Cloud manufacturing integrates cloud computing technologies to enable real-time data sharing, remote monitoring, and scalable production resources across distributed facilities, enhancing efficiency and collaboration. Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) utilize automated machinery and robotics to quickly adapt to product changes and varied production volumes, optimizing responsiveness to market demands. Explore the key differences and applications of cloud manufacturing and flexible manufacturing systems to maximize operational performance.
Why it is important
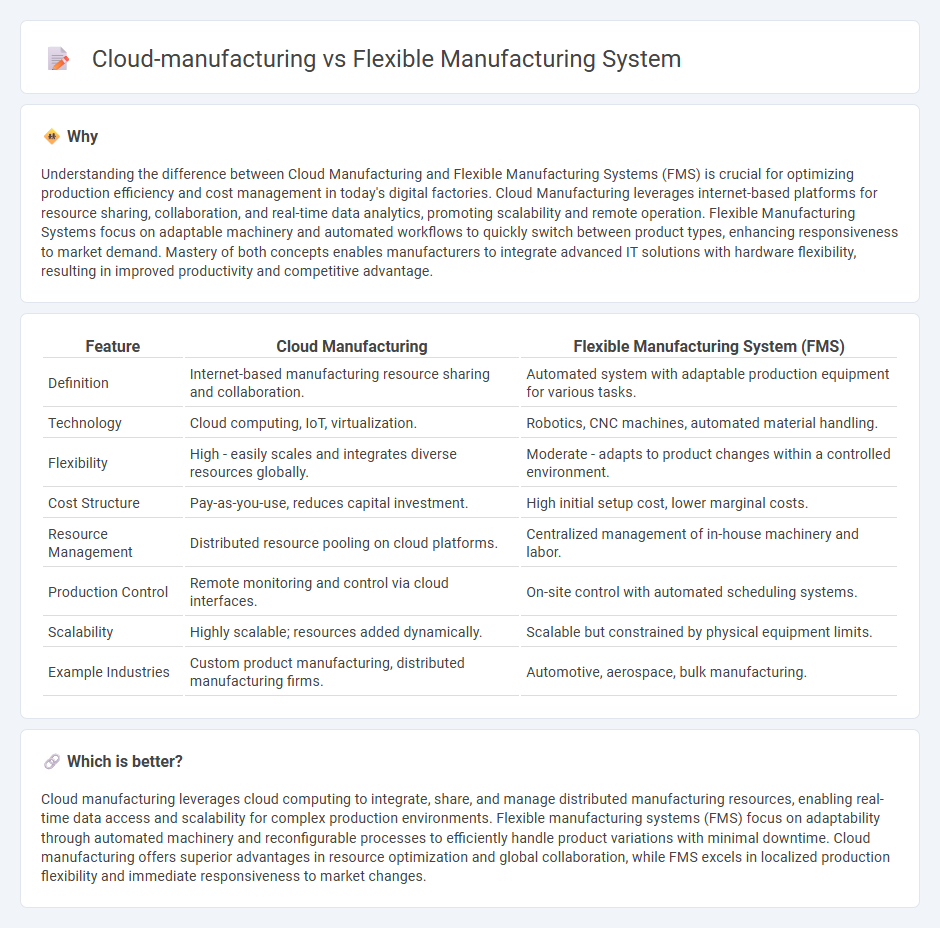
Understanding the difference between Cloud Manufacturing and Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and cost management in today's digital factories. Cloud Manufacturing leverages internet-based platforms for resource sharing, collaboration, and real-time data analytics, promoting scalability and remote operation. Flexible Manufacturing Systems focus on adaptable machinery and automated workflows to quickly switch between product types, enhancing responsiveness to market demand. Mastery of both concepts enables manufacturers to integrate advanced IT solutions with hardware flexibility, resulting in improved productivity and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Cloud Manufacturing | Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Internet-based manufacturing resource sharing and collaboration. | Automated system with adaptable production equipment for various tasks. |
| Technology | Cloud computing, IoT, virtualization. | Robotics, CNC machines, automated material handling. |
| Flexibility | High - easily scales and integrates diverse resources globally. | Moderate - adapts to product changes within a controlled environment. |
| Cost Structure | Pay-as-you-use, reduces capital investment. | High initial setup cost, lower marginal costs. |
| Resource Management | Distributed resource pooling on cloud platforms. | Centralized management of in-house machinery and labor. |
| Production Control | Remote monitoring and control via cloud interfaces. | On-site control with automated scheduling systems. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; resources added dynamically. | Scalable but constrained by physical equipment limits. |
| Example Industries | Custom product manufacturing, distributed manufacturing firms. | Automotive, aerospace, bulk manufacturing. |
Which is better?
Cloud manufacturing leverages cloud computing to integrate, share, and manage distributed manufacturing resources, enabling real-time data access and scalability for complex production environments. Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) focus on adaptability through automated machinery and reconfigurable processes to efficiently handle product variations with minimal downtime. Cloud manufacturing offers superior advantages in resource optimization and global collaboration, while FMS excels in localized production flexibility and immediate responsiveness to market changes.
Connection
Cloud manufacturing integrates internet-based technologies to enable real-time data sharing and remote management of production resources, enhancing the adaptability of manufacturing processes. Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) utilize automated machines and computer-controlled processes to quickly adjust to changing product demands and specifications. The connection lies in how cloud manufacturing amplifies the agility of FMS by providing scalable computing power, seamless collaboration, and data-driven decision-making, resulting in optimized production efficiency and reduced downtime.
Key Terms
Flexible manufacturing system:
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) integrate automated machines, computer control systems, and material handling to enable adaptive production processes capable of handling variable product types with minimal downtime. FMS increases efficiency by optimizing workflows, reducing labor costs, and allowing rapid retooling for small-to-medium batch production in industries like automotive and electronics. Explore the advantages of Flexible manufacturing systems to understand their impact on competitive manufacturing environments.
Automation
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) integrate automated machinery and computer-controlled processes to quickly adapt production lines for varying product types, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime. Cloud-manufacturing leverages IoT, big data, and cloud computing to enable remote monitoring, real-time data sharing, and scalable automation across multiple facilities. Explore the evolving landscape of automation to understand how these systems revolutionize manufacturing.
CNC Machines
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) integrate CNC machines through automated processes, enabling real-time adaptation to production changes and reducing downtime in manufacturing facilities. Cloud-manufacturing leverages internet-based platforms to connect CNC machines remotely, facilitating resource sharing, real-time monitoring, and data analytics for enhanced efficiency and scalability. Explore the latest advances in CNC machine integration within FMS and cloud-manufacturing to optimize your smart factory's performance.
Source and External Links
Flexible manufacturing system - Wikipedia - Flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is a manufacturing setup designed to adapt to changes in production requirements, offering flexibility in routing and machine operations to efficiently manufacture a variety of products in small batches.
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) - Autodesk - FMS is a computer-controlled system that can quickly adapt to changes such as new products, varying batch sizes, or sequence reordering, with routing and machine flexibility allowing manufacturers to maintain productivity despite disruptions or changing demands.
Flexible Manufacturing System Advantages And Disadvantages - FMS is an advanced, automated manufacturing approach that enables rapid adaptation to product variety and production volumes, supporting customization and scalability while reducing downtime and setup changes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com