Gig worker insurance provides tailored coverage for freelancers and independent contractors engaged in short-term or project-based work, addressing risks unique to platform-based jobs like ridesharing or delivery services. Self-employed insurance covers entrepreneurs and small business owners operating their own enterprises, offering protections such as liability, health, and income loss tailored to long-term solo business operation. Explore the essential differences and find the right insurance to safeguard your independent work.
Why it is important
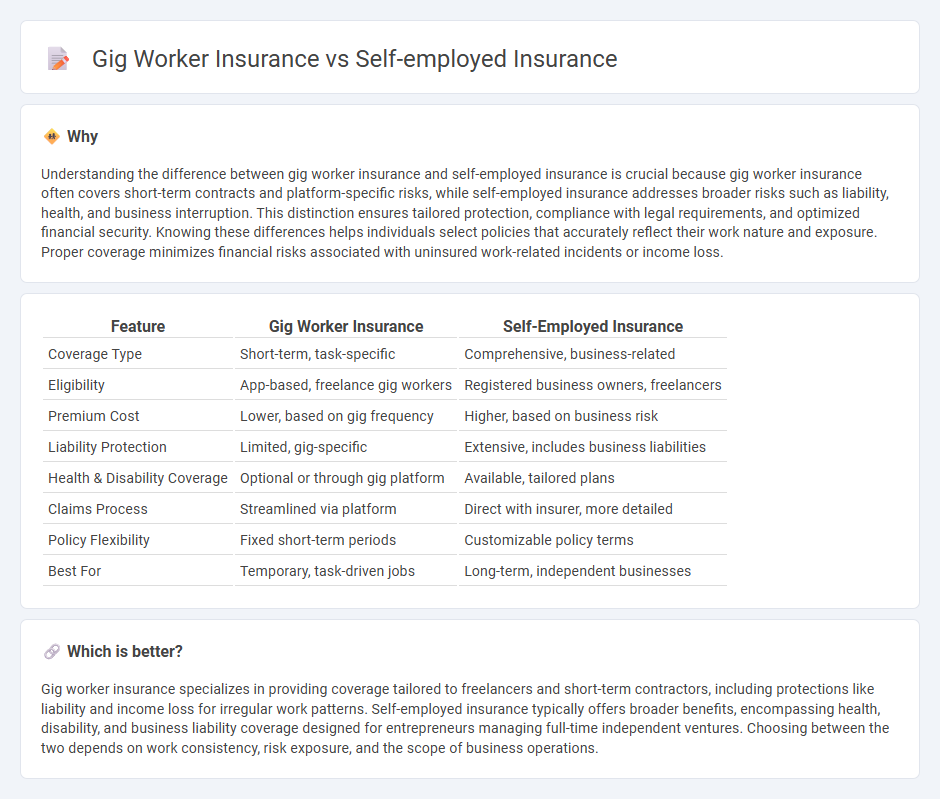
Understanding the difference between gig worker insurance and self-employed insurance is crucial because gig worker insurance often covers short-term contracts and platform-specific risks, while self-employed insurance addresses broader risks such as liability, health, and business interruption. This distinction ensures tailored protection, compliance with legal requirements, and optimized financial security. Knowing these differences helps individuals select policies that accurately reflect their work nature and exposure. Proper coverage minimizes financial risks associated with uninsured work-related incidents or income loss.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Gig Worker Insurance | Self-Employed Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Type | Short-term, task-specific | Comprehensive, business-related |
| Eligibility | App-based, freelance gig workers | Registered business owners, freelancers |
| Premium Cost | Lower, based on gig frequency | Higher, based on business risk |
| Liability Protection | Limited, gig-specific | Extensive, includes business liabilities |
| Health & Disability Coverage | Optional or through gig platform | Available, tailored plans |
| Claims Process | Streamlined via platform | Direct with insurer, more detailed |
| Policy Flexibility | Fixed short-term periods | Customizable policy terms |
| Best For | Temporary, task-driven jobs | Long-term, independent businesses |
Which is better?
Gig worker insurance specializes in providing coverage tailored to freelancers and short-term contractors, including protections like liability and income loss for irregular work patterns. Self-employed insurance typically offers broader benefits, encompassing health, disability, and business liability coverage designed for entrepreneurs managing full-time independent ventures. Choosing between the two depends on work consistency, risk exposure, and the scope of business operations.
Connection
Gig worker insurance and self-employed insurance both address the financial risks faced by independent workers who lack employer-provided coverage. These insurance types provide tailored protection for income loss, health expenses, and liability, recognizing the irregular income patterns typical of gig and freelance work. Shared features include flexible premiums, customizable policies, and coverage that supports business continuity in unpredictable work environments.
Key Terms
Premiums
Premiums for self-employed insurance often vary based on the individual's business size, income, and coverage needs, typically offering stable, predictable payments that reflect long-term risk assessments. Gig worker insurance premiums tend to be higher and more variable due to the irregular income and diverse risk profiles associated with short-term or freelance work. Discover more about how premiums specifically impact your insurance options based on your employment type.
Coverage scope
Self-employed insurance typically provides comprehensive coverage including liability, health, and income protection tailored to small business needs, while gig worker insurance focuses on protecting against income loss, accidents, and liability related to specific on-demand jobs. Gig worker policies often have more limited scopes, covering only the tasks performed within the platform's framework, contrasting with broader self-employed insurance options that cover diverse business activities. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which insurance best fits your coverage needs.
Eligibility criteria
Self-employed insurance typically requires proof of independent business ownership or freelance activity, while gig worker insurance eligibility focuses on short-term contracts or platform-based work evidence. Both types of insurance demand documentation verifying income sources, but gig worker policies often allow more flexibility concerning intermittent or multiple clients. Explore detailed eligibility nuances to select the best coverage suited to your work style.
Source and External Links
Health Insurance for the Self-Employed | Anthem - This webpage provides information on Anthem's individual and family plans for self-employed workers, offering options to suit unique healthcare needs and budgets.
Health Care Insurance Coverage for Self-Employed Individuals - This webpage explains how self-employed individuals can use the Health Insurance Marketplace to enroll in flexible health coverage, including premium tax credits and other savings.
Self-employed health insurance plans | Individuals & families - This webpage outlines UnitedHealthcare's health insurance plans for self-employed individuals, offering a large network of providers and easy-to-use tools to find suitable coverage.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com