Litigation funding involves third-party investors financing legal cases in exchange for a share of the settlement or judgment, providing access to justice without upfront costs. Peer-to-peer lending connects individual borrowers directly with investors, offering diversified loan options and potentially higher returns compared to traditional banking. Explore more about the benefits and risks of these alternative investment strategies.
Why it is important
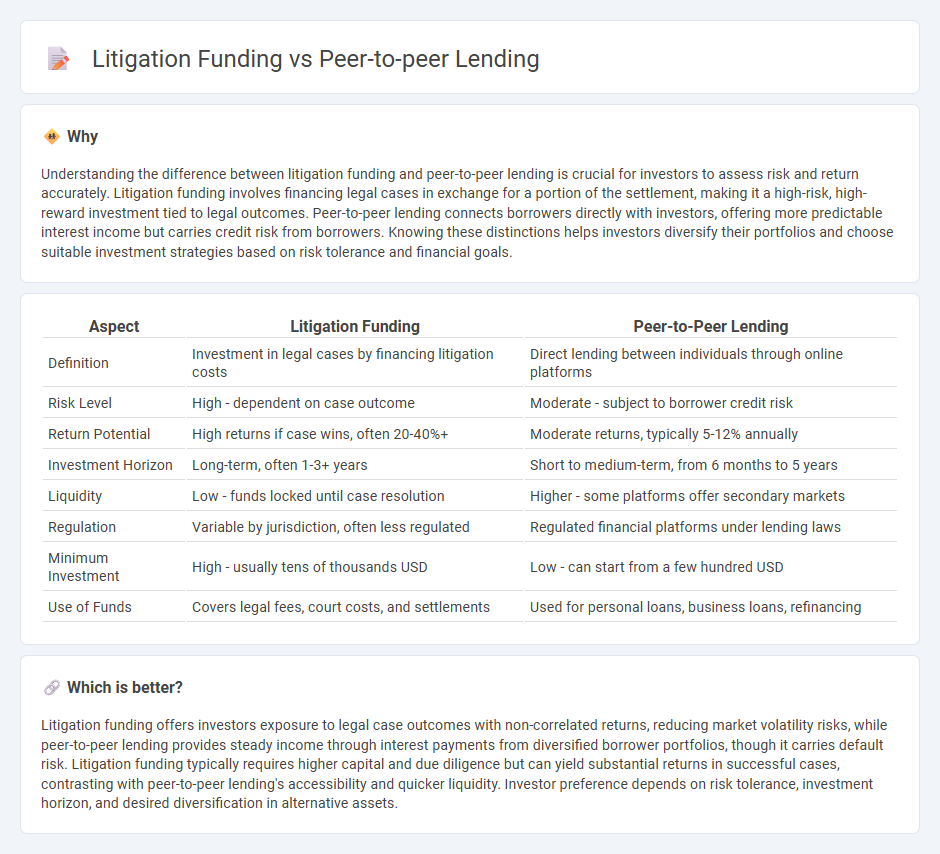
Understanding the difference between litigation funding and peer-to-peer lending is crucial for investors to assess risk and return accurately. Litigation funding involves financing legal cases in exchange for a portion of the settlement, making it a high-risk, high-reward investment tied to legal outcomes. Peer-to-peer lending connects borrowers directly with investors, offering more predictable interest income but carries credit risk from borrowers. Knowing these distinctions helps investors diversify their portfolios and choose suitable investment strategies based on risk tolerance and financial goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Litigation Funding | Peer-to-Peer Lending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in legal cases by financing litigation costs | Direct lending between individuals through online platforms |
| Risk Level | High - dependent on case outcome | Moderate - subject to borrower credit risk |
| Return Potential | High returns if case wins, often 20-40%+ | Moderate returns, typically 5-12% annually |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term, often 1-3+ years | Short to medium-term, from 6 months to 5 years |
| Liquidity | Low - funds locked until case resolution | Higher - some platforms offer secondary markets |
| Regulation | Variable by jurisdiction, often less regulated | Regulated financial platforms under lending laws |
| Minimum Investment | High - usually tens of thousands USD | Low - can start from a few hundred USD |
| Use of Funds | Covers legal fees, court costs, and settlements | Used for personal loans, business loans, refinancing |
Which is better?
Litigation funding offers investors exposure to legal case outcomes with non-correlated returns, reducing market volatility risks, while peer-to-peer lending provides steady income through interest payments from diversified borrower portfolios, though it carries default risk. Litigation funding typically requires higher capital and due diligence but can yield substantial returns in successful cases, contrasting with peer-to-peer lending's accessibility and quicker liquidity. Investor preference depends on risk tolerance, investment horizon, and desired diversification in alternative assets.
Connection
Litigation funding and peer-to-peer lending both facilitate alternative investment opportunities by connecting individual investors directly with specific financing needs, bypassing traditional financial institutions. Litigation funding channels capital into legal cases expecting returns from settlements or judgments, while peer-to-peer lending involves investors providing loans to borrowers via online platforms. Both models leverage technology to democratize access to unique asset classes, offering diversified risk profiles and potential for higher yields.
Key Terms
Risk Assessment
Peer-to-peer lending involves assessing borrower creditworthiness, loan purpose, and repayment capacity to mitigate default risk, while litigation funding requires evaluating case merits, legal strategy, and potential settlement or award outcomes to gauge investment viability. Risk assessment in peer-to-peer lending relies on financial data and historical credit behavior, whereas litigation funding depends heavily on legal expertise and case-specific factors. Explore the nuances of risk assessment in both to understand their distinct investment profiles.
Returns
Peer-to-peer lending offers returns typically ranging from 5% to 12% annually, depending on borrower credit risk and platform fees, while litigation funding can yield higher returns between 20% and 40% but involves greater legal and case outcome risks. P2P lending provides more predictable cash flow streams with diversified borrower pools, whereas litigation funding profits hinge on the successful resolution of legal claims and may take several years to realize. Explore in-depth comparisons and risk assessments to understand which investment aligns best with your return expectations.
Regulation
Peer-to-peer lending operates under financial regulations emphasizing transparency, borrower creditworthiness, and investor protections, with frameworks like the U.S. SEC's Regulation Crowdfunding and the UK's Financial Conduct Authority guidelines. Litigation funding is subject to specialty laws governing third-party financing, conflict of interest, and ethical considerations, varying significantly across jurisdictions such as the U.S., Australia, and the UK, where some regions impose stringent disclosure and licensing requirements. Discover the critical regulatory nuances differentiating these financing models and their impact on market dynamics.
Source and External Links
What is Peer-to-Peer Lending & How P2P Loans Work - This page explains how peer-to-peer lending works, allowing individuals to borrow and lend money without traditional financial institutions.
Peer-to-peer lending - This article provides an overview of peer-to-peer lending, including its characteristics and how it operates through online platforms.
Peer to peer lending: what you need to know - This guide discusses the basics of peer-to-peer lending, including its risks and benefits, as well as how it compares to traditional savings options.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com