Smart factories leverage advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and automation to enhance production efficiency, reduce operational costs, and improve product quality compared to traditional factories reliant on manual processes and fixed machinery. Data-driven decision-making and real-time monitoring enable smart factories to adapt quickly to changing demands and minimize downtime. Discover how transitioning to smart manufacturing can revolutionize your production capabilities.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between smart factories and traditional factories is crucial for optimizing production efficiency, reducing operational costs, and enhancing product quality. Smart factories leverage advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and automation to enable real-time data analysis and adaptive manufacturing processes. Traditional factories often rely on manual operations and fixed workflows, limiting flexibility and scalability. Knowing these differences allows businesses to implement the right strategies for innovation and competitive advantage in the manufacturing sector.
Comparison Table
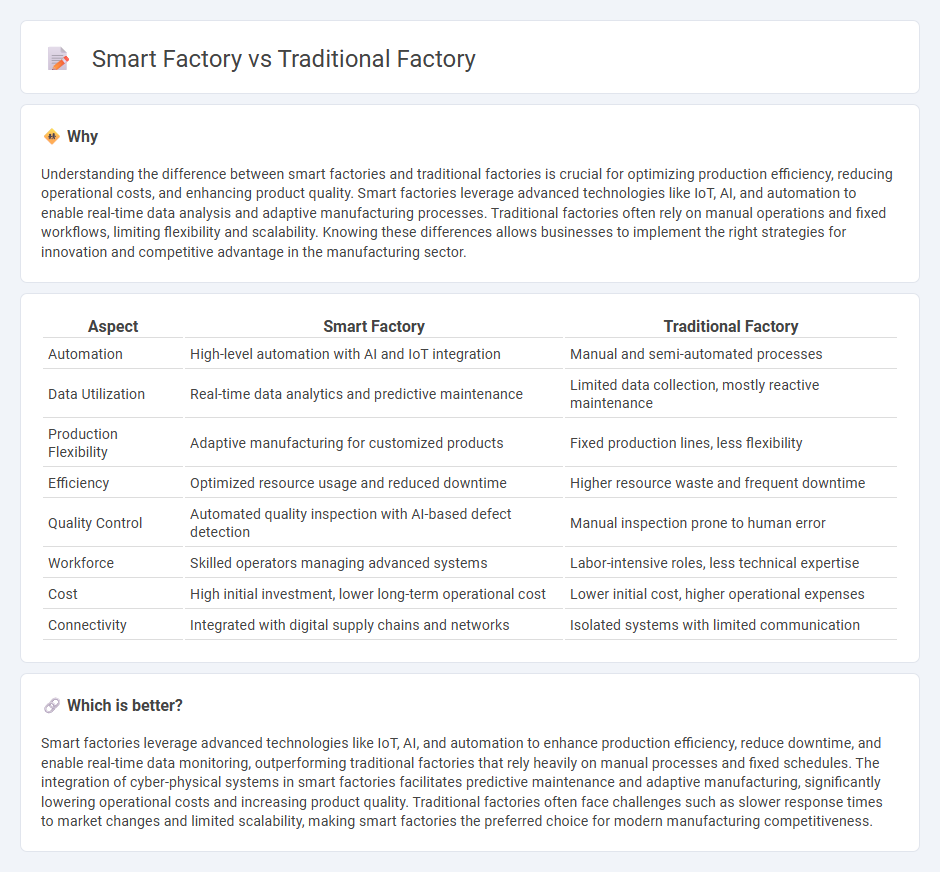
| Aspect | Smart Factory | Traditional Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Automation | High-level automation with AI and IoT integration | Manual and semi-automated processes |
| Data Utilization | Real-time data analytics and predictive maintenance | Limited data collection, mostly reactive maintenance |
| Production Flexibility | Adaptive manufacturing for customized products | Fixed production lines, less flexibility |
| Efficiency | Optimized resource usage and reduced downtime | Higher resource waste and frequent downtime |
| Quality Control | Automated quality inspection with AI-based defect detection | Manual inspection prone to human error |
| Workforce | Skilled operators managing advanced systems | Labor-intensive roles, less technical expertise |
| Cost | High initial investment, lower long-term operational cost | Lower initial cost, higher operational expenses |
| Connectivity | Integrated with digital supply chains and networks | Isolated systems with limited communication |
Which is better?
Smart factories leverage advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and automation to enhance production efficiency, reduce downtime, and enable real-time data monitoring, outperforming traditional factories that rely heavily on manual processes and fixed schedules. The integration of cyber-physical systems in smart factories facilitates predictive maintenance and adaptive manufacturing, significantly lowering operational costs and increasing product quality. Traditional factories often face challenges such as slower response times to market changes and limited scalability, making smart factories the preferred choice for modern manufacturing competitiveness.
Connection
Smart factories integrate IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics with traditional factory equipment to enhance real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Data from legacy machinery is digitized and fed into centralized control systems, enabling streamlined production workflows and increased operational efficiency. This connection transforms conventional manufacturing processes through automation and intelligent decision-making capabilities.
Key Terms
Source and External Links
From Traditional to Smart: The Evolution of Factories in Manufacturing - Traditional factories primarily rely on manual labor and mechanical technologies, featuring linear processes from raw materials to finished products, with heavy human intervention leading to inefficiencies, variable quality, and scalability challenges.
Advanced Manufacturing vs. Traditional Manufacturing - SixDe - Traditional manufacturing involves large-scale production using labor, machinery, tools, and physical processes and is typically hierarchical, mass-production focused, and reliant on mostly unskilled or semi-skilled workers.
Traditional manufacturing factory vs. smart factory - RoboticsBiz - Traditional factories operate with manual, isolated processes, limited technology, poor data visibility, legacy systems, and fixed production lines requiring manual reconfiguration, contrasting with digitized, integrated smart factories.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com