Collectibles investment involves acquiring rare items such as art, coins, or vintage cars that may appreciate in value due to rarity and demand, whereas commodities investment focuses on tangible goods like gold, oil, or agricultural products traded on global markets with prices influenced by supply and demand dynamics. Collectibles often require expertise in valuation and carry liquidity risks, while commodities offer more standardized trading and can serve as hedges against inflation. Explore the distinct benefits and challenges of both to tailor your investment strategy effectively.
Why it is important
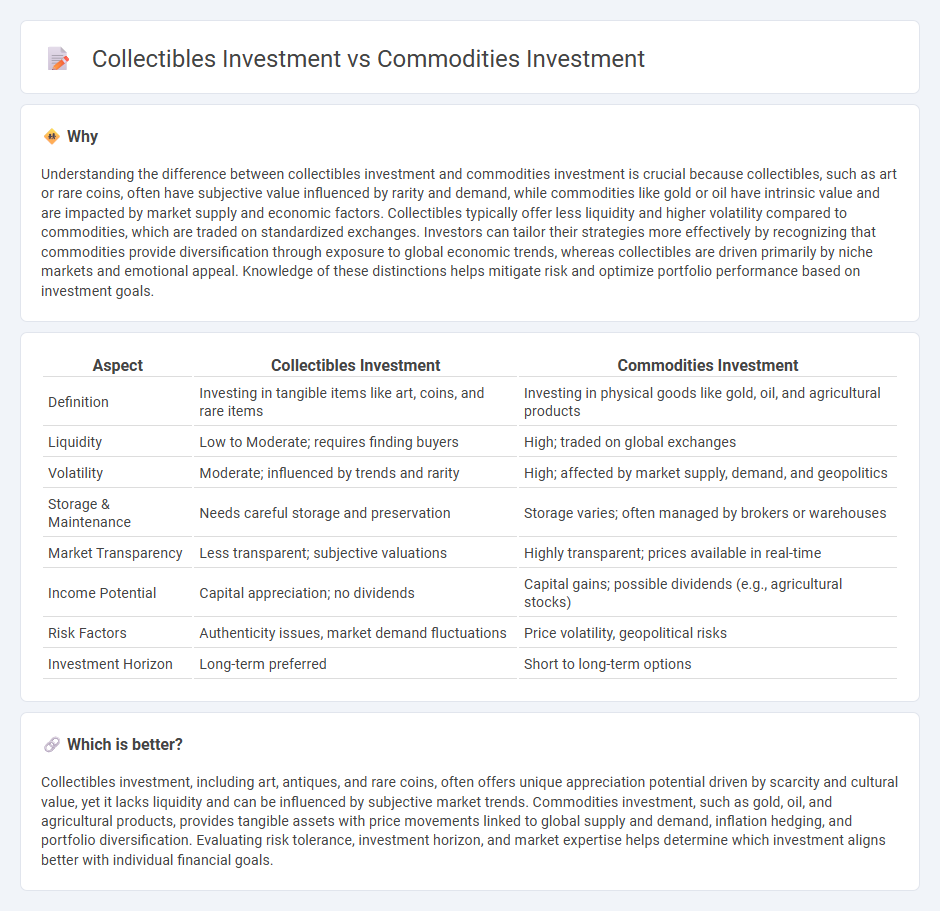
Understanding the difference between collectibles investment and commodities investment is crucial because collectibles, such as art or rare coins, often have subjective value influenced by rarity and demand, while commodities like gold or oil have intrinsic value and are impacted by market supply and economic factors. Collectibles typically offer less liquidity and higher volatility compared to commodities, which are traded on standardized exchanges. Investors can tailor their strategies more effectively by recognizing that commodities provide diversification through exposure to global economic trends, whereas collectibles are driven primarily by niche markets and emotional appeal. Knowledge of these distinctions helps mitigate risk and optimize portfolio performance based on investment goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Collectibles Investment | Commodities Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investing in tangible items like art, coins, and rare items | Investing in physical goods like gold, oil, and agricultural products |
| Liquidity | Low to Moderate; requires finding buyers | High; traded on global exchanges |
| Volatility | Moderate; influenced by trends and rarity | High; affected by market supply, demand, and geopolitics |
| Storage & Maintenance | Needs careful storage and preservation | Storage varies; often managed by brokers or warehouses |
| Market Transparency | Less transparent; subjective valuations | Highly transparent; prices available in real-time |
| Income Potential | Capital appreciation; no dividends | Capital gains; possible dividends (e.g., agricultural stocks) |
| Risk Factors | Authenticity issues, market demand fluctuations | Price volatility, geopolitical risks |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term preferred | Short to long-term options |
Which is better?
Collectibles investment, including art, antiques, and rare coins, often offers unique appreciation potential driven by scarcity and cultural value, yet it lacks liquidity and can be influenced by subjective market trends. Commodities investment, such as gold, oil, and agricultural products, provides tangible assets with price movements linked to global supply and demand, inflation hedging, and portfolio diversification. Evaluating risk tolerance, investment horizon, and market expertise helps determine which investment aligns better with individual financial goals.
Connection
Collectibles investment and commodities investment share a fundamental connection through their intrinsic value and tangible nature, often serving as alternative asset classes that diversify portfolios beyond traditional stocks and bonds. Both markets are influenced by factors such as scarcity, demand, and economic conditions, driving price fluctuations and long-term appreciation potential. Investors leverage the unique qualities of physical assets in collectibles and commodities to hedge against inflation and market volatility, enhancing overall investment strategy resilience.
Key Terms
**Commodities Investment:**
Commodities investment involves purchasing raw materials like gold, oil, and agricultural products, offering portfolio diversification and a hedge against inflation. Prices are influenced by global supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and economic indicators, making market analysis critical for informed decision-making. Explore the benefits and strategies of commodities investment to enhance your financial portfolio.
Futures Contracts
Futures contracts offer a transparent, regulated market for commodities investment, enabling hedging and speculation on assets like oil, gold, and agricultural products. Collectibles investment, in contrast, lacks standardized futures contracts, creating challenges in liquidity and price discovery for items such as art, coins, or rare wines. Explore the complexities and strategic considerations of futures contracts in commodities for a deeper understanding of investment dynamics.
Spot Price
Commodities investment centers on spot price, reflecting the current market value of tangible assets like gold, oil, or agricultural products, providing liquidity and real-time pricing transparency. Collectibles investment, in contrast, lacks a standardized spot price, with value driven by scarcity, demand, and condition, making it less liquid and more subjective. Explore deeper insights to understand how spot price dynamics influence your investment choices between commodities and collectibles.
Source and External Links
Commodity investing and its role in a portfolio - This Vanguard paper discusses how commodities can improve investment outcomes, especially in inflationary periods, by providing diversification benefits and protection against unexpected inflation.
Why Invest in Commodities? - This article outlines various ways to invest in commodities, including futures contracts, ETFs, mutual funds, and physical commodities, highlighting their potential for diversification and inflation hedging.
Understanding Commodities - PIMCO explains how commodities can offer three key benefits to portfolios: inflation protection, diversification, and potential returns, making them a valuable addition to investment strategies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com