Sports team ownership shares offer dynamic investment opportunities characterized by high-profile asset appreciation and fan-driven value, often influenced by team performance and market demand. Real estate investment trusts (REITs) provide diversified, income-generating real estate portfolios with liquidity and dividend yields, appealing to investors seeking stable cash flow and lower volatility. Explore the comparative benefits and risks of sports team ownership versus REITs to make informed investment decisions.
Why it is important
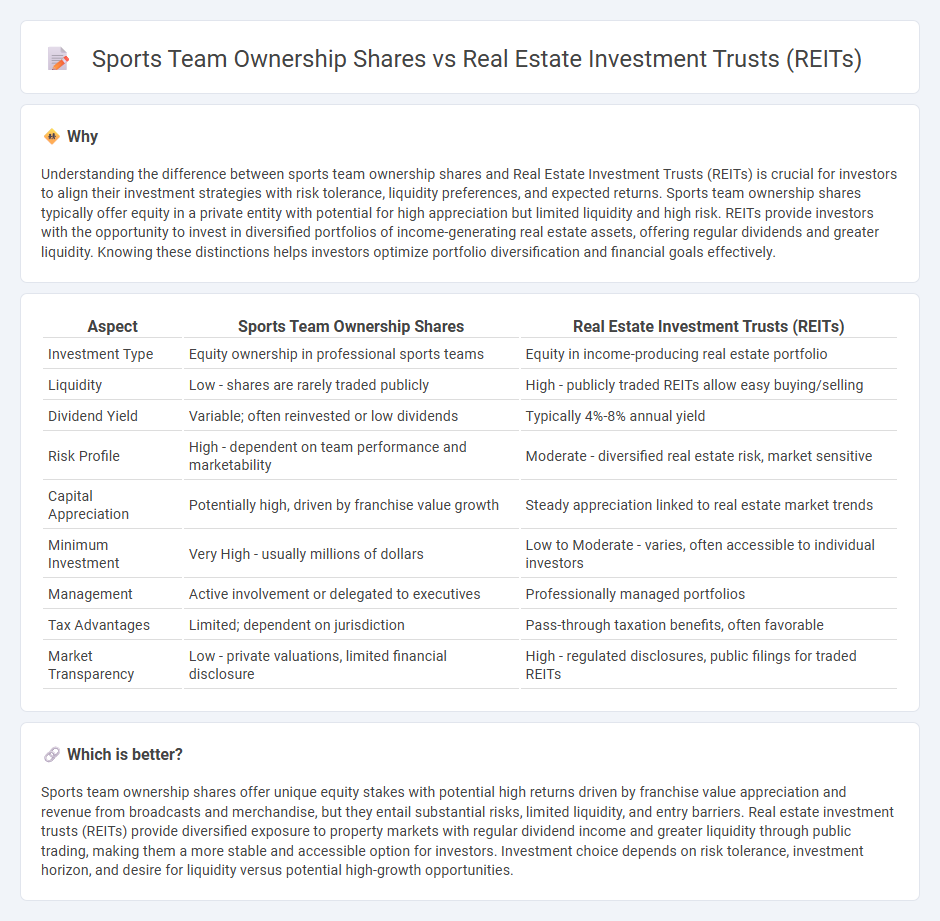
Understanding the difference between sports team ownership shares and Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) is crucial for investors to align their investment strategies with risk tolerance, liquidity preferences, and expected returns. Sports team ownership shares typically offer equity in a private entity with potential for high appreciation but limited liquidity and high risk. REITs provide investors with the opportunity to invest in diversified portfolios of income-generating real estate assets, offering regular dividends and greater liquidity. Knowing these distinctions helps investors optimize portfolio diversification and financial goals effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sports Team Ownership Shares | Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Type | Equity ownership in professional sports teams | Equity in income-producing real estate portfolio |
| Liquidity | Low - shares are rarely traded publicly | High - publicly traded REITs allow easy buying/selling |
| Dividend Yield | Variable; often reinvested or low dividends | Typically 4%-8% annual yield |
| Risk Profile | High - dependent on team performance and marketability | Moderate - diversified real estate risk, market sensitive |
| Capital Appreciation | Potentially high, driven by franchise value growth | Steady appreciation linked to real estate market trends |
| Minimum Investment | Very High - usually millions of dollars | Low to Moderate - varies, often accessible to individual investors |
| Management | Active involvement or delegated to executives | Professionally managed portfolios |
| Tax Advantages | Limited; dependent on jurisdiction | Pass-through taxation benefits, often favorable |
| Market Transparency | Low - private valuations, limited financial disclosure | High - regulated disclosures, public filings for traded REITs |
Which is better?
Sports team ownership shares offer unique equity stakes with potential high returns driven by franchise value appreciation and revenue from broadcasts and merchandise, but they entail substantial risks, limited liquidity, and entry barriers. Real estate investment trusts (REITs) provide diversified exposure to property markets with regular dividend income and greater liquidity through public trading, making them a more stable and accessible option for investors. Investment choice depends on risk tolerance, investment horizon, and desire for liquidity versus potential high-growth opportunities.
Connection
Sports team ownership shares and Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) intersect as alternative investment vehicles offering diversification and potential for appreciation in asset value. Ownership shares in sports teams provide equity stakes in franchises with lucrative revenue streams from media rights, sponsorships, and merchandise, while REITs offer exposure to income-generating real estate properties with steady dividend yields. Both investment types attract institutional and affluent investors seeking portfolio growth through assets with limited correlation to traditional stocks and bonds.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Real estate investment trusts (REITs) offer high liquidity by allowing investors to buy and sell shares on major stock exchanges with ease, providing quick access to capital. In contrast, sports team ownership shares are typically illiquid, as they are privately held and involve lengthy transfer processes, limiting immediate market availability and price transparency. Explore the distinctions in liquidity and investment potential between REITs and sports team ownership to make informed financial decisions.
Valuation
Real estate investment trusts (REITs) are typically valued based on metrics such as funds from operations (FFO), net asset value (NAV), and dividend yield, reflecting their income-generating property portfolios. Sports team ownership shares derive valuation from market demand, franchise profitability, brand equity, and league revenue sharing agreements, often resulting in more volatile and less transparent pricing. Explore detailed comparative analyses to understand how these valuation approaches impact investment decisions.
Dividend/Revenue Sharing
Real estate investment trusts (REITs) generate consistent dividend income by distributing at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders, making them a reliable source of passive income through real estate assets. In contrast, sports team ownership shares typically offer revenue sharing through profit participation but may provide less predictable income due to factors like team performance and league revenue. Explore the distinct financial dynamics of REIT dividends versus sports ownership revenue sharing for informed investment decisions.
Source and External Links
Real estate investment trust - Wikipedia - REITs are companies that own and usually operate income-producing real estate across various sectors, and they are often classified as equity or mortgage REITs, with public, private, or non-traded structures.
What's a REIT (Real Estate Investment Trust)? - Nareit - REITs provide investors with regular income, diversification, and potential for long-term capital appreciation by pooling capital to invest in real estate assets, and most trade on major stock exchanges.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) | Investor.gov - REITs enable individuals to invest in large-scale income-producing real estate--such as office buildings, malls, and hotels--without directly owning property, and they are available in publicly traded and non-traded forms with different risk profiles.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com