Fractional ownership allows individual investors to purchase a specific percentage of a tangible asset, such as real estate or art, providing direct control and potential for asset appreciation. Pooled investment combines funds from multiple investors into a single portfolio managed by professionals, offering diversification and reduced risk. Explore the advantages and differences between these investment strategies to decide which suits your financial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between fractional ownership and pooled investment is crucial for investors to align their risk tolerance and control preferences with the right investment structure. Fractional ownership offers direct equity in a specific asset, providing greater control and potential for appreciation, while pooled investment combines funds from multiple investors to diversify risk but often limits individual control. This knowledge helps investors optimize portfolio diversification and liquidity strategies effectively. Clear comprehension of these concepts ensures informed decisions, maximizing returns and minimizing potential conflicts.
Comparison Table
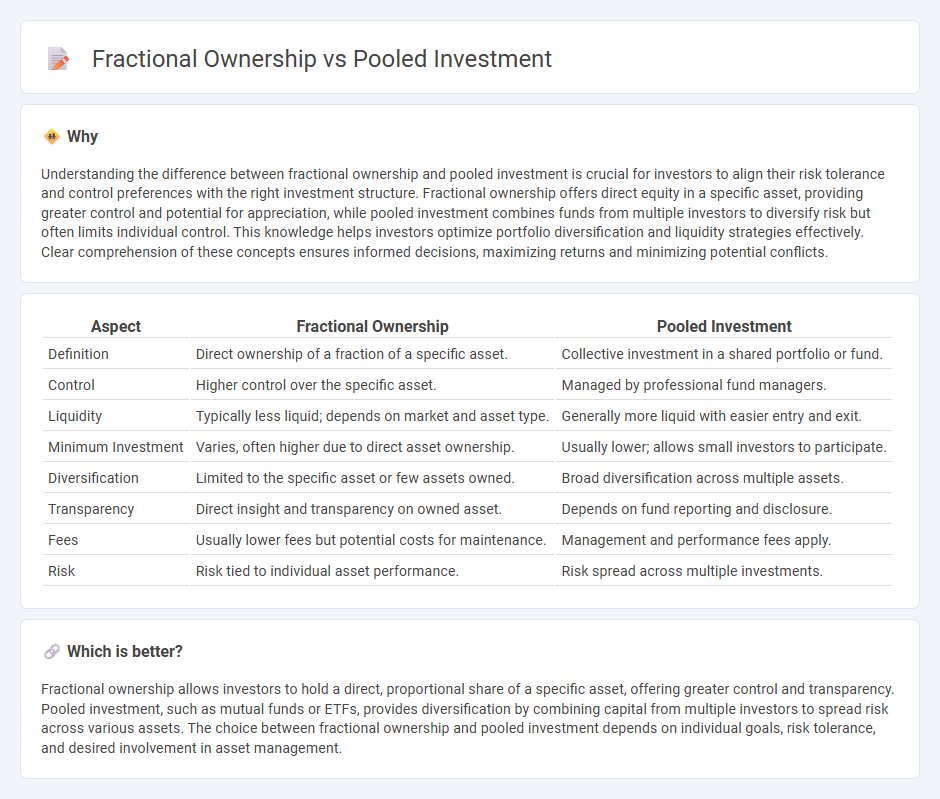
| Aspect | Fractional Ownership | Pooled Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct ownership of a fraction of a specific asset. | Collective investment in a shared portfolio or fund. |
| Control | Higher control over the specific asset. | Managed by professional fund managers. |
| Liquidity | Typically less liquid; depends on market and asset type. | Generally more liquid with easier entry and exit. |
| Minimum Investment | Varies, often higher due to direct asset ownership. | Usually lower; allows small investors to participate. |
| Diversification | Limited to the specific asset or few assets owned. | Broad diversification across multiple assets. |
| Transparency | Direct insight and transparency on owned asset. | Depends on fund reporting and disclosure. |
| Fees | Usually lower fees but potential costs for maintenance. | Management and performance fees apply. |
| Risk | Risk tied to individual asset performance. | Risk spread across multiple investments. |
Which is better?
Fractional ownership allows investors to hold a direct, proportional share of a specific asset, offering greater control and transparency. Pooled investment, such as mutual funds or ETFs, provides diversification by combining capital from multiple investors to spread risk across various assets. The choice between fractional ownership and pooled investment depends on individual goals, risk tolerance, and desired involvement in asset management.
Connection
Fractional ownership allows multiple investors to hold partial shares of high-value assets such as real estate or luxury goods, while pooled investment aggregates capital from various investors into a single entity like a mutual fund or REIT. Both methods democratize access to expensive investment opportunities by reducing the minimum capital requirement and spreading risk across multiple participants. The connection lies in their shared goal of enhancing portfolio diversification and liquidity through collective participation in valuable assets.
Key Terms
Diversification
Pooled investment funds combine capital from multiple investors to diversify across a broad range of assets, reducing individual risk through professional management and larger scale opportunities. Fractional ownership enables investors to purchase a specific share of a single asset, offering targeted exposure but limited diversification compared to pooled funds. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which strategy best aligns with your diversification goals.
Liquidity
Pooled investment typically offers higher liquidity due to diversified assets managed by professionals, allowing investors to buy or sell shares more easily compared to fractional ownership. Fractional ownership usually involves direct stakes in specific properties or assets, which can limit liquidity as selling a fractional interest may require finding a buyer for that particular asset. Explore more about how liquidity impacts your investment strategy and choosing between pooled investment and fractional ownership.
Ownership Structure
Pooled investment involves multiple investors combining funds into a single portfolio managed by professionals, allowing for diversified exposure and shared ownership of underlying assets without direct control. Fractional ownership grants investors a specific percentage of individual assets, offering direct rights and responsibilities tied to the property or item, often seen in real estate or luxury asset investments. Explore more about the legal distinctions and financial implications of these ownership structures to make informed investment decisions.
Source and External Links
Pooled Investment Vehicles: Definition and Types - SmartAsset - Provides an overview of pooled investment vehicles, where multiple investors combine resources for diversified portfolios managed by professionals.
Pooled Funds - Definition, How They Work, Pros and Cons - Explains pooled funds as a collective investment method benefiting from economies of scale, offering cost minimization and expanded investment opportunities.
What is a pooled fund? - Mass.gov - Describes pooled funds as investment vehicles including mutual funds and commingled funds, where multiple investors pool money for diverse investment portfolios.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com