Hedge fund replication employs quantitative models to mimic hedge fund returns by replicating their risk factors, offering cost-efficiency and transparency compared to traditional hedge funds. Synthetic funds utilize derivatives to artificially create hedge fund exposures, enabling access without direct investment in underlying assets. Discover the nuances between these innovative investment approaches to enhance portfolio diversification strategies.
Why it is important
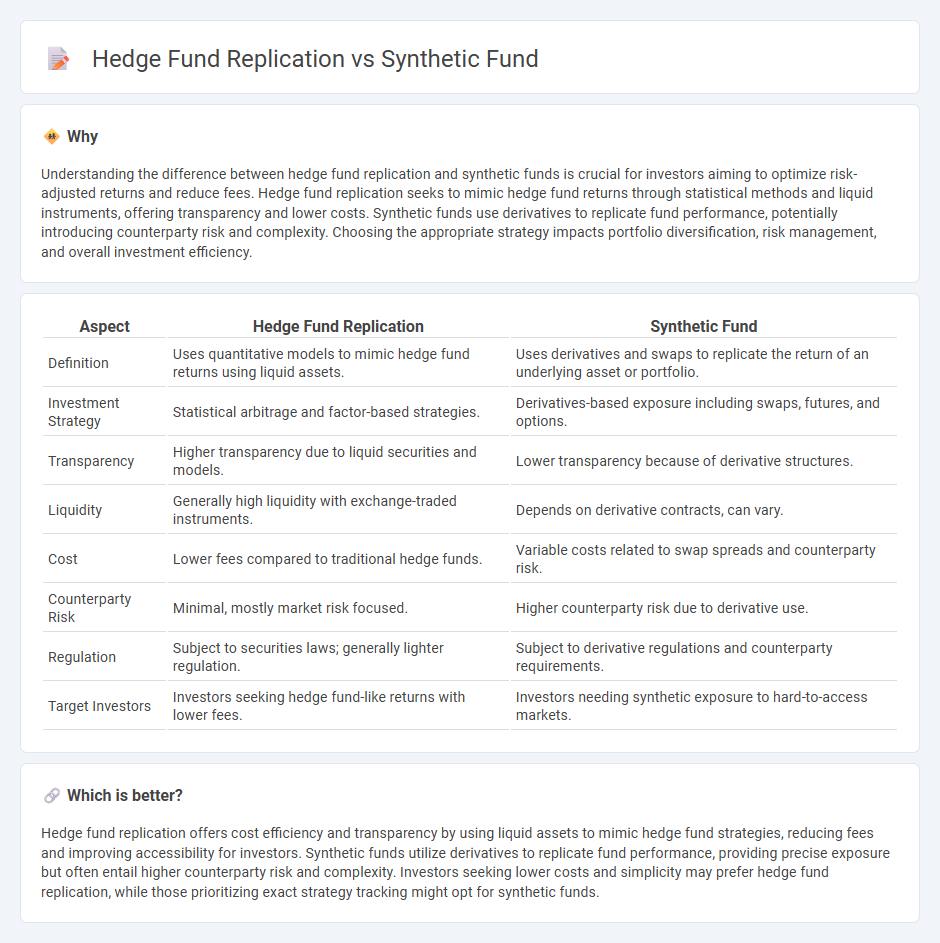
Understanding the difference between hedge fund replication and synthetic funds is crucial for investors aiming to optimize risk-adjusted returns and reduce fees. Hedge fund replication seeks to mimic hedge fund returns through statistical methods and liquid instruments, offering transparency and lower costs. Synthetic funds use derivatives to replicate fund performance, potentially introducing counterparty risk and complexity. Choosing the appropriate strategy impacts portfolio diversification, risk management, and overall investment efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Hedge Fund Replication | Synthetic Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses quantitative models to mimic hedge fund returns using liquid assets. | Uses derivatives and swaps to replicate the return of an underlying asset or portfolio. |
| Investment Strategy | Statistical arbitrage and factor-based strategies. | Derivatives-based exposure including swaps, futures, and options. |
| Transparency | Higher transparency due to liquid securities and models. | Lower transparency because of derivative structures. |
| Liquidity | Generally high liquidity with exchange-traded instruments. | Depends on derivative contracts, can vary. |
| Cost | Lower fees compared to traditional hedge funds. | Variable costs related to swap spreads and counterparty risk. |
| Counterparty Risk | Minimal, mostly market risk focused. | Higher counterparty risk due to derivative use. |
| Regulation | Subject to securities laws; generally lighter regulation. | Subject to derivative regulations and counterparty requirements. |
| Target Investors | Investors seeking hedge fund-like returns with lower fees. | Investors needing synthetic exposure to hard-to-access markets. |
Which is better?
Hedge fund replication offers cost efficiency and transparency by using liquid assets to mimic hedge fund strategies, reducing fees and improving accessibility for investors. Synthetic funds utilize derivatives to replicate fund performance, providing precise exposure but often entail higher counterparty risk and complexity. Investors seeking lower costs and simplicity may prefer hedge fund replication, while those prioritizing exact strategy tracking might opt for synthetic funds.
Connection
Hedge fund replication and synthetic funds are connected through their shared goal of mimicking hedge fund returns using alternative investment strategies. Hedge fund replication employs quantitative models and liquid assets to replicate hedge fund performance, while synthetic funds use derivatives and swaps to synthetically create exposure to hedge fund strategies. Both methods aim to provide investors with cost-effective, transparent access to hedge fund-like returns without direct investment in traditional hedge funds.
Key Terms
Derivatives
Synthetic funds use derivatives such as swaps and options to replicate the returns of an underlying asset without owning it directly, enabling cost efficiency and improved liquidity. Hedge fund replication involves constructing portfolios using liquid assets and derivatives to mimic hedge fund strategies while reducing fees and enhancing transparency. Explore more to understand the complexities and advantages of derivatives in synthetic fund and hedge fund replication.
Tracking Error
Synthetic funds use derivatives to mimic a hedge fund's performance, aiming to reduce tracking error by closely replicating returns without owning underlying assets directly. Hedge fund replication strategies analyze factor exposures to construct portfolios that minimize discrepancies in risk and return profiles, thereby lowering tracking error compared to traditional hedge funds. Explore the complexities of tracking error in synthetic and hedge fund replication to optimize your investment strategy.
Portfolio Construction
Synthetic funds utilize derivatives such as swaps to replicate the performance of target indices, enabling precise exposure with lower upfront capital and enhanced liquidity management compared to traditional hedge fund replication strategies. Hedge fund replication often involves statistically modeling hedge fund returns through factor-based portfolios, which may introduce tracking error and reduce transparency due to reliance on historical correlations. Explore the detailed methodologies and benefits of synthetic fund portfolio construction to optimize investment strategies.
Source and External Links
Introduction to Synthetic Funds - Synthetic funds replicate hedge fund returns by creating ideal risk-return profiles with zero or negative correlation to stocks and bonds, using backtested investment strategies to offer liquid and transparent alternatives to direct hedge fund investments.
What you need to know about physical and synthetic ETFs - Synthetic ETFs use swaps with counterparties to deliver returns of an index without physically holding securities, exposing investors to counterparty risk but allowing cost and access benefits compared to physical funds.
Synthetic ETF - Synthetic ETFs use derivative contracts, typically swaps, to track an index's performance rather than buying securities directly, offering efficient replication but carrying counterparty risk and less transparency around ESG factors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com