Artificial intelligence underwriting leverages machine learning algorithms and vast datasets to assess risk and determine insurance premiums with enhanced accuracy and efficiency compared to traditional methods. Genetic underwriting evaluates an individual's genetic information to predict susceptibility to diseases, enabling personalized risk assessments but raising ethical and privacy concerns. Explore how these innovative underwriting approaches are transforming the insurance industry and their implications for policyholders.
Why it is important
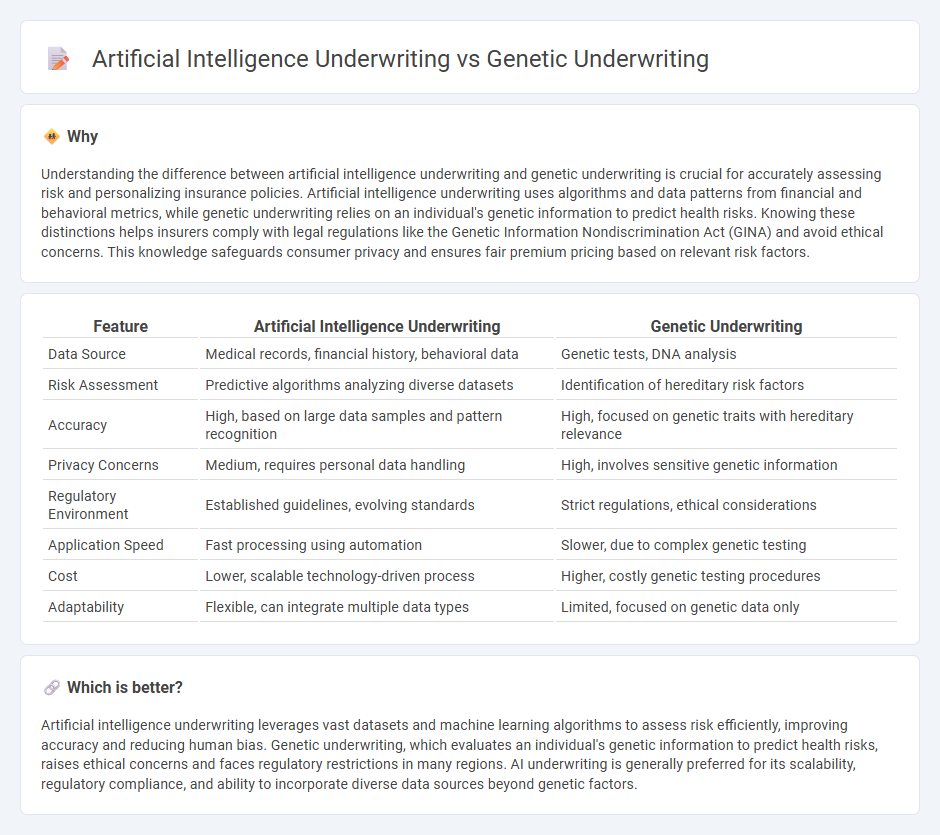
Understanding the difference between artificial intelligence underwriting and genetic underwriting is crucial for accurately assessing risk and personalizing insurance policies. Artificial intelligence underwriting uses algorithms and data patterns from financial and behavioral metrics, while genetic underwriting relies on an individual's genetic information to predict health risks. Knowing these distinctions helps insurers comply with legal regulations like the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA) and avoid ethical concerns. This knowledge safeguards consumer privacy and ensures fair premium pricing based on relevant risk factors.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Artificial Intelligence Underwriting | Genetic Underwriting |
|---|---|---|
| Data Source | Medical records, financial history, behavioral data | Genetic tests, DNA analysis |
| Risk Assessment | Predictive algorithms analyzing diverse datasets | Identification of hereditary risk factors |
| Accuracy | High, based on large data samples and pattern recognition | High, focused on genetic traits with hereditary relevance |
| Privacy Concerns | Medium, requires personal data handling | High, involves sensitive genetic information |
| Regulatory Environment | Established guidelines, evolving standards | Strict regulations, ethical considerations |
| Application Speed | Fast processing using automation | Slower, due to complex genetic testing |
| Cost | Lower, scalable technology-driven process | Higher, costly genetic testing procedures |
| Adaptability | Flexible, can integrate multiple data types | Limited, focused on genetic data only |
Which is better?
Artificial intelligence underwriting leverages vast datasets and machine learning algorithms to assess risk efficiently, improving accuracy and reducing human bias. Genetic underwriting, which evaluates an individual's genetic information to predict health risks, raises ethical concerns and faces regulatory restrictions in many regions. AI underwriting is generally preferred for its scalability, regulatory compliance, and ability to incorporate diverse data sources beyond genetic factors.
Connection
Artificial intelligence underwriting leverages machine learning algorithms to analyze vast datasets, including genetic information, to assess risk more accurately and personalize insurance policies. Genetic underwriting involves evaluating an individual's genetic data to predict susceptibility to certain diseases, which AI models can process efficiently to improve precision in risk assessment. Integrating AI with genetic underwriting enhances predictive accuracy, enabling insurers to tailor policies based on comprehensive genetic risk profiles.
Key Terms
Risk Assessment
Genetic underwriting evaluates risk by analyzing an individual's genetic predisposition to diseases, providing insights that traditional methods may overlook, while artificial intelligence underwriting leverages machine learning algorithms to assess vast datasets including medical history, lifestyle, and claims data for more accurate risk prediction. AI underwriting enhances precision and speed in identifying patterns that indicate higher or lower risk profiles without relying solely on genetic information. Discover how integrating these approaches can revolutionize risk assessment in insurance.
Predictive Modeling
Genetic underwriting uses hereditary information to assess risk, while artificial intelligence underwriting leverages predictive modeling techniques such as machine learning algorithms to analyze vast datasets for risk evaluation. AI predictive models identify complex patterns and trends beyond traditional genetic markers, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in underwriting decisions. Explore how AI-driven predictive modeling reshapes risk assessment and outperforms genetic underwriting in modern insurance practices.
Privacy Compliance
Genetic underwriting involves assessing insurance risk based on an individual's genetic information, raising significant privacy compliance challenges under laws like GINA and HIPAA. Artificial intelligence underwriting leverages machine learning algorithms to analyze diverse datasets while maintaining adherence to data privacy standards through anonymization and secure data handling. Explore further to understand how integrating AI can enhance privacy compliance without compromising risk accuracy.
Source and External Links
Genetic Testing in Insurance: Challenges and Opportunities I - RGA - Genetic underwriting involves the use or exclusion of genetic test results in life and health insurance applications; regulations vary globally, with some countries banning or restricting the use of genetic information in underwriting to prevent discrimination and anti-selection risk.
Insurance underwriting in the genetic era - PubMed - Advances in genetic technology influence insurance underwriting as genetic data can be relevant for risk classification, but withholding such information may affect the insurance market balance and public policy discussions are ongoing.
Genetic risk scores in life insurance underwriting fuel discrimination fears - News-Medical - The use of polygenic risk scores in life insurance underwriting raises ethical and legal concerns about genetic discrimination and gaps in regulatory protections, as these scores expand the scope of genetic risk assessment beyond rare conditions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com