Hedge fund replication strategies aim to mimic the risk-return profile of hedge funds using transparent and cost-effective financial instruments, while Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) offer diversified exposure to various asset classes with high liquidity and lower fees. Replication techniques often utilize factor-based models and systematic approaches to achieve hedge fund-like performance, whereas ETFs provide easy access to broad market indices and sectors. Explore the nuances and benefits of hedge fund replication and ETFs to optimize your investment portfolio.
Why it is important
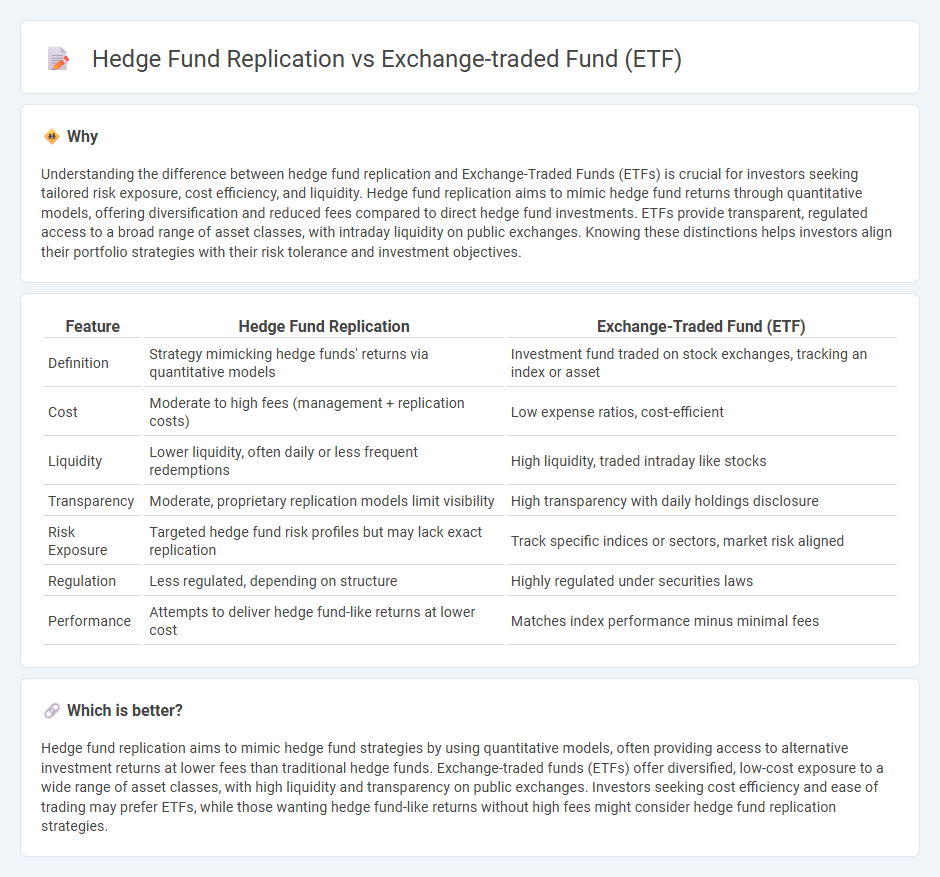
Understanding the difference between hedge fund replication and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) is crucial for investors seeking tailored risk exposure, cost efficiency, and liquidity. Hedge fund replication aims to mimic hedge fund returns through quantitative models, offering diversification and reduced fees compared to direct hedge fund investments. ETFs provide transparent, regulated access to a broad range of asset classes, with intraday liquidity on public exchanges. Knowing these distinctions helps investors align their portfolio strategies with their risk tolerance and investment objectives.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Hedge Fund Replication | Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy mimicking hedge funds' returns via quantitative models | Investment fund traded on stock exchanges, tracking an index or asset |
| Cost | Moderate to high fees (management + replication costs) | Low expense ratios, cost-efficient |
| Liquidity | Lower liquidity, often daily or less frequent redemptions | High liquidity, traded intraday like stocks |
| Transparency | Moderate, proprietary replication models limit visibility | High transparency with daily holdings disclosure |
| Risk Exposure | Targeted hedge fund risk profiles but may lack exact replication | Track specific indices or sectors, market risk aligned |
| Regulation | Less regulated, depending on structure | Highly regulated under securities laws |
| Performance | Attempts to deliver hedge fund-like returns at lower cost | Matches index performance minus minimal fees |
Which is better?
Hedge fund replication aims to mimic hedge fund strategies by using quantitative models, often providing access to alternative investment returns at lower fees than traditional hedge funds. Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) offer diversified, low-cost exposure to a wide range of asset classes, with high liquidity and transparency on public exchanges. Investors seeking cost efficiency and ease of trading may prefer ETFs, while those wanting hedge fund-like returns without high fees might consider hedge fund replication strategies.
Connection
Hedge fund replication strategies utilize quantitative models to mimic the risk-return profiles of hedge funds at significantly lower costs, often implemented through Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) that provide accessible, liquid exposure to alternative investment strategies. ETFs designed for hedge fund replication track indices constructed from hedge fund factors such as market-neutral, long-short equity, and managed futures, delivering diversified portfolio benefits without direct hedge fund ownership. This connection allows investors to achieve hedge fund-like performance transparently and efficiently through the tradable structure of ETFs.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) offer high liquidity through daily market trading and transparent pricing, enabling investors to buy or sell shares easily at market prices. Hedge fund replication strategies aim to mimic hedge fund returns with greater liquidity and lower costs but may face challenges in perfectly tracking complex hedge fund strategies. Explore the detailed comparison to understand how liquidity impacts investment choices between ETFs and hedge fund replication.
Transparency
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) provide high transparency by disclosing daily holdings, enabling investors to monitor asset allocation and risk exposure effectively. Hedge fund replication strategies often lack such transparency due to proprietary models and less frequent reporting, making it harder for investors to assess underlying positions. Explore more about these investment vehicles to understand their transparency features and implications for portfolio management.
Tracking error
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are designed to replicate the performance of an index with minimal tracking error, typically ranging between 0.05% to 0.30%, ensuring investors closely follow the benchmark returns. Hedge fund replication strategies aim to mimic hedge fund returns by using liquid assets and quantitative models but often experience higher tracking errors, around 1% to 3%, due to the complexity of hedge fund strategies. Explore in-depth comparisons and methodologies behind tracking error in ETF and hedge fund replication for better investment decisions.
Source and External Links
Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) - Investor.gov - An ETF is an exchange-traded investment product that pools money from many investors to invest in stocks, bonds, or other assets and trades on national securities exchanges at market prices with potential tax efficiency advantages over mutual funds.
What is an ETF? - Fidelity Investments - ETFs are tradeable funds containing grouped investments organized around strategies or themes, traded like stocks, providing diversification and flexibility through exposure to many securities in a single trade.
What is an ETF (Exchange-Traded Fund)? - Charles Schwab - ETFs combine stock-like trading and mutual fund diversification, offering affordable access to diverse asset classes with advantages like lower costs, trading flexibility, and tax efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com