Workers compensation carveout involves outsourcing specific claims to a third-party insurer for dedicated management and potential cost savings, while self-insurance means a company assumes full financial responsibility for workers compensation claims internally. Companies with predictable risk profiles often prefer self-insurance to control claim costs and tailor safety programs, whereas carveouts offer risk transfer benefits without full insurance premiums. Explore deeper into how these strategies impact risk management and financial planning.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between workers compensation carveout and self-insurance is crucial for businesses to manage liability and risk exposure effectively. Workers compensation carveout typically involves a third-party insurer handling specific high-risk claims separately from the main policy. Self-insurance means the company assumes full financial responsibility for workers compensation claims rather than transferring risk. Proper knowledge helps optimize cost savings, regulatory compliance, and claims management strategies.
Comparison Table
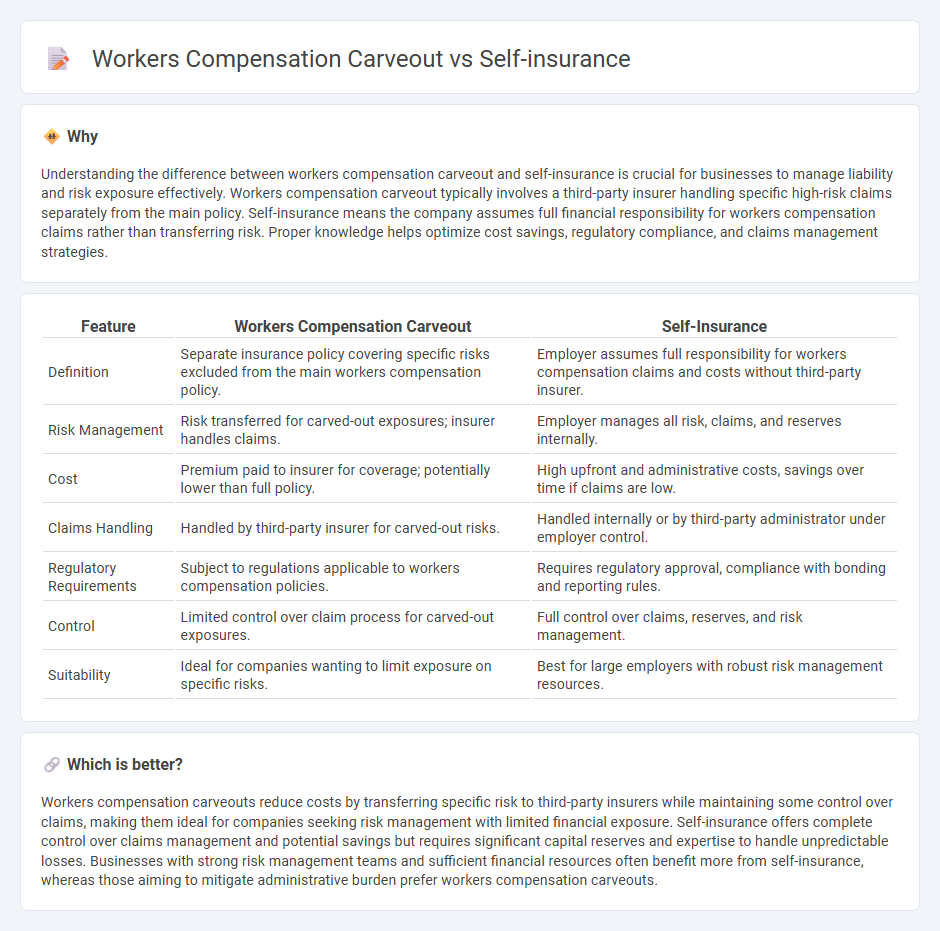
| Feature | Workers Compensation Carveout | Self-Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Separate insurance policy covering specific risks excluded from the main workers compensation policy. | Employer assumes full responsibility for workers compensation claims and costs without third-party insurer. |
| Risk Management | Risk transferred for carved-out exposures; insurer handles claims. | Employer manages all risk, claims, and reserves internally. |
| Cost | Premium paid to insurer for coverage; potentially lower than full policy. | High upfront and administrative costs, savings over time if claims are low. |
| Claims Handling | Handled by third-party insurer for carved-out risks. | Handled internally or by third-party administrator under employer control. |
| Regulatory Requirements | Subject to regulations applicable to workers compensation policies. | Requires regulatory approval, compliance with bonding and reporting rules. |
| Control | Limited control over claim process for carved-out exposures. | Full control over claims, reserves, and risk management. |
| Suitability | Ideal for companies wanting to limit exposure on specific risks. | Best for large employers with robust risk management resources. |
Which is better?
Workers compensation carveouts reduce costs by transferring specific risk to third-party insurers while maintaining some control over claims, making them ideal for companies seeking risk management with limited financial exposure. Self-insurance offers complete control over claims management and potential savings but requires significant capital reserves and expertise to handle unpredictable losses. Businesses with strong risk management teams and sufficient financial resources often benefit more from self-insurance, whereas those aiming to mitigate administrative burden prefer workers compensation carveouts.
Connection
Workers' compensation carveout and self-insurance are closely connected through risk management strategies where employers assume direct financial responsibility for employee injury claims. In a workers' compensation carveout, employers separate specific claims from traditional insurance coverage, often managing these liabilities internally as part of a self-insurance program. This approach reduces premium costs and provides greater control over claim handling and benefits administration.
Key Terms
Risk Retention
Risk Retention Groups (RRGs) enable companies to self-insure workers' compensation by pooling risks and reducing premiums compared to traditional workers' compensation carveouts. Self-insurance through RRGs offers greater control over claims management, tailored risk retention strategies, and potential cost savings for organizations with predictable risk profiles. Explore more about how risk retention impacts your workers' compensation strategy and financial stability.
Collective Bargaining Agreement
Self-insurance programs managed under a Collective Bargaining Agreement (CBA) often allow unions and employers to negotiate specific worker compensation carveouts tailored to workforce needs, potentially reducing premiums and enhancing claim control. These carveouts provide customized coverage options, optimizing risk management and aligning financial incentives with mutual goals established in the CBA. Explore detailed advantages of self-insurance carveouts in CBAs for strategic workforce cost management.
Regulatory Approval
Self-insurance programs and workers' compensation carveouts require distinct regulatory approvals that vary by state, often involving detailed compliance with local labor laws and insurance regulations. Obtaining regulatory approval ensures financial stability and legal adherence, preventing potential penalties and facilitating smoother claims processing. Explore more to understand the critical steps and jurisdictional nuances involved in securing regulatory approval for both self-insurance and workers' compensation carveouts.
Source and External Links
Self-insurance - Self-insurance is a risk management method where an organization assumes financial responsibility for potential losses itself instead of purchasing coverage from a third-party insurer.
What Is the Difference between Self-Insurance and Captive Insurance - In self-insurance, a company sets aside funds to cover future losses, retaining the risk rather than transferring it to a commercial insurer.
About Self-Insurance - Self-insured employers directly provide workers' compensation benefits to their employees and manage claims internally, under regulatory oversight.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com