Fractional ownership real estate offers investors the opportunity to purchase a portion of a property, allowing for lower entry costs and shared usage rights compared to whole ownership. Private equity real estate involves pooled capital from multiple investors managed by firms targeting large-scale properties with potential for higher returns but also increased risk and less liquidity. Explore the key differences between these investment approaches to determine which aligns best with your portfolio goals.
Why it is important
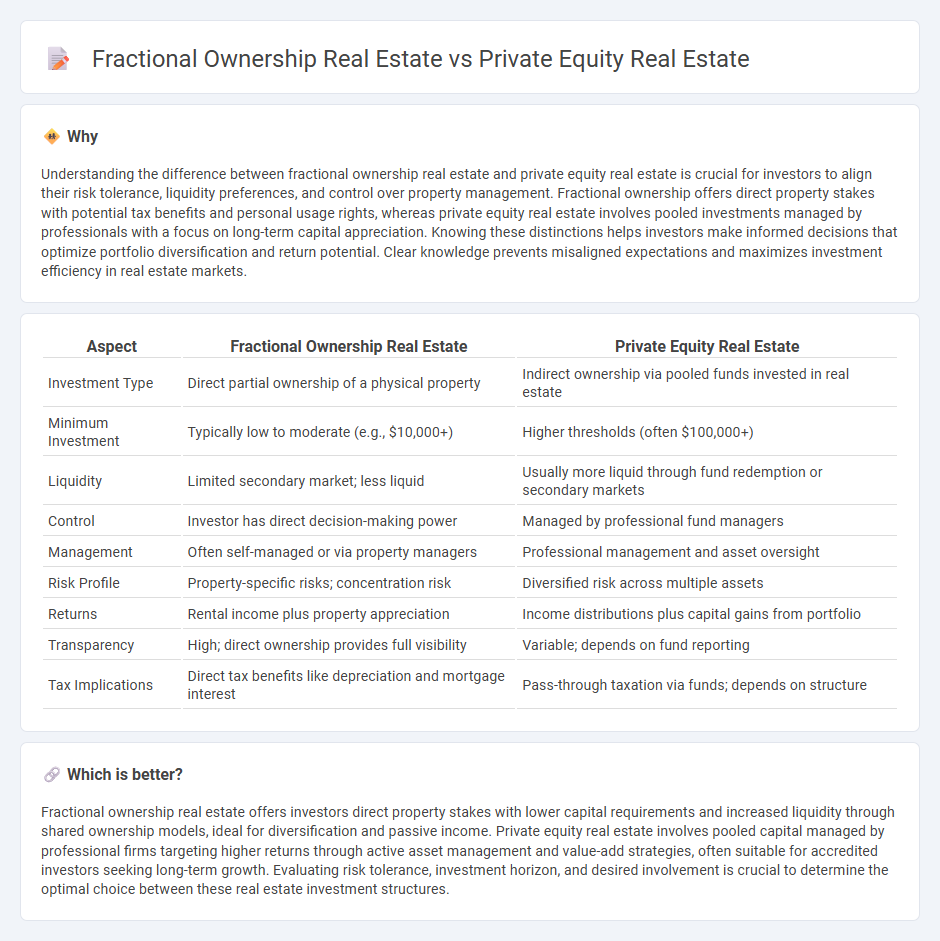
Understanding the difference between fractional ownership real estate and private equity real estate is crucial for investors to align their risk tolerance, liquidity preferences, and control over property management. Fractional ownership offers direct property stakes with potential tax benefits and personal usage rights, whereas private equity real estate involves pooled investments managed by professionals with a focus on long-term capital appreciation. Knowing these distinctions helps investors make informed decisions that optimize portfolio diversification and return potential. Clear knowledge prevents misaligned expectations and maximizes investment efficiency in real estate markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Fractional Ownership Real Estate | Private Equity Real Estate |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Type | Direct partial ownership of a physical property | Indirect ownership via pooled funds invested in real estate |
| Minimum Investment | Typically low to moderate (e.g., $10,000+) | Higher thresholds (often $100,000+) |
| Liquidity | Limited secondary market; less liquid | Usually more liquid through fund redemption or secondary markets |
| Control | Investor has direct decision-making power | Managed by professional fund managers |
| Management | Often self-managed or via property managers | Professional management and asset oversight |
| Risk Profile | Property-specific risks; concentration risk | Diversified risk across multiple assets |
| Returns | Rental income plus property appreciation | Income distributions plus capital gains from portfolio |
| Transparency | High; direct ownership provides full visibility | Variable; depends on fund reporting |
| Tax Implications | Direct tax benefits like depreciation and mortgage interest | Pass-through taxation via funds; depends on structure |
Which is better?
Fractional ownership real estate offers investors direct property stakes with lower capital requirements and increased liquidity through shared ownership models, ideal for diversification and passive income. Private equity real estate involves pooled capital managed by professional firms targeting higher returns through active asset management and value-add strategies, often suitable for accredited investors seeking long-term growth. Evaluating risk tolerance, investment horizon, and desired involvement is crucial to determine the optimal choice between these real estate investment structures.
Connection
Fractional ownership real estate and private equity real estate both enable investors to access real estate markets with lower capital requirements by pooling funds from multiple participants. Fractional ownership divides a single property into shares, allowing investors direct equity stakes, while private equity real estate involves investment in real estate funds or companies that manage a portfolio of properties. Both models enhance diversification and liquidity opportunities for investors seeking exposure to commercial or residential real estate assets.
Key Terms
Fund Structure
Private equity real estate funds aggregate capital from limited partners to invest in large-scale property portfolios managed by general partners, offering diversified exposure and professional management. Fractional ownership structures divide a single property into shares, enabling individual investors to purchase a portion, often with direct involvement and simplified entry thresholds. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which fund structure aligns with your investment strategy.
Ownership Model
Private equity real estate involves pooled capital from accredited investors managed by professionals, offering indirect ownership through shares or partnership interests in diversified property portfolios. Fractional ownership real estate grants individuals direct, deeded partial ownership of a specific property, typically marketed to retail investors seeking tangible asset control with shared usage rights. Explore these distinct ownership models to determine which aligns best with your investment strategy and risk tolerance.
Liquidity
Private equity real estate typically involves longer holding periods with limited liquidity, as investors commit capital for 5 to 10 years before exit options arise through asset sales or fund liquidations. Fractional ownership real estate offers enhanced liquidity by allowing investors to buy and sell shares more frequently on secondary markets or through trading platforms, often with shorter investment horizons. Explore further to understand which liquidity option aligns best with your real estate investment strategy.
Source and External Links
Real Estate Private Equity: Overview, Careers, Salaries & Interviews - Real estate private equity (REPE) firms raise capital from outside investors (Limited Partners) to acquire, develop, operate, and sell commercial properties, focusing mainly on offices, industrial, retail, and multifamily assets rather than residential real estate.
Private equity real estate - Wikipedia - Private equity real estate involves direct ownership and financing of individual properties or portfolios through various fund structures, typically accessible to accredited investors and institutional entities who participate via private funds or partnerships.
Private Real Estate Investments: What You Need to Know - KKR - Private real estate investments include equity (ownership) and credit (loans), offering potential portfolio diversification, inflation hedging, and exposure to a large commercial real estate market with returns driven by rental income, appreciation, and property sales.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com