Virtual land real estate offers a unique investment opportunity by leveraging blockchain technology and digital platforms, providing liquidity and global access absent in traditional farmland. Farmland investments deliver tangible value through agricultural productivity and long-term appreciation, supported by global food demand and sustainable farming practices. Explore the advantages and challenges of each asset class to make informed investment decisions.
Why it is important
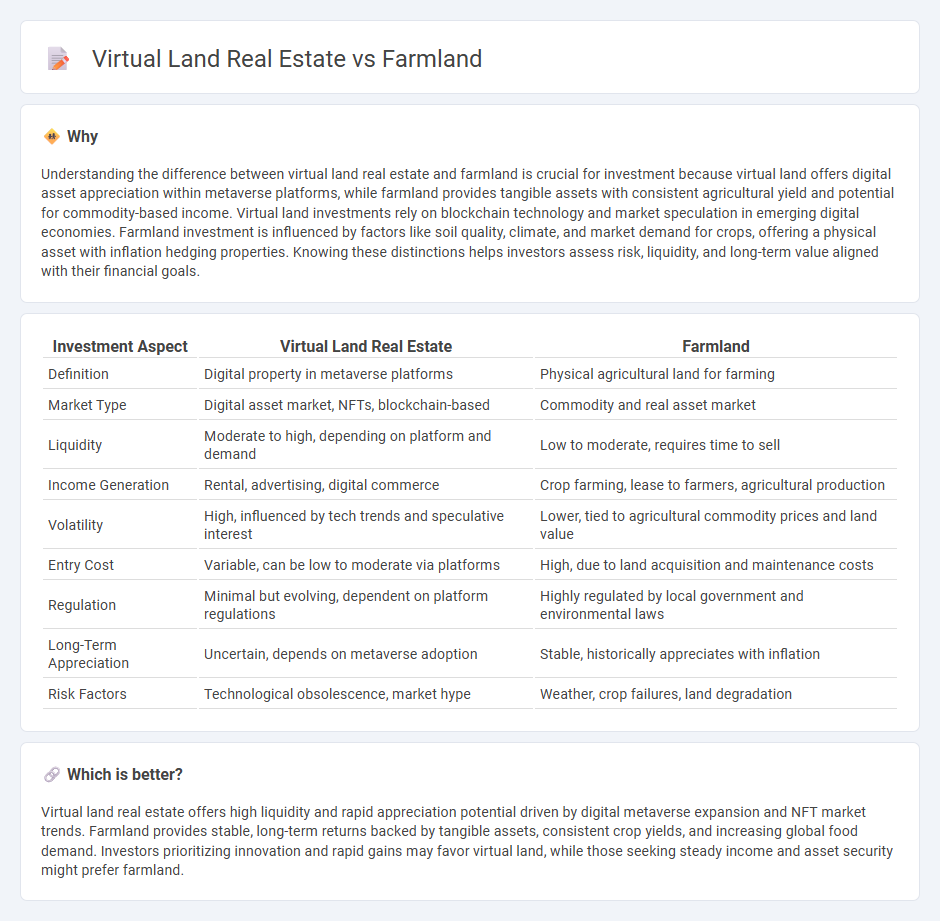
Understanding the difference between virtual land real estate and farmland is crucial for investment because virtual land offers digital asset appreciation within metaverse platforms, while farmland provides tangible assets with consistent agricultural yield and potential for commodity-based income. Virtual land investments rely on blockchain technology and market speculation in emerging digital economies. Farmland investment is influenced by factors like soil quality, climate, and market demand for crops, offering a physical asset with inflation hedging properties. Knowing these distinctions helps investors assess risk, liquidity, and long-term value aligned with their financial goals.
Comparison Table
| Investment Aspect | Virtual Land Real Estate | Farmland |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital property in metaverse platforms | Physical agricultural land for farming |
| Market Type | Digital asset market, NFTs, blockchain-based | Commodity and real asset market |
| Liquidity | Moderate to high, depending on platform and demand | Low to moderate, requires time to sell |
| Income Generation | Rental, advertising, digital commerce | Crop farming, lease to farmers, agricultural production |
| Volatility | High, influenced by tech trends and speculative interest | Lower, tied to agricultural commodity prices and land value |
| Entry Cost | Variable, can be low to moderate via platforms | High, due to land acquisition and maintenance costs |
| Regulation | Minimal but evolving, dependent on platform regulations | Highly regulated by local government and environmental laws |
| Long-Term Appreciation | Uncertain, depends on metaverse adoption | Stable, historically appreciates with inflation |
| Risk Factors | Technological obsolescence, market hype | Weather, crop failures, land degradation |
Which is better?
Virtual land real estate offers high liquidity and rapid appreciation potential driven by digital metaverse expansion and NFT market trends. Farmland provides stable, long-term returns backed by tangible assets, consistent crop yields, and increasing global food demand. Investors prioritizing innovation and rapid gains may favor virtual land, while those seeking steady income and asset security might prefer farmland.
Connection
Virtual land real estate and farmland share foundational investment principles centered on scarcity and value appreciation, with virtual land rising in digital ecosystems similarly to how farmland retains intrinsic agricultural value. Both asset types benefit from long-term demand--virtual land through expanding metaverse platforms and farmland through consistent food production needs. Investors leverage these parallels, viewing them as complementary diversification options within a real asset portfolio driven by inflation hedging and portfolio resilience.
Key Terms
Tangible Asset
Farmland represents a tangible real estate asset with intrinsic value rooted in physical land, agricultural productivity, and natural resources. Virtual land, while emerging as a digital real estate asset within metaverse platforms, lacks physical presence and relies on blockchain technology for ownership verification. Explore the detailed differences and investment potential of tangible versus virtual real estate assets for strategic asset diversification.
Digital Ownership
Farmland ownership involves tangible assets linked to agricultural production and natural resources, providing physical utility and income through crop yields and land leases. Virtual land real estate, driven by blockchain technology and NFTs, offers digital property rights within online metaverse environments, emphasizing decentralized ownership and programmable assets. Explore the intricacies of digital ownership and investment opportunities in both real and virtual land sectors.
Yield Potential
Farmland offers consistent yield potential through agricultural crop production and livestock grazing, providing tangible returns influenced by soil quality, weather, and crop prices. Virtual land in the metaverse offers yield potential from digital asset appreciation, virtual events, and advertising revenue driven by user engagement and platform growth. Explore the unique yield opportunities and investment strategies in both farmland and virtual land real estate to make informed decisions.
Source and External Links
American Farmland Trust - A national organization dedicated to protecting farmland, promoting sustainable farming practices, and supporting farmers to preserve agricultural land for future generations.
Ohio Farmland Preservation Office - Works with landowners and partners to permanently preserve Ohio farms, contributing to the state's largest industry by protecting farmland and supporting agricultural growth.
Farm Land - Farming life game - A free mobile farming simulator game where players grow crops, raise animals, and manage their farm life with various farming activities and expansions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com