Investing in viticulture land offers potential for profitable wine production with increasing global demand and premium market prices, while timberland investments provide long-term returns through timber harvesting and carbon credit opportunities. Viticulture demands intensive management and climate consideration, contrasting with timberland's relatively passive growth and diversification benefits across ecological zones. Explore the distinct financial and environmental advantages of viticulture land versus timberland investments to make an informed decision.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between viticulture land acquisition and timberland investment is crucial for optimizing returns, as viticulture land requires specialized knowledge of grape cultivation and climate suitability for wine production, whereas timberland focuses on long-term growth cycles and sustainable forest management. Viticulture land offers potentially higher short-term cash flows through harvest cycles and wine tourism, while timberland provides steady, long-term capital appreciation and carbon credit opportunities. Investors must assess soil quality, zoning laws, and market demand specific to vineyards versus the ecological impact, harvest schedules, and timber market prices for timberland. Clear differentiation ensures tailored investment strategies that align with risk tolerance, investment horizon, and operational expertise.
Comparison Table
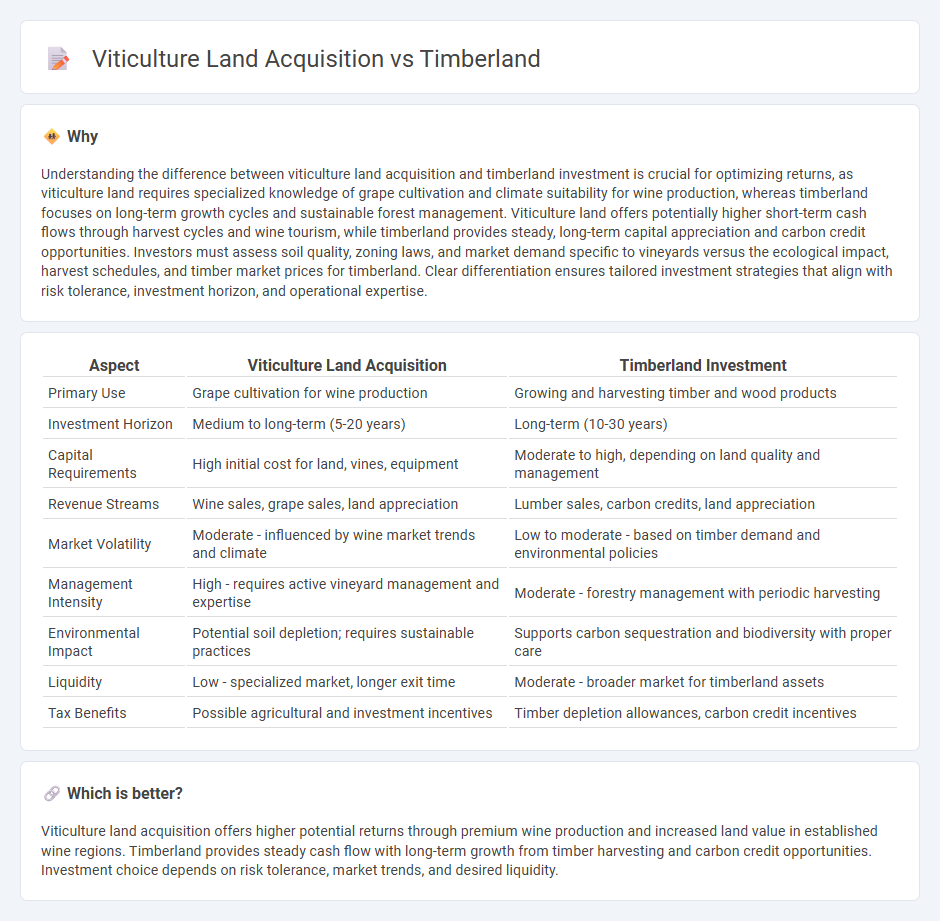
| Aspect | Viticulture Land Acquisition | Timberland Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Grape cultivation for wine production | Growing and harvesting timber and wood products |
| Investment Horizon | Medium to long-term (5-20 years) | Long-term (10-30 years) |
| Capital Requirements | High initial cost for land, vines, equipment | Moderate to high, depending on land quality and management |
| Revenue Streams | Wine sales, grape sales, land appreciation | Lumber sales, carbon credits, land appreciation |
| Market Volatility | Moderate - influenced by wine market trends and climate | Low to moderate - based on timber demand and environmental policies |
| Management Intensity | High - requires active vineyard management and expertise | Moderate - forestry management with periodic harvesting |
| Environmental Impact | Potential soil depletion; requires sustainable practices | Supports carbon sequestration and biodiversity with proper care |
| Liquidity | Low - specialized market, longer exit time | Moderate - broader market for timberland assets |
| Tax Benefits | Possible agricultural and investment incentives | Timber depletion allowances, carbon credit incentives |
Which is better?
Viticulture land acquisition offers higher potential returns through premium wine production and increased land value in established wine regions. Timberland provides steady cash flow with long-term growth from timber harvesting and carbon credit opportunities. Investment choice depends on risk tolerance, market trends, and desired liquidity.
Connection
Viticulture land acquisition and timberland investment share a strategic connection through their roles in sustainable land management and diversification of asset portfolios. Both asset types capitalize on natural resource value appreciation while offering environmental benefits such as carbon sequestration and soil conservation. Investors often integrate these land assets to balance agricultural productivity with long-term ecological and economic returns.
Key Terms
Yield Potential
Timberland offers consistent yield potential through sustainable forest growth, typically generating returns around 5-7% annually driven by timber sales and carbon credits. Viticulture land, while riskier due to climate variability and disease, can achieve significantly higher yields with premium grape varieties, often surpassing 10% ROI when managed effectively. Explore detailed comparative analyses to understand which land acquisition aligns best with your investment yield goals.
Market Volatility
Timberland investments are generally less sensitive to market volatility due to long growth cycles and stable demand for wood products, while viticulture land acquisition often faces higher risk from fluctuating commodity prices and variable wine market trends. Timberland offers diversification benefits and inflation hedging through steady cash flows, whereas viticulture land values can be significantly impacted by changing consumer preferences and climatic factors. Explore in-depth analyses to better understand market volatility impacts on both timberland and viticulture land acquisitions.
Regulatory Environment
Timberland acquisition often involves stringent environmental regulations, including sustainable forestry practices mandated by agencies such as the U.S. Forest Service and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), ensuring conservation and biodiversity protection. Viticulture land acquisition requires compliance with agricultural zoning laws, water rights, pesticide use regulations, and often face local land-use restrictions due to the delicate nature of vineyard ecosystems. Explore deeper insights into regulatory challenges for land acquisition in timberland and viticulture to optimize your investment strategy.
Source and External Links
Timberland (company) - Wikipedia - Timberland LLC is an American manufacturer and retailer of outdoor footwear and apparel known for its iconic waterproof boots, founded by Nathan Swartz in 1918 and now owned by VF Corporation.
Timberland(r) Boots, Shoes, Clothing and Accessories | Timberland - Timberland offers boots, clothing, and outerwear featuring iconic style, outdoor performance, and eco-conscious innovation, popular for bold adventures and workwear.
Timberland Apparel and Footwear at Pennyworth's - A retail collection of Timberland and Timberland PRO footwear and apparel products including boots, outerwear, pants, and accessories for men, women, and children.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com