Viticulture land acquisition offers tangible assets with the potential for long-term appreciation driven by agricultural productivity and terroir value in renowned wine regions. Art investment, however, provides portfolio diversification through culturally significant works that can appreciate based on artist reputation and market trends. Explore deeper insights into these investment strategies to optimize your portfolio.
Why it is important
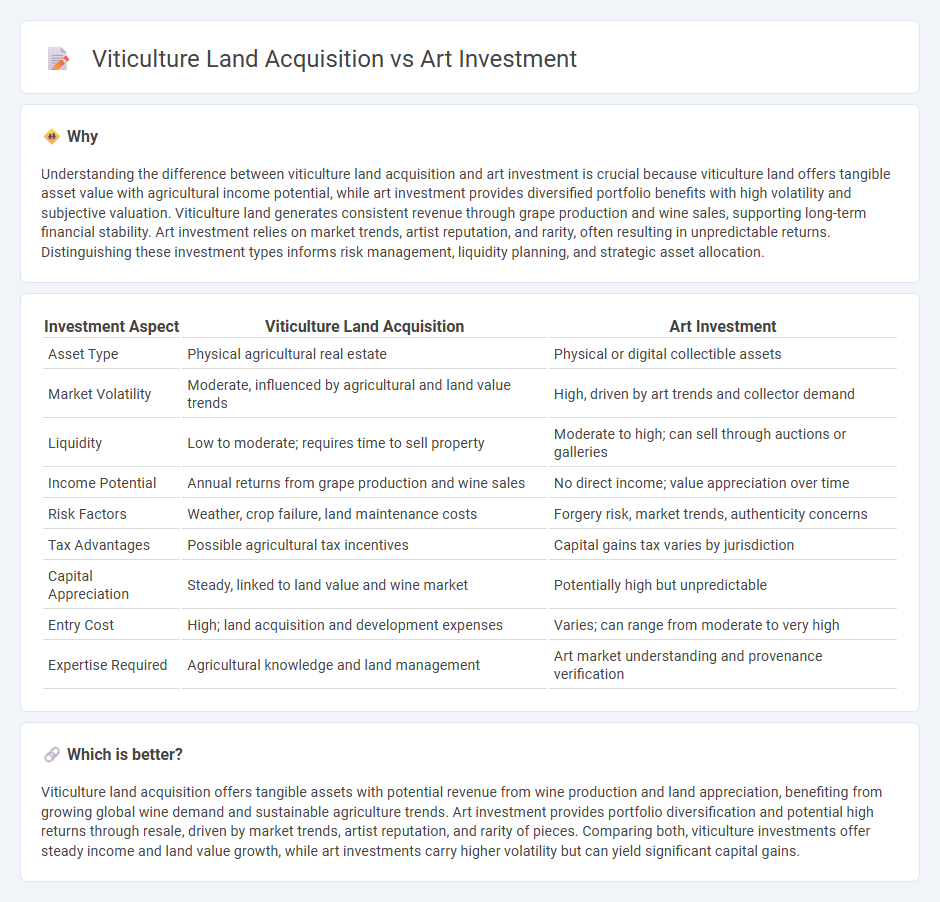
Understanding the difference between viticulture land acquisition and art investment is crucial because viticulture land offers tangible asset value with agricultural income potential, while art investment provides diversified portfolio benefits with high volatility and subjective valuation. Viticulture land generates consistent revenue through grape production and wine sales, supporting long-term financial stability. Art investment relies on market trends, artist reputation, and rarity, often resulting in unpredictable returns. Distinguishing these investment types informs risk management, liquidity planning, and strategic asset allocation.
Comparison Table
| Investment Aspect | Viticulture Land Acquisition | Art Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Type | Physical agricultural real estate | Physical or digital collectible assets |
| Market Volatility | Moderate, influenced by agricultural and land value trends | High, driven by art trends and collector demand |
| Liquidity | Low to moderate; requires time to sell property | Moderate to high; can sell through auctions or galleries |
| Income Potential | Annual returns from grape production and wine sales | No direct income; value appreciation over time |
| Risk Factors | Weather, crop failure, land maintenance costs | Forgery risk, market trends, authenticity concerns |
| Tax Advantages | Possible agricultural tax incentives | Capital gains tax varies by jurisdiction |
| Capital Appreciation | Steady, linked to land value and wine market | Potentially high but unpredictable |
| Entry Cost | High; land acquisition and development expenses | Varies; can range from moderate to very high |
| Expertise Required | Agricultural knowledge and land management | Art market understanding and provenance verification |
Which is better?
Viticulture land acquisition offers tangible assets with potential revenue from wine production and land appreciation, benefiting from growing global wine demand and sustainable agriculture trends. Art investment provides portfolio diversification and potential high returns through resale, driven by market trends, artist reputation, and rarity of pieces. Comparing both, viticulture investments offer steady income and land value growth, while art investments carry higher volatility but can yield significant capital gains.
Connection
Viticulture land acquisition and art investment both serve as alternative asset classes offering portfolio diversification and potential long-term appreciation. Investing in vineyard properties provides tangible assets with agricultural and real estate value, while art investments capitalize on cultural and aesthetic appreciation, often hedging against market volatility. Both require expert knowledge and due diligence to assess market trends, authenticity, and future value growth.
Key Terms
Art investment:
Art investment offers high potential returns driven by the global market for contemporary and historical artworks, with pieces from renowned artists often appreciating over time. Unlike viticulture land acquisition, art assets provide liquidity through auctions and private sales, appealing to investors seeking portfolio diversification in alternative assets. Explore the advantages and risks of art investment to make informed financial decisions.
Provenance
Provenance plays a crucial role in both art investment and viticulture land acquisition, as verifying the origin and historical ownership of a painting can significantly influence its market value, while the documented history and terroir of vineyard land determine its agricultural and commercial potential. Investment in art demands rigorous provenance research to authenticate works and minimize forgery risks, whereas acquiring vineyard property requires detailed knowledge of soil quality, climate history, and past cultivation practices to ensure optimal grape production and brand prestige. Discover more about how provenance shapes value in these distinct yet valuable asset classes.
Authenticity
Art investment offers unique value through historical significance and provenance authenticity, often verified by expert appraisal and documented records. Viticulture land acquisition emphasizes terroir authenticity, where soil composition, climate, and traditional cultivation methods define genuine wine production potential. Explore deeper insights into how authenticity shapes investment value in art and viticulture sectors.
Source and External Links
Basics of Art Funds and their Managers - Art investment funds use various strategies such as buy and hold, geographic arbitrage, and focusing on periods or regions to generate returns, and art can diversify portfolios and act as an inflation hedge with potential for price appreciation.
Investing in art: What to know about turning a passion into ... - Art investment carries risks including illiquidity, condition and provenance concerns, and market trend fluctuations, but can offer portfolio diversification, inflation protection, tax benefits, and cultural value when chosen carefully.
Guide to Art as an Investment - Art investing ranges from buying individual works to newer methods like fractional shares and NFTs, requiring due diligence on artist reputation and artwork value, with risks including fraud and maintenance costs, and often needing a long holding period to realize returns.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com