Climate risk insurance provides direct coverage to individuals, businesses, or governments facing losses from climate-related events, while reinsurance pools aggregate risks from multiple insurers to enhance financial stability and capacity in catastrophes. These reinsurance pools distribute the financial burden of large-scale climate disasters by sharing risks across a network of insurers, enabling more comprehensive and affordable climate risk protection. Explore the differences and benefits of climate risk insurance versus reinsurance pools to better understand effective climate resilience strategies.
Why it is important
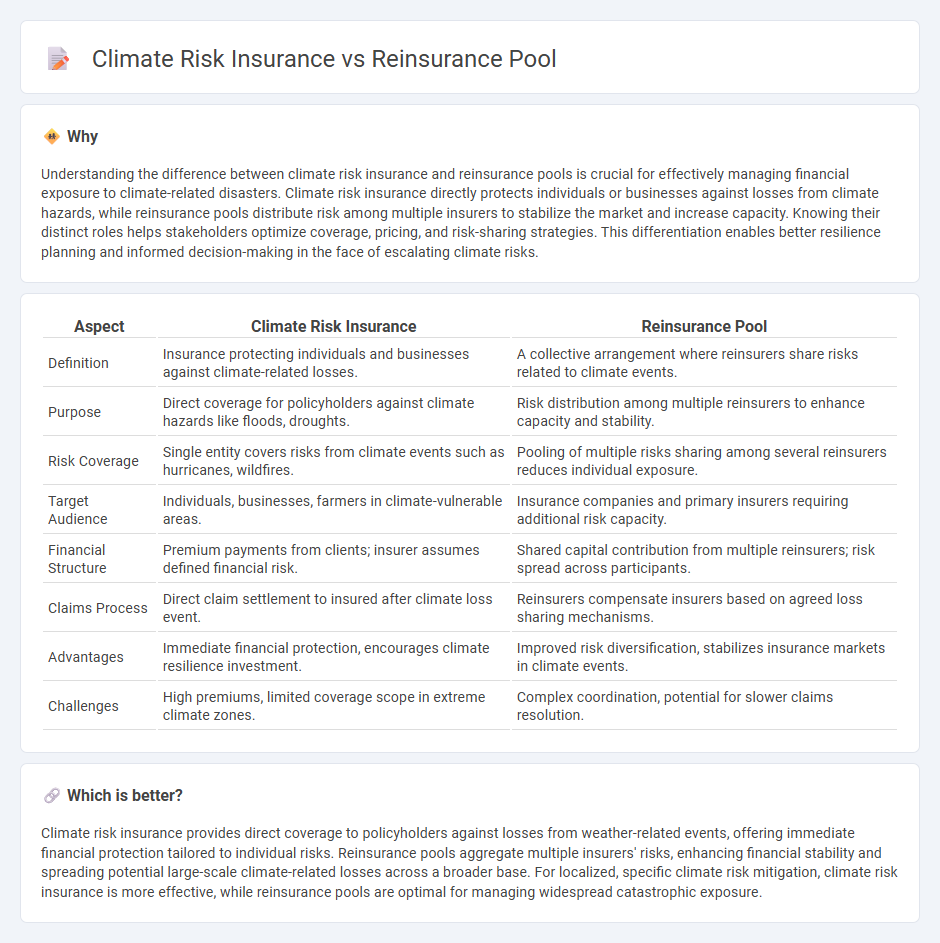
Understanding the difference between climate risk insurance and reinsurance pools is crucial for effectively managing financial exposure to climate-related disasters. Climate risk insurance directly protects individuals or businesses against losses from climate hazards, while reinsurance pools distribute risk among multiple insurers to stabilize the market and increase capacity. Knowing their distinct roles helps stakeholders optimize coverage, pricing, and risk-sharing strategies. This differentiation enables better resilience planning and informed decision-making in the face of escalating climate risks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Climate Risk Insurance | Reinsurance Pool |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insurance protecting individuals and businesses against climate-related losses. | A collective arrangement where reinsurers share risks related to climate events. |
| Purpose | Direct coverage for policyholders against climate hazards like floods, droughts. | Risk distribution among multiple reinsurers to enhance capacity and stability. |
| Risk Coverage | Single entity covers risks from climate events such as hurricanes, wildfires. | Pooling of multiple risks sharing among several reinsurers reduces individual exposure. |
| Target Audience | Individuals, businesses, farmers in climate-vulnerable areas. | Insurance companies and primary insurers requiring additional risk capacity. |
| Financial Structure | Premium payments from clients; insurer assumes defined financial risk. | Shared capital contribution from multiple reinsurers; risk spread across participants. |
| Claims Process | Direct claim settlement to insured after climate loss event. | Reinsurers compensate insurers based on agreed loss sharing mechanisms. |
| Advantages | Immediate financial protection, encourages climate resilience investment. | Improved risk diversification, stabilizes insurance markets in climate events. |
| Challenges | High premiums, limited coverage scope in extreme climate zones. | Complex coordination, potential for slower claims resolution. |
Which is better?
Climate risk insurance provides direct coverage to policyholders against losses from weather-related events, offering immediate financial protection tailored to individual risks. Reinsurance pools aggregate multiple insurers' risks, enhancing financial stability and spreading potential large-scale climate-related losses across a broader base. For localized, specific climate risk mitigation, climate risk insurance is more effective, while reinsurance pools are optimal for managing widespread catastrophic exposure.
Connection
Climate risk insurance and reinsurance pools are interconnected by distributing financial risks associated with climate-related disasters across multiple insurers, enhancing overall market stability. Climate risk insurance pools aggregate resources from various insurance companies to provide coverage for large-scale events like hurricanes, floods, and droughts, mitigating the impact on individual insurers. Reinsurance pools further support this system by sharing excess risk, enabling primary insurers to underwrite more policies while maintaining solvency amid extreme climate events.
Key Terms
**Reinsurance Pool:**
Reinsurance pools aggregate multiple insurers' risks to spread large-scale liabilities, offering enhanced financial stability and capacity during catastrophic events. These pools are essential for managing systemic risks and providing cost-effective coverage in volatile markets, especially for climate-induced disasters such as hurricanes and floods. Explore further to understand how reinsurance pools optimize risk sharing and protect against climate-related losses.
Risk Sharing
Reinsurance pools aggregate risks from multiple insurers to distribute losses more broadly, enhancing financial stability against catastrophic events. Climate risk insurance specifically targets losses from climate-related hazards, promoting resilience by pooling climate risks across diverse geographic regions. Explore how these mechanisms optimize risk sharing to safeguard economies and communities against escalating climate impacts.
Ceding Company
Reinsurance pools aggregate multiple insurers' risks to spread financial exposure, offering ceding companies enhanced risk diversification and potentially lower premiums. Climate risk insurance specifically addresses losses from weather-related events, providing ceding companies with tailored coverage for natural disasters linked to climate change. Explore further to understand how these mechanisms optimize risk management strategies for ceding companies in volatile markets.
Source and External Links
Reinsurance Pool - IRMI - A reinsurance pool is a risk financing mechanism used by insurance companies to increase their ability to underwrite specific types of risks.
Reinsurance Pools and Different Types - Reinsurance pools are a mechanism for managing and underwriting risks, particularly useful in times of natural catastrophes, often backed by sovereign guarantees.
Reinsurance Pools - ARPC - The Australian Reinsurance Pool Corporation operates pools like the Terrorism Reinsurance Pool and Cyclone Reinsurance Pool to provide reinsurance for specific risks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com