Regenerative agriculture investing focuses on funding farming practices that restore soil health, enhance biodiversity, and sequester carbon, offering long-term environmental benefits. Socially responsible investing (SRI) emphasizes ethical standards by excluding companies involved in harmful industries while promoting social justice and corporate governance. Explore the key differences and potential impacts of these investment strategies to align your portfolio with your values.
Why it is important
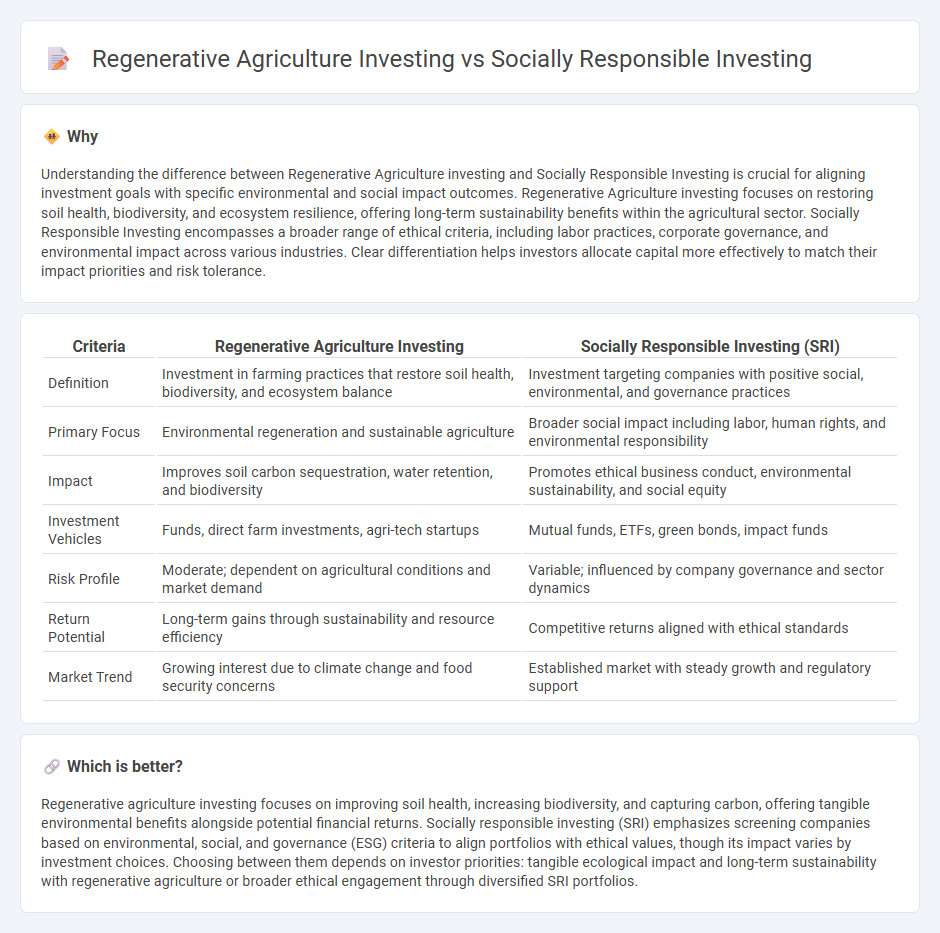
Understanding the difference between Regenerative Agriculture investing and Socially Responsible Investing is crucial for aligning investment goals with specific environmental and social impact outcomes. Regenerative Agriculture investing focuses on restoring soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem resilience, offering long-term sustainability benefits within the agricultural sector. Socially Responsible Investing encompasses a broader range of ethical criteria, including labor practices, corporate governance, and environmental impact across various industries. Clear differentiation helps investors allocate capital more effectively to match their impact priorities and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Regenerative Agriculture Investing | Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in farming practices that restore soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem balance | Investment targeting companies with positive social, environmental, and governance practices |
| Primary Focus | Environmental regeneration and sustainable agriculture | Broader social impact including labor, human rights, and environmental responsibility |
| Impact | Improves soil carbon sequestration, water retention, and biodiversity | Promotes ethical business conduct, environmental sustainability, and social equity |
| Investment Vehicles | Funds, direct farm investments, agri-tech startups | Mutual funds, ETFs, green bonds, impact funds |
| Risk Profile | Moderate; dependent on agricultural conditions and market demand | Variable; influenced by company governance and sector dynamics |
| Return Potential | Long-term gains through sustainability and resource efficiency | Competitive returns aligned with ethical standards |
| Market Trend | Growing interest due to climate change and food security concerns | Established market with steady growth and regulatory support |
Which is better?
Regenerative agriculture investing focuses on improving soil health, increasing biodiversity, and capturing carbon, offering tangible environmental benefits alongside potential financial returns. Socially responsible investing (SRI) emphasizes screening companies based on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to align portfolios with ethical values, though its impact varies by investment choices. Choosing between them depends on investor priorities: tangible ecological impact and long-term sustainability with regenerative agriculture or broader ethical engagement through diversified SRI portfolios.
Connection
Regenerative agriculture investing and socially responsible investing are connected through their shared goal of promoting sustainable, ethical, and environmentally friendly practices. Both investment strategies prioritize long-term positive impact by supporting projects that restore ecosystems, improve soil health, and enhance community well-being. Investors in these fields seek to generate financial returns while driving social equity and environmental resilience.
Key Terms
**Socially Responsible Investing:**
Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) prioritizes companies with ethical practices, environmental stewardship, and positive social impact, integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to guide investment decisions. This approach targets sectors like renewable energy, fair labor practices, and corporate transparency, aiming to generate competitive financial returns alongside measurable societal benefits. Explore how SRI can align your portfolio with your values and drive meaningful change.
ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance)
Socially responsible investing (SRI) emphasizes ESG criteria by screening companies for ethical practices, social impact, and governance transparency, while regenerative agriculture investing targets sustainable farming methods that restore soil health, enhance biodiversity, and sequester carbon emissions. Both investment strategies integrate ESG principles but regenerative agriculture offers direct environmental benefits by promoting carbon-negative practices and improving ecosystem resilience. Explore how aligning your portfolio with these ESG-focused approaches can drive positive change and long-term value.
Negative Screening
Negative screening in socially responsible investing (SRI) excludes companies involved in harmful activities such as tobacco, fossil fuels, or weapons, focusing on ethical consumption and corporate governance. In regenerative agriculture investing, negative screening targets operations that degrade soil health, use synthetic chemicals, or contribute to biodiversity loss, emphasizing ecological restoration and sustainable farming practices. Explore how these distinct negative screening criteria shape investment portfolios aligned with environmental and social impact goals.
Source and External Links
Socially Responsible Investing - Green America - Socially responsible investing (SRI) integrates your values with your investment decisions, focusing on companies with strong environmental, social, and governance practices, and avoiding those that do not meet these standards.
Socially responsible investing - Wikipedia - SRI is an investment strategy considering financial return alongside ethical, social, or environmental goals, often using environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria and including practices like negative screening, shareholder advocacy, and impact investing.
What Is Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) and How to Get Started - NerdWallet - Socially responsible investing aims to achieve both social change and financial returns, with rapidly growing interest and numerous available sustainable mutual funds and ETFs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com