Song catalog purchases offer investors long-term royalty income and portfolio diversification through ownership of music rights, while peer-to-peer lending provides direct lending opportunities with potential for higher returns and risk diversification via multiple borrower profiles. Both investment types cater to alternative asset strategies, balancing income generation with risk exposure in unique ways. Explore more to determine which investment aligns best with your financial goals and risk appetite.
Why it is important
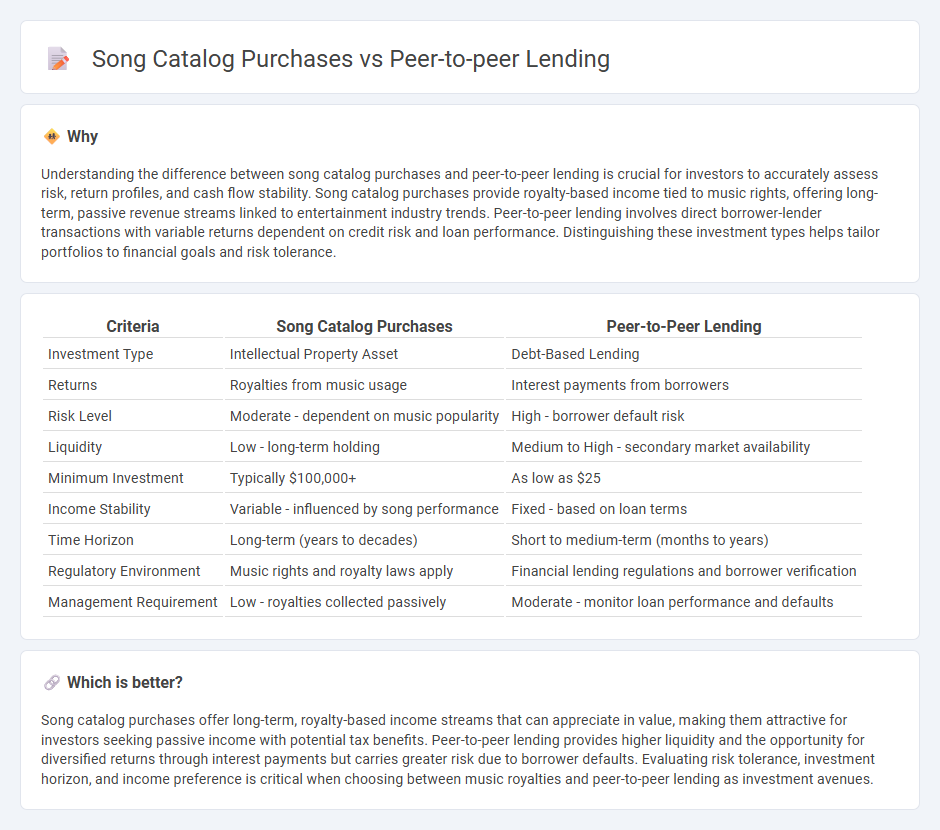
Understanding the difference between song catalog purchases and peer-to-peer lending is crucial for investors to accurately assess risk, return profiles, and cash flow stability. Song catalog purchases provide royalty-based income tied to music rights, offering long-term, passive revenue streams linked to entertainment industry trends. Peer-to-peer lending involves direct borrower-lender transactions with variable returns dependent on credit risk and loan performance. Distinguishing these investment types helps tailor portfolios to financial goals and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Song Catalog Purchases | Peer-to-Peer Lending |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Type | Intellectual Property Asset | Debt-Based Lending |
| Returns | Royalties from music usage | Interest payments from borrowers |
| Risk Level | Moderate - dependent on music popularity | High - borrower default risk |
| Liquidity | Low - long-term holding | Medium to High - secondary market availability |
| Minimum Investment | Typically $100,000+ | As low as $25 |
| Income Stability | Variable - influenced by song performance | Fixed - based on loan terms |
| Time Horizon | Long-term (years to decades) | Short to medium-term (months to years) |
| Regulatory Environment | Music rights and royalty laws apply | Financial lending regulations and borrower verification |
| Management Requirement | Low - royalties collected passively | Moderate - monitor loan performance and defaults |
Which is better?
Song catalog purchases offer long-term, royalty-based income streams that can appreciate in value, making them attractive for investors seeking passive income with potential tax benefits. Peer-to-peer lending provides higher liquidity and the opportunity for diversified returns through interest payments but carries greater risk due to borrower defaults. Evaluating risk tolerance, investment horizon, and income preference is critical when choosing between music royalties and peer-to-peer lending as investment avenues.
Connection
Song catalog purchases and peer-to-peer lending both serve as alternative investment opportunities, offering investors diversification beyond traditional stocks and bonds. Investing in song catalogs generates steady royalty income driven by intellectual property rights, while peer-to-peer lending provides interest returns through direct loans between individuals. Both investment types leverage asset-backed cash flows, appealing to those seeking passive income streams with varying risk profiles.
Key Terms
Default Risk
Peer-to-peer lending carries a higher default risk, as borrowers may fail to repay loans due to varying creditworthiness and economic conditions, whereas song catalog purchases typically offer a more stable revenue stream through royalty payments with less exposure to default risk. Song catalogs generate income from diverse sources such as streaming, licensing, and synchronization, providing consistent cash flow and lowering the likelihood of financial loss. Explore further to understand how default risk impacts investment strategies between these two asset classes.
Royalties
Peer-to-peer lending offers investors returns based on loan interest, while song catalog purchases generate income through royalties from music usage and licensing. Royalty streams provide passive, long-term cash flow tied to song performance across platforms like streaming services, radio, and advertising. Explore further to understand which investment aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Platform Fees
Peer-to-peer lending platforms typically charge platform fees ranging from 1% to 5% of the loan amount, which cover origination, servicing, and investor management. In contrast, song catalog purchases often involve fees tied to due diligence, legal processing, and royalty management, usually negotiated as a percentage of the total transaction or ongoing revenue share. Explore detailed comparisons of fee structures to optimize your investment strategy in both domains.
Source and External Links
What is Peer-to-Peer Lending & How P2P Loans Work - Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending connects individual lenders to borrowers through online platforms, bypassing traditional banks, and offers potentially flexible terms and competitive rates.
Peer-to-peer lending - P2P lending is an online service that matches lenders with borrowers directly, often offering more control over investment choices and lacking government insurance protections typically found with traditional banks.
Peer to peer lending: what you need to know - P2P lending allows individuals to lend money directly to others or businesses via online marketplaces, generally offering higher interest rates than savings accounts but with greater risk of borrower default.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com