Patent monetization involves generating revenue by licensing, selling, or leveraging intellectual property rights, creating a steady income stream from innovations. Private equity focuses on acquiring equity stakes in private companies, aiming for capital appreciation through operational improvements and strategic growth. Explore the distinctions and benefits of these investment strategies to enhance your portfolio performance.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between patent monetization and private equity is crucial for investors to optimize asset allocation and risk management. Patent monetization involves generating revenue through licensing or selling intellectual property, while private equity focuses on investing capital in private companies for ownership stakes and growth. Understanding these distinctions helps in aligning investment strategies with targeted returns and liquidity preferences. This knowledge maximizes financial outcomes and supports informed decision-making in diverse investment portfolios.
Comparison Table
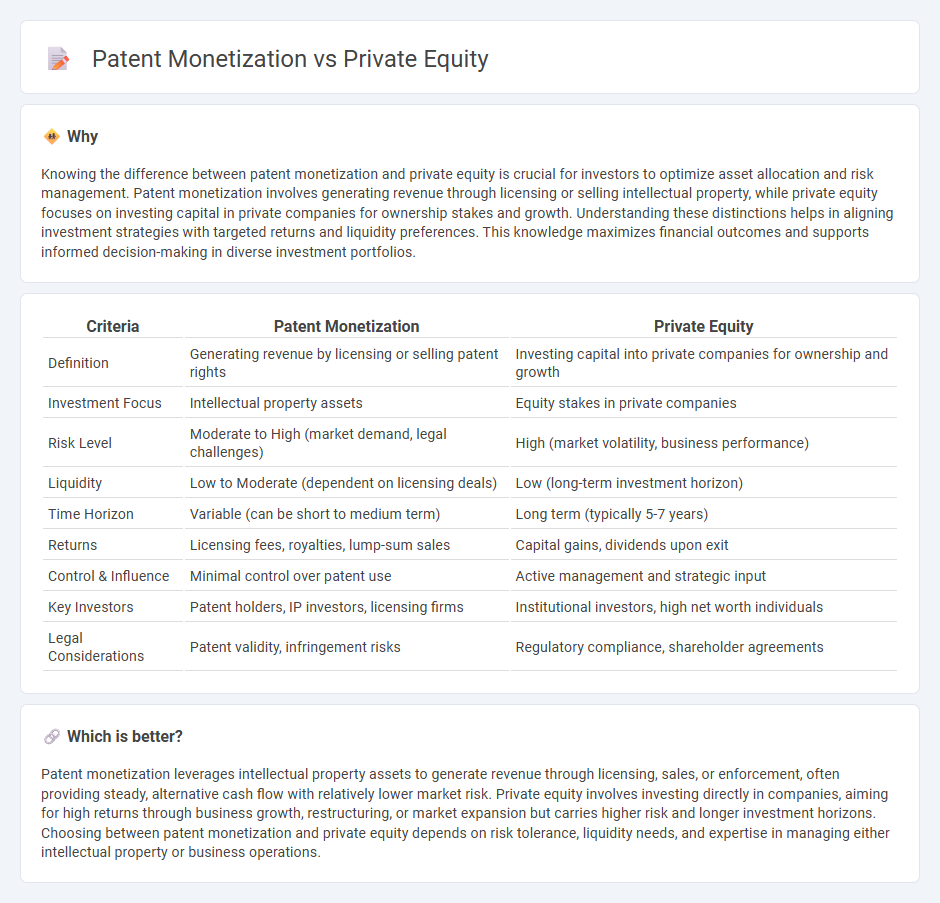
| Criteria | Patent Monetization | Private Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generating revenue by licensing or selling patent rights | Investing capital into private companies for ownership and growth |
| Investment Focus | Intellectual property assets | Equity stakes in private companies |
| Risk Level | Moderate to High (market demand, legal challenges) | High (market volatility, business performance) |
| Liquidity | Low to Moderate (dependent on licensing deals) | Low (long-term investment horizon) |
| Time Horizon | Variable (can be short to medium term) | Long term (typically 5-7 years) |
| Returns | Licensing fees, royalties, lump-sum sales | Capital gains, dividends upon exit |
| Control & Influence | Minimal control over patent use | Active management and strategic input |
| Key Investors | Patent holders, IP investors, licensing firms | Institutional investors, high net worth individuals |
| Legal Considerations | Patent validity, infringement risks | Regulatory compliance, shareholder agreements |
Which is better?
Patent monetization leverages intellectual property assets to generate revenue through licensing, sales, or enforcement, often providing steady, alternative cash flow with relatively lower market risk. Private equity involves investing directly in companies, aiming for high returns through business growth, restructuring, or market expansion but carries higher risk and longer investment horizons. Choosing between patent monetization and private equity depends on risk tolerance, liquidity needs, and expertise in managing either intellectual property or business operations.
Connection
Patent monetization enhances the value of intellectual property by converting patents into revenue streams through licensing or sales, attracting private equity investments seeking high-return assets. Private equity firms invest in companies with robust patent portfolios to leverage these intangible assets for competitive advantage and market growth. This synergy drives innovation funding and amplifies portfolio diversification, integrating intellectual property strategy with financial capital deployment.
Key Terms
Fund Structure
Private equity fund structures typically involve limited partnerships where general partners manage investments and limited partners provide capital, emphasizing long-term value creation through equity stakes in portfolio companies. Patent monetization funds often use specialized vehicles designed to acquire, manage, and license intellectual property, focusing on generating revenue from patent portfolios rather than operational businesses. Explore detailed comparisons of fund structures to optimize investment strategies and risk management in these distinct models.
Intellectual Property Valuation
Private equity investments often rely on comprehensive intellectual property valuation to assess the potential returns and risks of portfolio companies, emphasizing patents as critical assets. Patent monetization strategies, including licensing or sales, require precise IP valuation to maximize revenue and protect innovation value. Explore detailed methodologies to optimize intellectual property valuation for strategic financial decisions.
Exit Strategy
Exit strategy in private equity primarily involves selling portfolio companies through initial public offerings (IPOs), mergers, or acquisitions to realize returns for investors. Patent monetization exit strategies often include licensing agreements, patent sales, or litigation settlements aimed at maximizing intellectual property value. Explore the critical differences and advantages of each approach to optimize your exit strategy.
Source and External Links
Private equity - Wikipedia - Private equity (PE) is stock in a private company not publicly traded, raised by investment managers from institutional investors, focusing on buying equity stakes using equity and debt financing to generate returns through revenue growth, margin expansion, cash flow, and valuation multiple expansion over 4-7 years.
What is Private Equity? - BVCA - Private equity provides medium to long-term finance for equity stakes in mature, high-growth companies with close operational involvement from PE managers to drive growth, efficiency, and value creation typically held for 4-7 years before exit.
Private Equity: What You Need to Know - KKR - Private equity invests in non-publicly traded companies aiming to enhance their performance via management strengthening, strategy, operations, new products, and capital structuring to achieve total returns and diversification benefits amid a shrinking public company universe.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com