Patent monetization transforms intellectual property into revenue by licensing or selling patents, offering inventors immediate capital without relinquishing control. Venture capital involves investment in startups or early-stage companies in exchange for equity, focusing on high-growth potential and long-term returns. Discover how to leverage these strategies to maximize your financial growth.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between patent monetization and venture capital is crucial for maximizing investment returns and aligning funding strategies with business goals. Patent monetization focuses on generating revenue from intellectual property rights through licensing, sales, or litigation, whereas venture capital involves investing equity in startups or high-growth companies for potential equity appreciation. Knowing these distinctions helps investors assess risk profiles, liquidity, and time horizons effectively. Strategic allocation of resources to the appropriate mechanism drives better portfolio diversification and innovation support.
Comparison Table
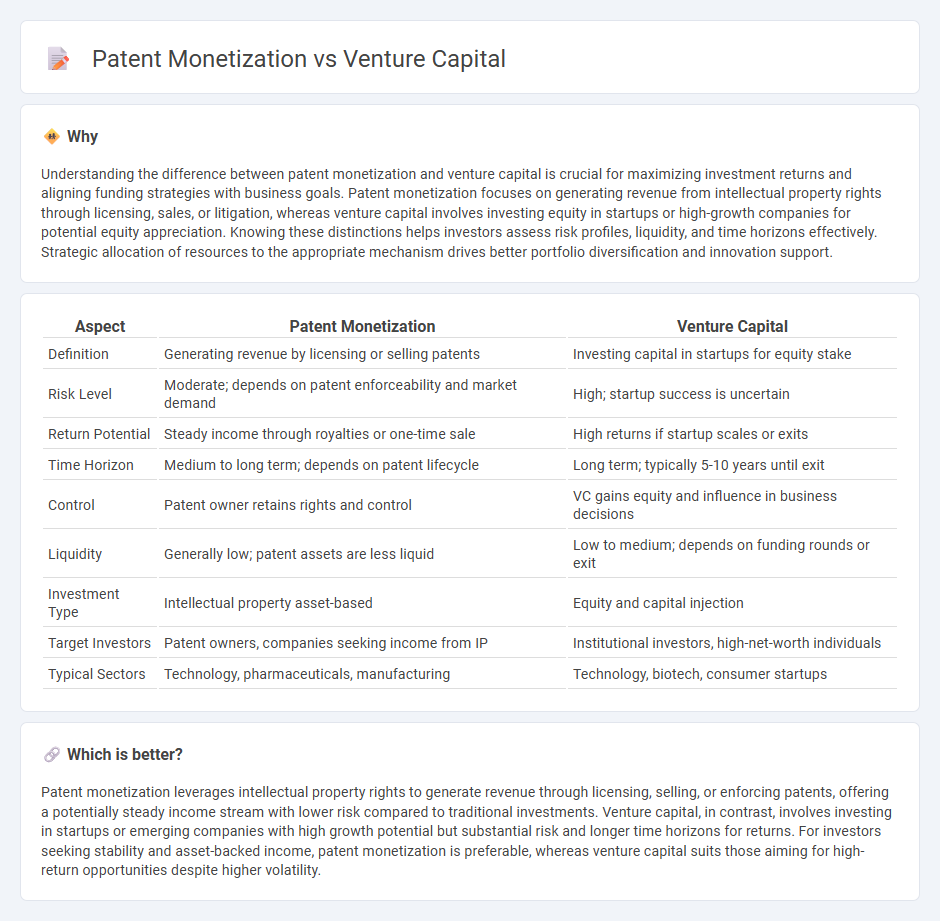
| Aspect | Patent Monetization | Venture Capital |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generating revenue by licensing or selling patents | Investing capital in startups for equity stake |
| Risk Level | Moderate; depends on patent enforceability and market demand | High; startup success is uncertain |
| Return Potential | Steady income through royalties or one-time sale | High returns if startup scales or exits |
| Time Horizon | Medium to long term; depends on patent lifecycle | Long term; typically 5-10 years until exit |
| Control | Patent owner retains rights and control | VC gains equity and influence in business decisions |
| Liquidity | Generally low; patent assets are less liquid | Low to medium; depends on funding rounds or exit |
| Investment Type | Intellectual property asset-based | Equity and capital injection |
| Target Investors | Patent owners, companies seeking income from IP | Institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals |
| Typical Sectors | Technology, pharmaceuticals, manufacturing | Technology, biotech, consumer startups |
Which is better?
Patent monetization leverages intellectual property rights to generate revenue through licensing, selling, or enforcing patents, offering a potentially steady income stream with lower risk compared to traditional investments. Venture capital, in contrast, involves investing in startups or emerging companies with high growth potential but substantial risk and longer time horizons for returns. For investors seeking stability and asset-backed income, patent monetization is preferable, whereas venture capital suits those aiming for high-return opportunities despite higher volatility.
Connection
Patent monetization leverages intellectual property as a financial asset, enabling inventors and companies to generate revenue through licensing, sales, or collateral for loans. Venture capital firms actively seek startups with strong patent portfolios, recognizing that robust intellectual property enhances market valuation and competitive advantage. This synergy drives investment decisions, as patents increase the likelihood of successful commercialization and scalable growth.
Key Terms
Equity
Venture capital involves investing equity in startups with high growth potential, providing not only funds but strategic support and mentorship. Patent monetization focuses on leveraging intellectual property assets to generate revenue through licensing or sales, often preserving equity ownership but potentially limiting long-term control. Explore the distinct benefits and strategic implications of equity-focused venture capital versus patent monetization to enhance your investment decisions.
Intellectual Property
Venture capital provides funding for startups with high growth potential, often in exchange for equity, enabling innovation but diluting ownership. Patent monetization involves generating revenue directly from intellectual property assets through licensing, sales, or enforcement strategies, preserving control over core technologies. Explore detailed strategies and benefits to leverage intellectual property value effectively.
Exit Strategy
Venture capital exit strategies primarily involve initial public offerings (IPOs) or acquisitions, allowing investors to realize returns through equity liquidation. Patent monetization focuses on leveraging intellectual property assets via licensing agreements or patent sales to generate revenue without relinquishing company control. To explore strategic advantages and maximize returns, discover how each approach fits different business models and growth stages.
Source and External Links
What is Venture Capital? - Venture capital is financing that turns innovative ideas and research into high-growth companies, providing long-term equity investment and strategic support to startups that typically cannot get traditional bank loans, often fueling major economic impact and job creation in the U.S.
Fund your business | U.S. Small Business Administration - Venture capital is funding provided to high-growth startups in exchange for equity ownership and often board influence, involving a process of finding investors, sharing business plans, due diligence, and agreeing on investment terms, with venture capitalists taking higher risk for potential higher returns.
What is venture capital? - Silicon Valley Bank - Venture capital is a form of private equity funding aimed at early-stage startups with rapid growth potential, where VCs invest capital in exchange for ownership stakes and often provide managerial expertise in addition to financial support.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com