Carbon credit trading enables companies to offset emissions by purchasing credits from entities that have reduced their carbon footprint, creating a market-driven approach to sustainability. Green bonds provide investors with a fixed-income opportunity directly funding environmentally friendly projects, fostering long-term ecological and financial benefits. Explore the distinct advantages of both strategies to make informed investment decisions in the growing green economy.
Why it is important
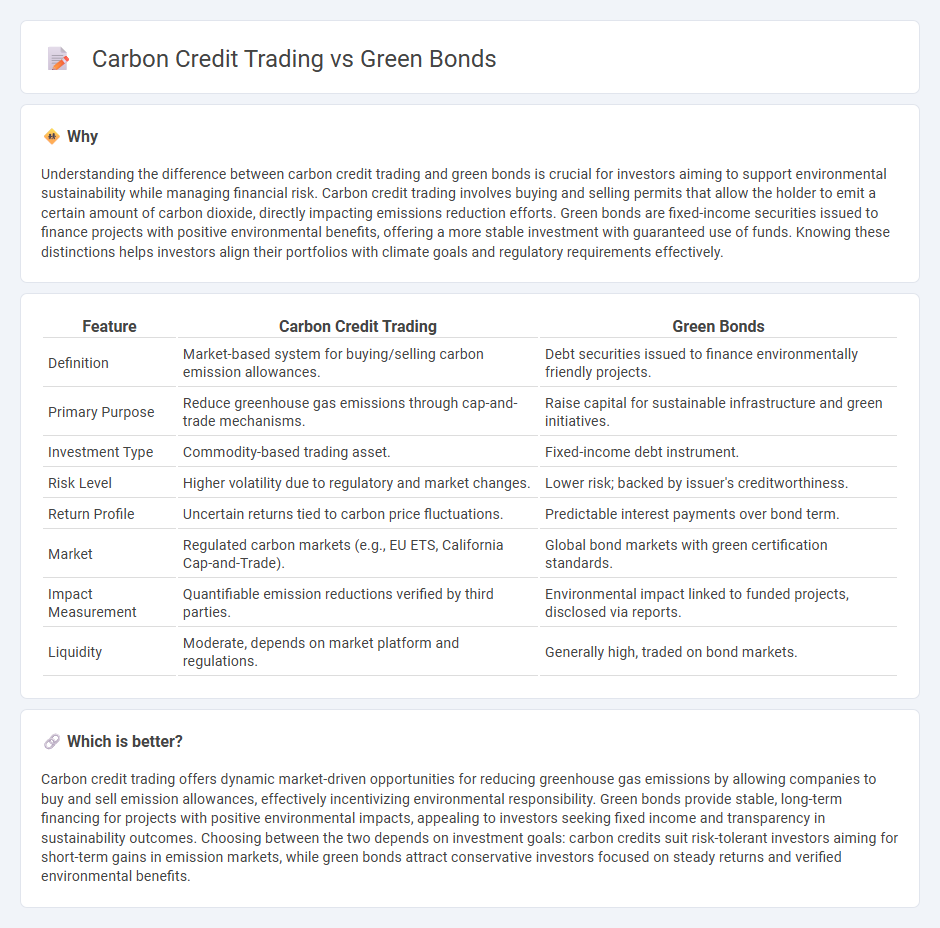
Understanding the difference between carbon credit trading and green bonds is crucial for investors aiming to support environmental sustainability while managing financial risk. Carbon credit trading involves buying and selling permits that allow the holder to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide, directly impacting emissions reduction efforts. Green bonds are fixed-income securities issued to finance projects with positive environmental benefits, offering a more stable investment with guaranteed use of funds. Knowing these distinctions helps investors align their portfolios with climate goals and regulatory requirements effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Carbon Credit Trading | Green Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market-based system for buying/selling carbon emission allowances. | Debt securities issued to finance environmentally friendly projects. |
| Primary Purpose | Reduce greenhouse gas emissions through cap-and-trade mechanisms. | Raise capital for sustainable infrastructure and green initiatives. |
| Investment Type | Commodity-based trading asset. | Fixed-income debt instrument. |
| Risk Level | Higher volatility due to regulatory and market changes. | Lower risk; backed by issuer's creditworthiness. |
| Return Profile | Uncertain returns tied to carbon price fluctuations. | Predictable interest payments over bond term. |
| Market | Regulated carbon markets (e.g., EU ETS, California Cap-and-Trade). | Global bond markets with green certification standards. |
| Impact Measurement | Quantifiable emission reductions verified by third parties. | Environmental impact linked to funded projects, disclosed via reports. |
| Liquidity | Moderate, depends on market platform and regulations. | Generally high, traded on bond markets. |
Which is better?
Carbon credit trading offers dynamic market-driven opportunities for reducing greenhouse gas emissions by allowing companies to buy and sell emission allowances, effectively incentivizing environmental responsibility. Green bonds provide stable, long-term financing for projects with positive environmental impacts, appealing to investors seeking fixed income and transparency in sustainability outcomes. Choosing between the two depends on investment goals: carbon credits suit risk-tolerant investors aiming for short-term gains in emission markets, while green bonds attract conservative investors focused on steady returns and verified environmental benefits.
Connection
Carbon credit trading and green bonds are interconnected financial mechanisms that drive sustainable investment by funding projects aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon credit trading creates a market-driven incentive for companies to lower their carbon footprint, while green bonds raise capital specifically for environmental initiatives such as renewable energy and conservation efforts. Together, they accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy by mobilizing private and public sector investments toward climate-positive outcomes.
Key Terms
Environmental Impact
Green bonds fund projects that generate measurable environmental benefits, such as renewable energy and sustainable infrastructure, directly reducing carbon emissions. Carbon credit trading allows companies to buy and sell emission allowances, creating a market-driven approach to cap and reduce global greenhouse gases. Explore the nuances of these financial instruments to understand their unique roles in combating climate change.
Financial Instruments
Green bonds are debt securities issued to finance projects with positive environmental impacts, offering investors fixed returns while supporting sustainable development. Carbon credit trading involves buying and selling permits that allow companies to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide, creating a market-driven approach to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Explore the nuances and advantages of these financial instruments to deepen your understanding of green finance.
Regulatory Compliance
Green bonds are debt instruments specifically earmarked for environmental projects, requiring adherence to strict regulatory frameworks such as the Green Bond Principles and third-party verification to ensure transparency and impact integrity. Carbon credit trading involves a market-based approach where companies must comply with emissions caps set by regulatory bodies like the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) or California Cap-and-Trade Program, with compliance verified through carbon accounting and reporting standards. Explore the nuances of regulatory compliance in green finance to optimize your sustainability strategy.
Source and External Links
Green bond - Wikipedia - Green bonds are fixed-income financial instruments used to fund projects with positive environmental benefits, such as renewable energy and pollution prevention, allowing investors to support climate change mitigation and ESG goals through dedicated funding.
What are Green Bonds and what projects do they finance? - Iberdrola - Green bonds are debt instruments issued by public or private entities exclusively to finance environmentally sustainable and socially responsible projects like renewable energy, energy efficiency, and clean transportation, contributing to Sustainable Development Goals.
Green Bond Principles (GBP) - ICMA - The Green Bond Principles provide voluntary guidelines to ensure transparency, disclosure, and integrity in issuing green bonds, supporting projects that foster a net-zero emissions economy and protect the environment with clear tracking of proceeds and impact reporting.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com