Parametric insurance provides predetermined payouts based on specific triggers, such as weather events or earthquake magnitude, eliminating the need for traditional loss assessments. Proportional insurance reimburses a percentage of the actual loss incurred, requiring detailed claims adjustment and verification processes. Explore more to understand which insurance model best fits your risk management strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between parametric insurance and proportional insurance is crucial for selecting the right coverage that aligns with specific risk management needs. Parametric insurance pays out predetermined amounts based on the occurrence of predefined events, ensuring quick claims without loss assessment delays. Proportional insurance involves indemnity payments proportional to the actual loss suffered, offering tailored compensation but with longer claim processing. Choosing the appropriate type enhances financial resilience and optimizes risk transfer strategies in sectors like agriculture, disaster management, and business protection.
Comparison Table
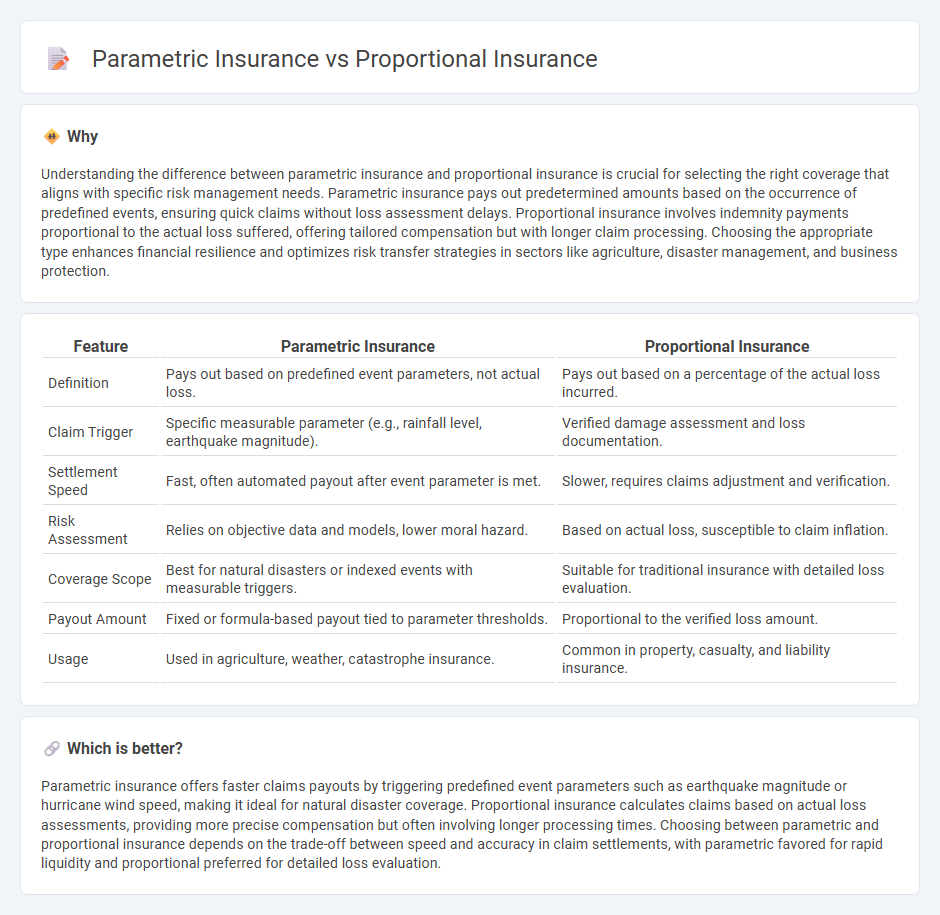
| Feature | Parametric Insurance | Proportional Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pays out based on predefined event parameters, not actual loss. | Pays out based on a percentage of the actual loss incurred. |
| Claim Trigger | Specific measurable parameter (e.g., rainfall level, earthquake magnitude). | Verified damage assessment and loss documentation. |
| Settlement Speed | Fast, often automated payout after event parameter is met. | Slower, requires claims adjustment and verification. |
| Risk Assessment | Relies on objective data and models, lower moral hazard. | Based on actual loss, susceptible to claim inflation. |
| Coverage Scope | Best for natural disasters or indexed events with measurable triggers. | Suitable for traditional insurance with detailed loss evaluation. |
| Payout Amount | Fixed or formula-based payout tied to parameter thresholds. | Proportional to the verified loss amount. |
| Usage | Used in agriculture, weather, catastrophe insurance. | Common in property, casualty, and liability insurance. |
Which is better?
Parametric insurance offers faster claims payouts by triggering predefined event parameters such as earthquake magnitude or hurricane wind speed, making it ideal for natural disaster coverage. Proportional insurance calculates claims based on actual loss assessments, providing more precise compensation but often involving longer processing times. Choosing between parametric and proportional insurance depends on the trade-off between speed and accuracy in claim settlements, with parametric favored for rapid liquidity and proportional preferred for detailed loss evaluation.
Connection
Parametric insurance and proportional insurance are connected through their shared goal of risk mitigation, yet they differ in claim assessment methods; parametric insurance pays out based on predefined event metrics like rainfall levels or wind speed, while proportional insurance compensates based on the percentage of actual loss incurred. Both models provide financial protection but cater to distinct needs--parametric insurance offers rapid payouts using objective triggers, whereas proportional insurance aligns payouts more closely with the insured's specific damage. This connection highlights the evolution of insurance mechanisms to address diverse risk profiles and improve claim efficiency.
Key Terms
Indemnity
Proportional insurance indemnifies policyholders based on the actual loss sustained, ensuring compensation aligns with the damage value, whereas parametric insurance pays a predetermined amount triggered by specific parameters like rainfall or earthquake magnitude, regardless of actual loss. This indemnity-based distinction is crucial for businesses evaluating coverage precision versus speed of payout. Explore more to understand which indemnity model suits your risk management needs best.
Trigger event
Proportional insurance involves compensation based on the actual loss incurred, requiring detailed loss assessment after a triggering event such as fire or theft. Parametric insurance activates a pre-agreed payout following a predefined trigger event, like an earthquake exceeding a specific magnitude or a hurricane reaching a certain wind speed, without the need for loss adjustment. Explore further to understand which insurance model suits specific risk management needs.
Sum insured
Proportional insurance provides coverage based on the sum insured and indemnifies losses up to the policy limit, adjusting payouts according to the actual damage assessed. Parametric insurance, however, triggers a fixed payment when predefined parameters or events, such as rainfall levels or earthquake magnitude, exceed set thresholds, independent of the loss amount or the sum insured. Explore the specific benefits and applications of each insurance type to determine the best fit for risk management needs.
Source and External Links
Definition of 'proportional reinsurance coverage' - Proportional insurance is a reinsurance arrangement where the insurer and reinsurer share premiums and losses in a specified proportion, meaning both share risks and premiums based on agreed ratios between them.
Proportional Reinsurance: A Comprehensive Guide - Proportional insurance involves the reinsurer accepting a share of the insurer's risk and receiving a corresponding share of premiums, enabling insurers to manage risk and increase underwriting capacity while sharing claims according to the same proportion.
Proportional Reinsurance - Proportional insurance includes quota share and surplus share arrangements, where premiums, expenses, and losses are divided between insurer and reinsurer based on predetermined percentages, each form serving different purposes such as financing or capacity enhancement.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com