Royalty streaming offers investors recurring revenue through a percentage of a project's income without acquiring physical assets, while direct ownership involves holding tangible property or equity with associated management responsibilities. This approach provides lower entry barriers and diversification across multiple income streams, contrasting with the higher control and potential for asset appreciation found in direct ownership. Explore the nuances and benefits of each strategy to determine which aligns with your investment goals.
Why it is important
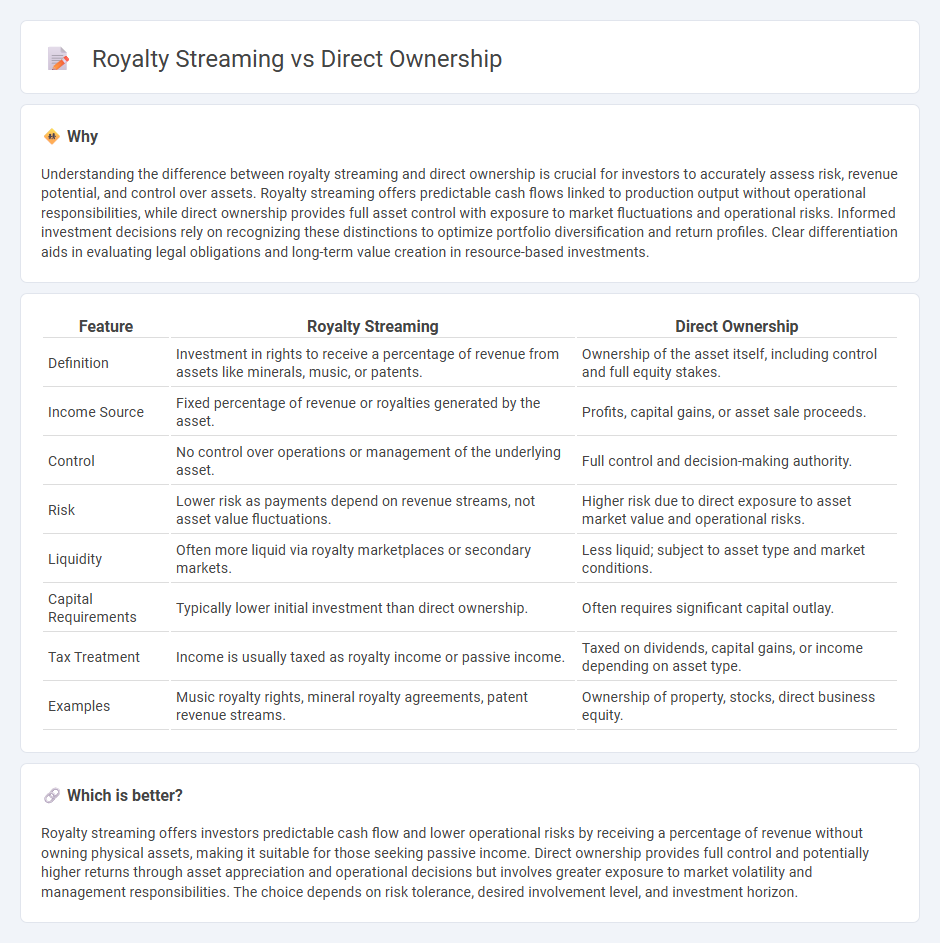
Understanding the difference between royalty streaming and direct ownership is crucial for investors to accurately assess risk, revenue potential, and control over assets. Royalty streaming offers predictable cash flows linked to production output without operational responsibilities, while direct ownership provides full asset control with exposure to market fluctuations and operational risks. Informed investment decisions rely on recognizing these distinctions to optimize portfolio diversification and return profiles. Clear differentiation aids in evaluating legal obligations and long-term value creation in resource-based investments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Royalty Streaming | Direct Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in rights to receive a percentage of revenue from assets like minerals, music, or patents. | Ownership of the asset itself, including control and full equity stakes. |
| Income Source | Fixed percentage of revenue or royalties generated by the asset. | Profits, capital gains, or asset sale proceeds. |
| Control | No control over operations or management of the underlying asset. | Full control and decision-making authority. |
| Risk | Lower risk as payments depend on revenue streams, not asset value fluctuations. | Higher risk due to direct exposure to asset market value and operational risks. |
| Liquidity | Often more liquid via royalty marketplaces or secondary markets. | Less liquid; subject to asset type and market conditions. |
| Capital Requirements | Typically lower initial investment than direct ownership. | Often requires significant capital outlay. |
| Tax Treatment | Income is usually taxed as royalty income or passive income. | Taxed on dividends, capital gains, or income depending on asset type. |
| Examples | Music royalty rights, mineral royalty agreements, patent revenue streams. | Ownership of property, stocks, direct business equity. |
Which is better?
Royalty streaming offers investors predictable cash flow and lower operational risks by receiving a percentage of revenue without owning physical assets, making it suitable for those seeking passive income. Direct ownership provides full control and potentially higher returns through asset appreciation and operational decisions but involves greater exposure to market volatility and management responsibilities. The choice depends on risk tolerance, desired involvement level, and investment horizon.
Connection
Royalty streaming and direct ownership are connected through their roles in providing investors with income-generating assets in sectors such as mining, entertainment, and intellectual property. Royalty streaming allows investors to earn a percentage of revenue from a specific asset without owning the underlying property, while direct ownership involves holding equity or physical assets directly. Both strategies enable portfolio diversification and potential cash flow, balancing risk and reward in alternative investment portfolios.
Key Terms
Asset Ownership
Direct ownership provides investors full control and legal title to the asset, enabling potential appreciation and strategic management benefits. Royalty streaming offers a fixed income stream based on asset production without ownership rights, reducing risk exposure but limiting upside potential. Explore deeper insights into asset management strategies and financial implications by learning more about these investment structures.
Royalty Payments
Royalty streaming involves investors receiving a percentage of revenue generated from royalties without owning the underlying asset, offering a steady cash flow tied directly to product performance. In contrast, direct ownership gives full control and equity, but income depends on overall business profitability and asset management. Explore more to understand which model best suits your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Capital Outlay
Direct ownership requires significant capital outlay upfront, involving the purchase of full asset rights, which ties up considerable investment resources. Royalty streaming reduces initial capital expenditure by providing a cash flow based on revenue streams without acquiring full ownership, offering a more flexible investment model. Explore further to understand how these investment strategies impact portfolio risk and returns.
Source and External Links
How would you differentiate between direct or indirect ownership or control? - Direct ownership means individuals or entities hold shares in a legal entity without any intermediary, such as a company or person directly owning 20% of another company's shares.
Direct Ownership and Ultimate Beneficial Ownership - Direct ownership refers to holding shares or partnership stakes outright in a business entity, where the owner can be either a person or another company.
What's the Difference Between Direct and Indirect Shares? - With direct ownership, you possess voting rights and direct control over the shares, including decisions about buying, selling, and realizing gains or losses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com