Carbon credit arbitrage leverages the price differentials between carbon markets to generate profits while promoting emissions reduction, offering a dynamic approach to climate finance. Sustainable infrastructure funds focus on long-term investments in projects that enhance environmental resilience and resource efficiency, aligning capital with global sustainability goals. Discover more about the strategic advantages and risk profiles of these innovative investment pathways.
Why it is important
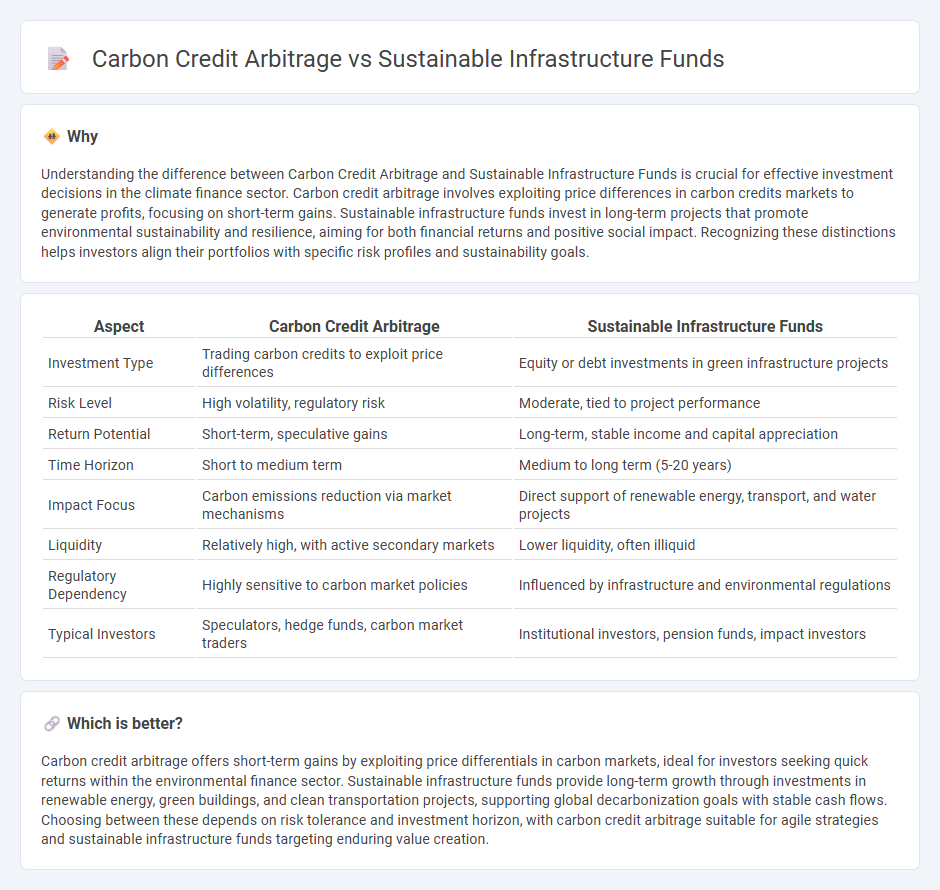
Understanding the difference between Carbon Credit Arbitrage and Sustainable Infrastructure Funds is crucial for effective investment decisions in the climate finance sector. Carbon credit arbitrage involves exploiting price differences in carbon credits markets to generate profits, focusing on short-term gains. Sustainable infrastructure funds invest in long-term projects that promote environmental sustainability and resilience, aiming for both financial returns and positive social impact. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors align their portfolios with specific risk profiles and sustainability goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Credit Arbitrage | Sustainable Infrastructure Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Type | Trading carbon credits to exploit price differences | Equity or debt investments in green infrastructure projects |
| Risk Level | High volatility, regulatory risk | Moderate, tied to project performance |
| Return Potential | Short-term, speculative gains | Long-term, stable income and capital appreciation |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term | Medium to long term (5-20 years) |
| Impact Focus | Carbon emissions reduction via market mechanisms | Direct support of renewable energy, transport, and water projects |
| Liquidity | Relatively high, with active secondary markets | Lower liquidity, often illiquid |
| Regulatory Dependency | Highly sensitive to carbon market policies | Influenced by infrastructure and environmental regulations |
| Typical Investors | Speculators, hedge funds, carbon market traders | Institutional investors, pension funds, impact investors |
Which is better?
Carbon credit arbitrage offers short-term gains by exploiting price differentials in carbon markets, ideal for investors seeking quick returns within the environmental finance sector. Sustainable infrastructure funds provide long-term growth through investments in renewable energy, green buildings, and clean transportation projects, supporting global decarbonization goals with stable cash flows. Choosing between these depends on risk tolerance and investment horizon, with carbon credit arbitrage suitable for agile strategies and sustainable infrastructure funds targeting enduring value creation.
Connection
Carbon credit arbitrage leverages price differences in carbon markets to generate profits while promoting emission reductions, directly aligning with the goals of sustainable infrastructure funds that invest in eco-friendly projects. Sustainable infrastructure funds channel capital into renewable energy, green buildings, and low-carbon transportation, creating demand for carbon credits and enhancing their market value. This symbiotic relationship accelerates decarbonization efforts by integrating financial returns with environmental impact through strategic investment flows.
Key Terms
Sustainable infrastructure funds:
Sustainable infrastructure funds channel investments into projects that prioritize renewable energy, efficient water management, and green transportation, driving long-term environmental and social benefits. These funds focus on tangible asset development that reduces carbon footprints while promoting economic growth, making them a critical component of ESG portfolios. Explore how sustainable infrastructure funds can align your investments with impactful climate goals.
Green bonds
Sustainable infrastructure funds primarily invest in projects that deliver long-term environmental benefits, such as renewable energy and green transportation, while carbon credit arbitrage exploits price differences in carbon markets for profit. Green bonds are financial instruments that fund sustainable infrastructure projects by providing capital to environmentally responsible initiatives, offering both investors and issuers a path toward climate-friendly development. Explore how green bonds bridge investment strategies and environmental impact in the evolving sustainable finance landscape.
ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance)
Sustainable infrastructure funds invest in projects that enhance environmental resilience, promote social welfare, and uphold strong governance practices, aligning closely with ESG criteria to generate long-term value. Carbon credit arbitrage exploits price differences in carbon markets to maximize financial gains but may carry higher regulatory and reputational risks related to ESG standards. Explore how these investment strategies uniquely impact sustainable finance and ESG outcomes.
Source and External Links
Impax Global Sustainable Infrastructure Fund - Seeks long-term capital growth with income by investing in companies deriving at least 20% of revenue from sustainable infrastructure, aiming for lower carbon intensity compared to traditional infrastructure portfolios.
JPMorgan Sustainable Infrastructure Fund - Primarily invests in global equities and REITs that support sustainable and inclusive economic development, managed with a blend of fundamental, quantitative, and sustainable investing expertise.
Sustainable Infrastructure (GI Hub) - Provides resources, data, and tools to help governments and industry scale up investment in infrastructure delivering long-term economic, social, and environmental benefits, addressing a global investment gap estimated at $2.6 trillion annually through 2030.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com