Natural catastrophe bonds are financial instruments that transfer catastrophe risk from insurers to investors, providing coverage against events like hurricanes and earthquakes. Insurance-linked securities (ILS) encompass a broader range of products, including cat bonds, that allow insurers to access capital markets for risk diversification and capital relief. Explore the distinctions and benefits of natural catastrophe bonds versus other insurance-linked securities for strategic risk management.
Why it is important
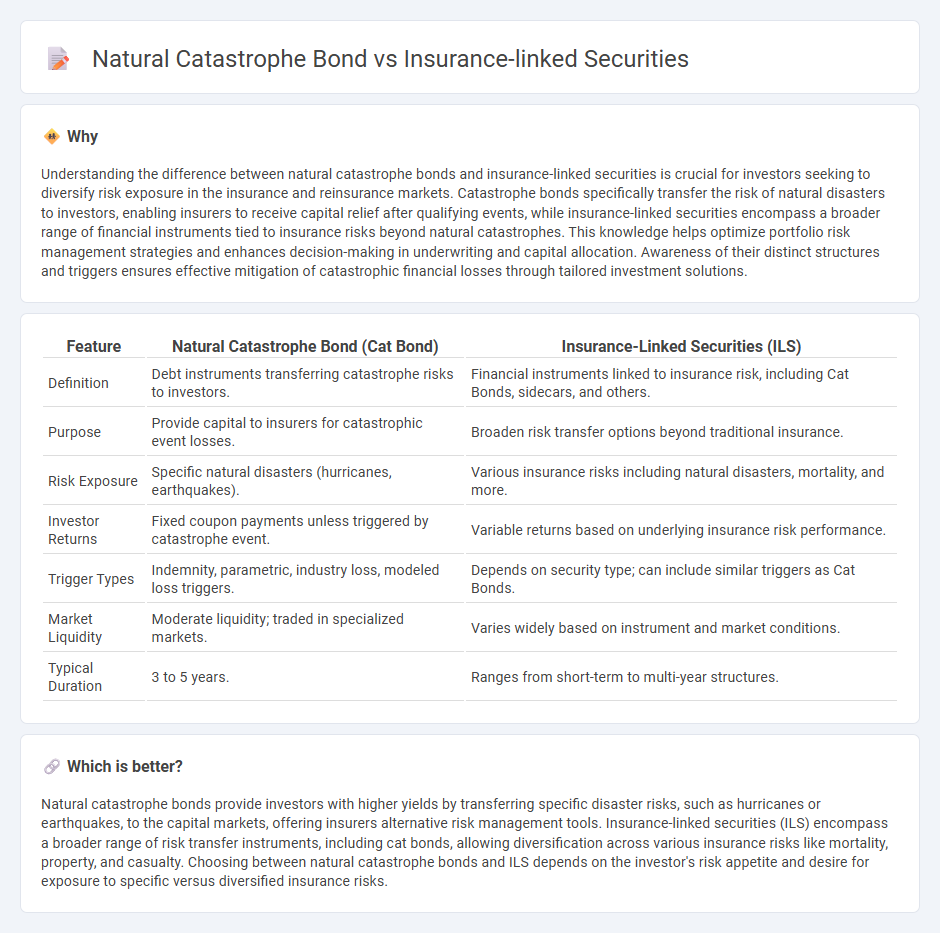
Understanding the difference between natural catastrophe bonds and insurance-linked securities is crucial for investors seeking to diversify risk exposure in the insurance and reinsurance markets. Catastrophe bonds specifically transfer the risk of natural disasters to investors, enabling insurers to receive capital relief after qualifying events, while insurance-linked securities encompass a broader range of financial instruments tied to insurance risks beyond natural catastrophes. This knowledge helps optimize portfolio risk management strategies and enhances decision-making in underwriting and capital allocation. Awareness of their distinct structures and triggers ensures effective mitigation of catastrophic financial losses through tailored investment solutions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Natural Catastrophe Bond (Cat Bond) | Insurance-Linked Securities (ILS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Debt instruments transferring catastrophe risks to investors. | Financial instruments linked to insurance risk, including Cat Bonds, sidecars, and others. |
| Purpose | Provide capital to insurers for catastrophic event losses. | Broaden risk transfer options beyond traditional insurance. |
| Risk Exposure | Specific natural disasters (hurricanes, earthquakes). | Various insurance risks including natural disasters, mortality, and more. |
| Investor Returns | Fixed coupon payments unless triggered by catastrophe event. | Variable returns based on underlying insurance risk performance. |
| Trigger Types | Indemnity, parametric, industry loss, modeled loss triggers. | Depends on security type; can include similar triggers as Cat Bonds. |
| Market Liquidity | Moderate liquidity; traded in specialized markets. | Varies widely based on instrument and market conditions. |
| Typical Duration | 3 to 5 years. | Ranges from short-term to multi-year structures. |
Which is better?
