Collectibles investment offers diversification through unique assets like art, rare coins, and vintage items that can appreciate based on rarity and demand, while real estate investment provides tangible property ownership with potential for rental income and long-term capital growth. Both investment types carry distinct risks and liquidity considerations, with real estate generally requiring more capital and longer commitment periods compared to collectibles. Explore the advantages and challenges of collectibles versus real estate investment to determine the best fit for your portfolio goals.
Why it is important
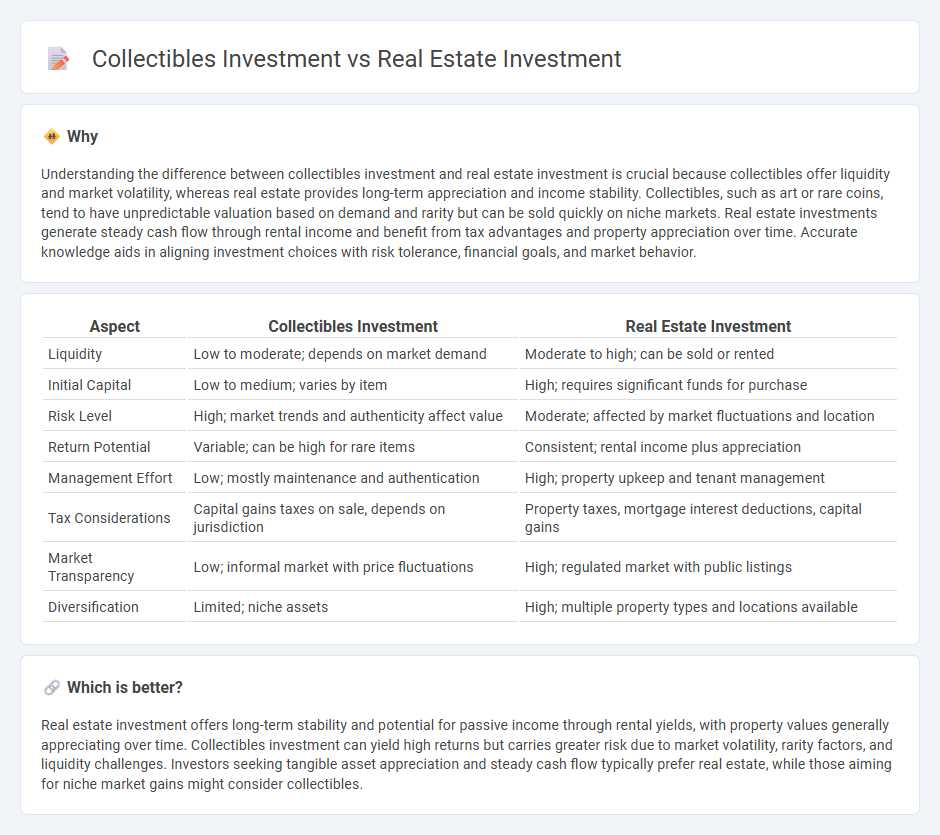
Understanding the difference between collectibles investment and real estate investment is crucial because collectibles offer liquidity and market volatility, whereas real estate provides long-term appreciation and income stability. Collectibles, such as art or rare coins, tend to have unpredictable valuation based on demand and rarity but can be sold quickly on niche markets. Real estate investments generate steady cash flow through rental income and benefit from tax advantages and property appreciation over time. Accurate knowledge aids in aligning investment choices with risk tolerance, financial goals, and market behavior.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Collectibles Investment | Real Estate Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Liquidity | Low to moderate; depends on market demand | Moderate to high; can be sold or rented |
| Initial Capital | Low to medium; varies by item | High; requires significant funds for purchase |
| Risk Level | High; market trends and authenticity affect value | Moderate; affected by market fluctuations and location |
| Return Potential | Variable; can be high for rare items | Consistent; rental income plus appreciation |
| Management Effort | Low; mostly maintenance and authentication | High; property upkeep and tenant management |
| Tax Considerations | Capital gains taxes on sale, depends on jurisdiction | Property taxes, mortgage interest deductions, capital gains |
| Market Transparency | Low; informal market with price fluctuations | High; regulated market with public listings |
| Diversification | Limited; niche assets | High; multiple property types and locations available |
Which is better?
Real estate investment offers long-term stability and potential for passive income through rental yields, with property values generally appreciating over time. Collectibles investment can yield high returns but carries greater risk due to market volatility, rarity factors, and liquidity challenges. Investors seeking tangible asset appreciation and steady cash flow typically prefer real estate, while those aiming for niche market gains might consider collectibles.
Connection
Collectibles investment and real estate investment both serve as alternative asset classes that diversify traditional investment portfolios and hedge against market volatility. Both types of investments require careful valuation, market research, and an understanding of liquidity, as collectibles like art or antiques and real estate properties often appreciate over time based on rarity, location, and demand. Investors leverage tangible assets in these markets to preserve wealth and achieve long-term capital growth beyond stocks and bonds.
Key Terms
Real Estate Investment:
Real estate investment offers tangible assets with potential for steady rental income and long-term capital appreciation, supported by property value trends and market demand. Unlike collectibles, real estate provides tax benefits, leverage options, and inflation hedging through physical property ownership. Explore detailed strategies and market insights to maximize returns in real estate investing.
Capital Appreciation
Real estate investment offers significant capital appreciation driven by property value increases in emerging and high-demand locations, often supported by rental income and market stability. Collectibles investment, including art, antiques, and rare items, provides capital appreciation through scarcity and uniqueness, though it tends to be more volatile and less liquid compared to real estate. Discover detailed comparisons and strategies to optimize capital growth in these investment categories.
Rental Yield
Rental yield is a key metric for real estate investments, typically ranging from 4% to 10% annually depending on location and property type. Collectibles, such as art or rare items, often lack regular income streams and rely on appreciation, which can be unpredictable and illiquid. Explore detailed analyses to understand the nuances of rental yields and long-term value in both asset classes.
Source and External Links
Real Estate Investing: 5 Ways to Get Started - NerdWallet - Provides five common methods to invest in real estate, including REITs, rental properties, flipping properties, and platforms that offer scalable options without landlord responsibilities, highlighting that real estate can diversify portfolios and offer passive income opportunities.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) | Investor.gov - Explains what REITs are, their structure as companies owning income-producing real estate, types of REITs (publicly traded and non-traded), and how they allow investors to earn income from commercial properties without direct ownership responsibilities.
Real estate investment made easy - Start today - Yieldstreet - Offers access to private real estate investment opportunities with minimum investments around $10,000, emphasizing historical inflation outperformance and providing a tech-driven platform for diversified real estate investing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com