D printing hubs, boutique assembly units. | OEM partnerships, electronics manufacturing services (EMS). |
Which is better?
Microfactories offer greater flexibility, faster product iteration, and reduced overhead costs by enabling localized, small-scale production ideal for customized or niche products. Contract manufacturing excels in large-scale production efficiency, cost savings through economies of scale, and access to specialized manufacturing expertise, making it suitable for mass-market goods. The choice depends on business goals: microfactories maximize agility and innovation, while contract manufacturing prioritizes volume and cost-effectiveness.
Connection
Microfactories and contract manufacturing are interconnected through their focus on flexible and efficient production processes that cater to specific client needs. Microfactories enable localized, small-scale manufacturing with rapid prototyping, which contract manufacturers leverage to deliver customized products without large capital investments. This synergy enhances scalability and reduces time-to-market for various industries, including electronics, apparel, and automotive sectors.
Key Terms
Scalability
Contract manufacturing offers high scalability by leveraging established production facilities and extensive supplier networks to rapidly increase output. Microfactories provide flexible scalability through modular designs and localized production, allowing swift adaptation to demand fluctuations without massive capital investment. Explore how these models compare to decide the best scalable solution for your manufacturing needs.
Customization
Contract manufacturing offers scalable production with lower upfront investment but limited flexibility for customization, often adhering to standardized processes and long lead times. Microfactories emphasize high customization and agility, enabling rapid product iterations and localized manufacturing with minimal inventory. Explore how businesses can leverage both models to optimize customization and responsiveness in production.
Capital Investment
Contract manufacturing often requires substantial upfront capital investment in large-scale facilities and specialized machinery, making it ideal for mass production with economies of scale. Microfactories, by contrast, demand lower initial capital expenditure due to their compact size and flexible, modular equipment, allowing for rapid scalability and customization. Explore more to understand how capital investment strategies impact manufacturing efficiency and innovation.
Source and External Links
Overview of Contract Manufacturing - Contract manufacturing is a business process where an original equipment manufacturer (OEM) outsources manufacturing to a contract manufacturer to produce parts or products to exact specifications, allowing the OEM to fully outsource production while tracking progress and inventory in real time.
What is OEM vs Contract Manufacturing? - Contract manufacturing involves a client providing designs and intellectual property to a manufacturer who produces and possibly assembles the product, focusing purely on manufacturing services without owning design rights.
Top Contract Manufacturing Companies | Service Providers - Contract manufacturing services cover machining, assembly, secondary processes, custom fabrication, and production volume flexibility, serving diverse industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and consumer goods, originating from the flexible manufacturing needs since the 1970s.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com