Carbon offset investing focuses on funding projects that reduce or capture greenhouse gas emissions, directly addressing climate change through verifiable carbon credits. Socially responsible investing (SRI) involves selecting companies based on broader ethical criteria, including environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors to promote sustainable business practices. Explore the distinctions and benefits of these investment strategies to align your portfolio with your values.
Why it is important
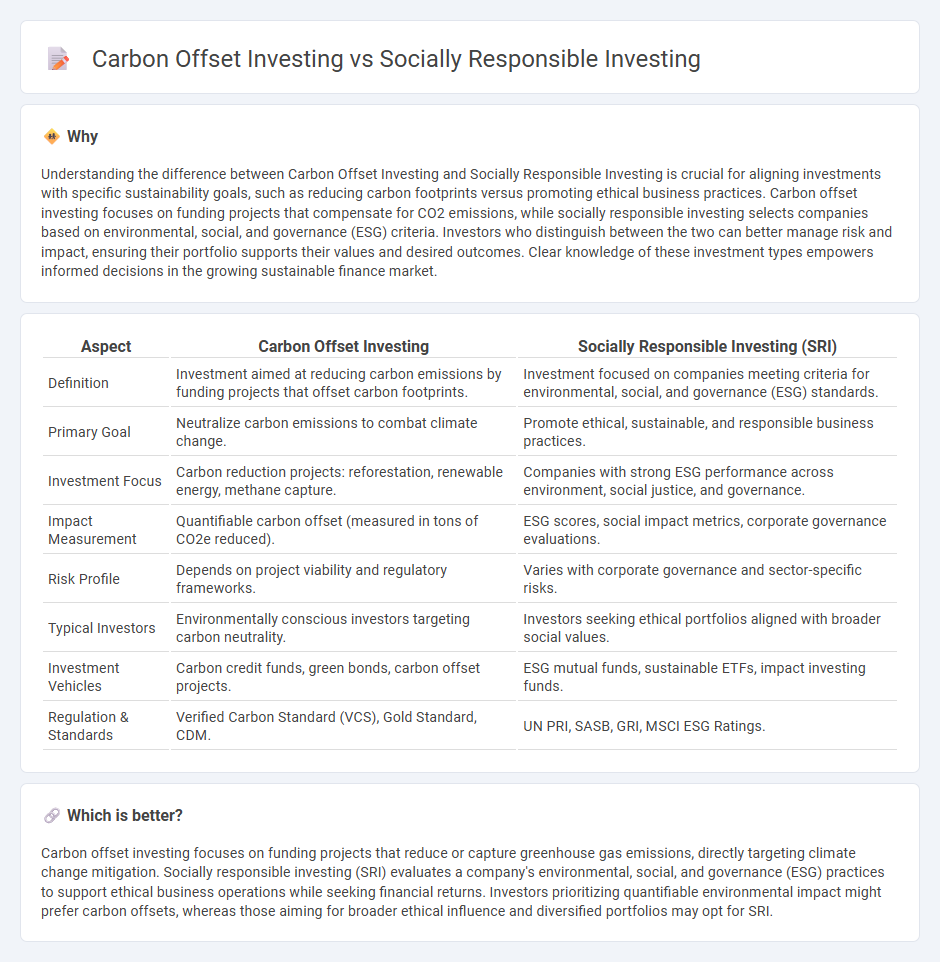
Understanding the difference between Carbon Offset Investing and Socially Responsible Investing is crucial for aligning investments with specific sustainability goals, such as reducing carbon footprints versus promoting ethical business practices. Carbon offset investing focuses on funding projects that compensate for CO2 emissions, while socially responsible investing selects companies based on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. Investors who distinguish between the two can better manage risk and impact, ensuring their portfolio supports their values and desired outcomes. Clear knowledge of these investment types empowers informed decisions in the growing sustainable finance market.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Offset Investing | Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment aimed at reducing carbon emissions by funding projects that offset carbon footprints. | Investment focused on companies meeting criteria for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards. |
| Primary Goal | Neutralize carbon emissions to combat climate change. | Promote ethical, sustainable, and responsible business practices. |
| Investment Focus | Carbon reduction projects: reforestation, renewable energy, methane capture. | Companies with strong ESG performance across environment, social justice, and governance. |
| Impact Measurement | Quantifiable carbon offset (measured in tons of CO2e reduced). | ESG scores, social impact metrics, corporate governance evaluations. |
| Risk Profile | Depends on project viability and regulatory frameworks. | Varies with corporate governance and sector-specific risks. |
| Typical Investors | Environmentally conscious investors targeting carbon neutrality. | Investors seeking ethical portfolios aligned with broader social values. |
| Investment Vehicles | Carbon credit funds, green bonds, carbon offset projects. | ESG mutual funds, sustainable ETFs, impact investing funds. |
| Regulation & Standards | Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), Gold Standard, CDM. | UN PRI, SASB, GRI, MSCI ESG Ratings. |
Which is better?
Carbon offset investing focuses on funding projects that reduce or capture greenhouse gas emissions, directly targeting climate change mitigation. Socially responsible investing (SRI) evaluates a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices to support ethical business operations while seeking financial returns. Investors prioritizing quantifiable environmental impact might prefer carbon offsets, whereas those aiming for broader ethical influence and diversified portfolios may opt for SRI.
Connection
Carbon offset investing and socially responsible investing (SRI) both prioritize environmental sustainability by funding projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions or support renewable energy. These investment strategies align to promote ethical financial growth while addressing climate change and social impact criteria. Integrating carbon offsets within SRI portfolios enhances positive environmental outcomes and meets increasing investor demand for transparency and accountability.
Key Terms
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance)
Socially responsible investing (SRI) integrates Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria to screen companies based on ethical performance, promoting sustainable business practices and corporate accountability. Carbon offset investing specifically targets projects that reduce or capture greenhouse gas emissions, focusing primarily on environmental impact to mitigate climate change. Explore the nuances between SRI and carbon offset investing to align your investment strategy with your values and environmental goals.
Carbon Credits
Socially responsible investing (SRI) integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to foster ethical business practices, while carbon offset investing specifically targets the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions through the purchase of carbon credits verified by standards like the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) or Gold Standard. Carbon credits represent quantifiable, verifiable emission reductions from projects such as reforestation or renewable energy, enabling investors to directly support climate action and achieve net-zero goals. Explore how carbon credits can enhance your investment strategy and promote sustainable impact.
Impact Measurement
Socially responsible investing (SRI) emphasizes ethical criteria and ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) metrics to evaluate corporate behavior, while carbon offset investing specifically targets the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions through verified projects like reforestation or renewable energy. Impact measurement in SRI relies on comprehensive sustainability ratings, stakeholder engagement, and social impact assessments, whereas carbon offset investing demands precise quantification of CO2 equivalents reduced or sequestered, certified by standards such as the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) or Gold Standard. Explore how these approaches differ in driving measurable environmental and social change by learning more about their impact assessment methodologies.
Source and External Links
Socially Responsible Investing - Green America - Socially responsible investing (SRI) integrates your values with investment decisions, focusing on companies with transparency, positive environmental policies, respect for human rights, and community involvement while avoiding those that fall short in these areas.
Socially responsible investing - Wikipedia - SRI is an investment strategy that considers financial return alongside ethical, social, or environmental goals, typically linked to ESG issues, and includes practices like impact investing, shareholder advocacy, and community investing.
What Is Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) and How to Get Started - NerdWallet - SRI aims to generate both social change and financial returns, has become increasingly popular and accessible, and includes investing in companies aligned with sustainable, impact, or ethical criteria.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com