Natural catastrophe bonds provide investors with higher yields by transferring specific disaster risks, such as hurricanes or earthquakes, to the capital markets, offering insurers alternative risk management tools. Insurance-linked securities (ILS) encompass a broader range of risk transfer instruments, including cat bonds, allowing diversification across various insurance risks like mortality, property, and casualty. Choosing between natural catastrophe bonds and ILS depends on the investor's risk appetite and desire for exposure to specific versus diversified insurance risks.
Connection
Natural catastrophe bonds and insurance-linked securities (ILS) are financial instruments designed to transfer insurance risk from insurers to capital market investors, providing liquidity in the event of disasters like hurricanes or earthquakes. These bonds pay high yields but face principal loss if predefined catastrophic events occur, aligning investor returns directly with disaster outcomes. By bridging insurance liabilities with capital markets, natural catastrophe bonds and ILS help insurers manage large-scale risk exposure beyond traditional reinsurance.
Key Terms
Risk Transfer
Insurance-linked securities (ILS) are financial instruments used to transfer insurance risk to capital markets, with natural catastrophe bonds (cat bonds) being a prominent subset specifically designed to cover losses from disasters like hurricanes and earthquakes. Cat bonds transfer catastrophe risk from insurers to investors by providing capital that insurers can access if predefined disaster triggers occur, allowing effective risk diversification. Explore more about how these instruments redefine risk transfer in the insurance and capital markets.
Trigger Event
Insurance-linked securities (ILS) transfer insurance risks to the capital markets, often triggered by events like hurricanes or earthquakes, providing payouts based on predefined criteria. Natural catastrophe bonds (cat bonds), a subset of ILS, specifically focus on loss events tied to natural disasters, with payout triggers based on parametric, indemnity, or modeled loss methods linked to the catastrophe's severity. Explore further to understand how trigger event structures impact risk transfer and investor returns.
Securitization
Insurance-linked securities (ILS) are financial instruments whose value is affected by insurance loss events, enabling transfer of insurance risks to capital markets, with natural catastrophe bonds (cat bonds) as a prominent subset specifically designed for catastrophe risk securitization. Cat bonds transform catastrophe-related insurance risks such as hurricanes or earthquakes into tradable securities, providing insurers with capital relief and investors with returns uncorrelated to financial markets. Explore how securitization of insurance risks through ILS and cat bonds innovates risk management and drives capital market integration.
Source and External Links
What are insurance-linked securities (or ILS)? - Artemis.bm - Insurance-linked securities (ILS) are financial instruments whose value is affected by insured loss events, allowing insurance and reinsurance companies to transfer risk to capital markets; they are typically invested in by large institutional investors and enable access to global capital for risk transfer and disaster financing.
What are insurance linked securities (or ILS)? - Schroders Capital - ILS allow transfer of insurance risk from reinsurers to capital market investors in exchange for a risk premium, offering sustainable, long-term, inflation-shielded investment returns that are historically uncorrelated with traditional asset classes.
Insurance-linked security - Wikipedia - Insurance-linked securities are financial assets whose value depends on insurance loss events, particularly from natural catastrophes, and serve as an alternative risk transfer mechanism that diversifies insurer risk and provides high returns to investors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com