Ghost broking involves fraudulent insurance brokers who manipulate policies to earn illicit commissions, often leaving clients underinsured or uninsured, while twisting refers to unethical agents persuading policyholders to cancel existing policies and buy new ones, usually to increase their own commissions without benefiting the client. Both practices violate insurance regulations and can result in significant financial losses and legal consequences for consumers. Learn more about how to protect yourself from ghost broking and twisting in insurance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between ghost broking and twisting is crucial to avoid fraudulent insurance practices that can lead to invalid policies and financial loss. Ghost broking involves criminals illegally selling fake or altered insurance policies, putting buyers at risk of being uninsured. Twisting refers to unauthorized advisors persuading policyholders to cancel existing policies and switch to new ones for personal gain, often resulting in higher costs or reduced coverage. Recognizing these scams helps consumers make informed decisions and protects their financial security.
Comparison Table
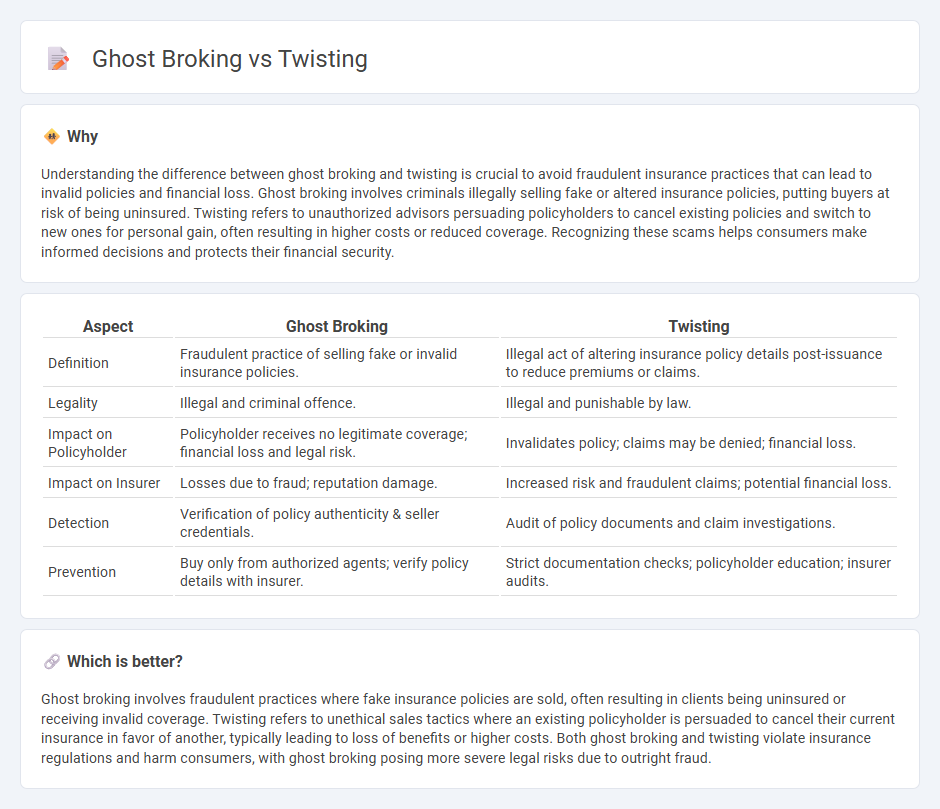
| Aspect | Ghost Broking | Twisting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fraudulent practice of selling fake or invalid insurance policies. | Illegal act of altering insurance policy details post-issuance to reduce premiums or claims. |
| Legality | Illegal and criminal offence. | Illegal and punishable by law. |
| Impact on Policyholder | Policyholder receives no legitimate coverage; financial loss and legal risk. | Invalidates policy; claims may be denied; financial loss. |
| Impact on Insurer | Losses due to fraud; reputation damage. | Increased risk and fraudulent claims; potential financial loss. |
| Detection | Verification of policy authenticity & seller credentials. | Audit of policy documents and claim investigations. |
| Prevention | Buy only from authorized agents; verify policy details with insurer. | Strict documentation checks; policyholder education; insurer audits. |
Which is better?
Ghost broking involves fraudulent practices where fake insurance policies are sold, often resulting in clients being uninsured or receiving invalid coverage. Twisting refers to unethical sales tactics where an existing policyholder is persuaded to cancel their current insurance in favor of another, typically leading to loss of benefits or higher costs. Both ghost broking and twisting violate insurance regulations and harm consumers, with ghost broking posing more severe legal risks due to outright fraud.
Connection
Ghost broking involves fraudsters impersonating legitimate brokers to sell fake or invalid insurance policies, while twisting refers to unethical practices where agents pressure policyholders to switch insurers unfairly, often resulting in lapses or losses. Both practices exploit trust within the insurance market, leading to financial harm for consumers and undermining regulatory compliance. Regulatory bodies like the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) actively monitor and combat ghost broking and twisting to protect policyholders and maintain market integrity.
Key Terms
Misrepresentation
Twisting involves misrepresentation by persuading policyholders to switch insurance policies for the broker's benefit, often neglecting the client's best interests and leading to potential financial loss. Ghost broking entails fraudulently selling forged or non-existent insurance policies, causing severe legal and financial repercussions for unsuspecting buyers. Explore more to understand how to identify and protect yourself from these deceptive practices.
Unauthorized Intermediary
Unauthorized intermediaries engage in illegal insurance practices such as twisting and ghost broking, both of which deceive customers by misrepresenting or fabricating policies. Twisting involves persuading policyholders to cancel existing coverage and purchase new policies with little benefit, while ghost broking typically involves selling fraudulent or non-existent insurance using stolen broker credentials. Explore deeper insights into unauthorized intermediary risks and how to protect yourself against such insurance frauds.
Policyholder Deception
Twisting involves persuading policyholders to replace an existing insurance policy with a new one that may not offer better benefits, often causing financial loss and coverage gaps. Ghost broking refers to fraudsters selling counterfeit or non-existent insurance policies, leaving policyholders unprotected and vulnerable to legal penalties. Learn more about how these deceptive practices impact policyholders and protect yourself from insurance scams.
Source and External Links
TWISTING | definition in the Cambridge English Dictionary - Describes "twisting" as having many turns or changes of direction, and also refers to the act of persuading a client to replace something as a business tactic.
TWISTING Definition & Meaning - Defines "twisting" as the act of squirming or turning about, or something characterized by being twisted and winding.
258 Synonyms & Antonyms for TWISTING - Lists synonyms such as bending, circuitous, crooked, curving, and serpentine, emphasizing its descriptive use for winding or irregular paths.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com