Embedded insurance integrates coverage directly into the purchase of products or services, offering seamless protection without requiring a separate policy acquisition. Traditional insurance involves standalone policies purchased independently, often requiring separate underwriting and administrative processes. Explore how embedded insurance is transforming risk management and customer experience compared to traditional models.
Why it is important
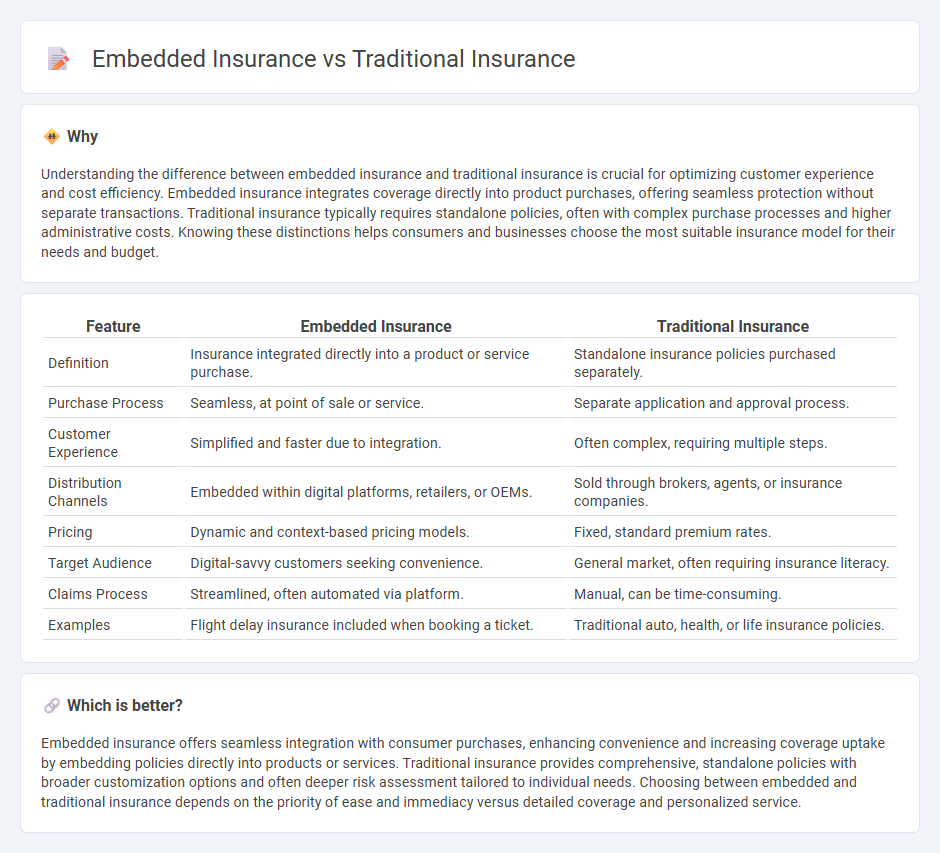
Understanding the difference between embedded insurance and traditional insurance is crucial for optimizing customer experience and cost efficiency. Embedded insurance integrates coverage directly into product purchases, offering seamless protection without separate transactions. Traditional insurance typically requires standalone policies, often with complex purchase processes and higher administrative costs. Knowing these distinctions helps consumers and businesses choose the most suitable insurance model for their needs and budget.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Embedded Insurance | Traditional Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insurance integrated directly into a product or service purchase. | Standalone insurance policies purchased separately. |
| Purchase Process | Seamless, at point of sale or service. | Separate application and approval process. |
| Customer Experience | Simplified and faster due to integration. | Often complex, requiring multiple steps. |
| Distribution Channels | Embedded within digital platforms, retailers, or OEMs. | Sold through brokers, agents, or insurance companies. |
| Pricing | Dynamic and context-based pricing models. | Fixed, standard premium rates. |
| Target Audience | Digital-savvy customers seeking convenience. | General market, often requiring insurance literacy. |
| Claims Process | Streamlined, often automated via platform. | Manual, can be time-consuming. |
| Examples | Flight delay insurance included when booking a ticket. | Traditional auto, health, or life insurance policies. |
Which is better?
Embedded insurance offers seamless integration with consumer purchases, enhancing convenience and increasing coverage uptake by embedding policies directly into products or services. Traditional insurance provides comprehensive, standalone policies with broader customization options and often deeper risk assessment tailored to individual needs. Choosing between embedded and traditional insurance depends on the priority of ease and immediacy versus detailed coverage and personalized service.
Connection
Embedded insurance integrates coverage options directly into the purchase of products or services, streamlining the consumer experience by bundling insurance with primary transactions. Traditional insurance operates through standalone policies requiring separate acquisition and management, often involving dedicated brokers or insurers. The connection lies in embedded insurance leveraging the foundations and regulatory frameworks of traditional insurance to deliver seamless, context-specific protection within digital platforms and marketplaces.
Key Terms
Distribution Channel
Traditional insurance relies on direct sales through agents, brokers, and company-owned branches, often requiring customers to actively seek coverage. Embedded insurance integrates policies seamlessly within the purchase of products or services, leveraging digital platforms and partner ecosystems to simplify access. Explore how these distribution channel strategies shape customer experience and market reach.
Product Customization
Traditional insurance typically offers standardized policies with limited customization options, often resulting in coverage that may not fully meet specific customer needs. Embedded insurance integrates directly into the purchase of products or services, allowing for tailored coverage that adapts to the unique requirements of each transaction or consumer profile. Explore how embedded insurance enhances product customization and transforms customer experiences by delivering more relevant and flexible insurance solutions.
Customer Experience
Traditional insurance requires customers to navigate complex policies and lengthy claim processes, often resulting in delayed satisfaction and lower engagement. Embedded insurance integrates coverage seamlessly within the purchase journey of products or services, enhancing convenience and immediate protection, leading to higher customer trust and retention. Discover how embedded insurance transforms the customer experience by simplifying access and delivery.
Source and External Links
What Is Traditional Insurance Plan | ABSLI - Traditional insurance plans, especially in life insurance, are conventional products that provide life coverage, fixed incomes, tax benefits, and bonuses, and include pure life protection plans like term insurance and mixed plans like endowment and annuity plans that combine insurance with guaranteed returns.
Traditional Indemnity Insurance Plans - Virginia Health Information - Traditional indemnity insurance plans reimburse patients based on usual, customary, and reasonable fees after paying a deductible and coinsurance, generally allowing freedom of provider choice and often involving fee-for-service arrangements.
Comparing Costs: Subscription Health Plans vs. Traditional Insurance - Traditional insurance requires monthly or annual premiums and usually includes deductibles, co-pays, and coinsurance, thus covering comprehensive health care but often resulting in higher out-of-pocket costs compared to subscription health plans.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com