Social prescribing insurance focuses on covering non-clinical interventions like community activities and holistic therapies that support mental and physical health, enhancing overall well-being. Private medical insurance provides coverage for direct medical treatments, hospital stays, and specialist consultations, ensuring faster access to conventional healthcare services. Explore the differences and benefits of each to determine the best fit for your health needs.
Why it is important
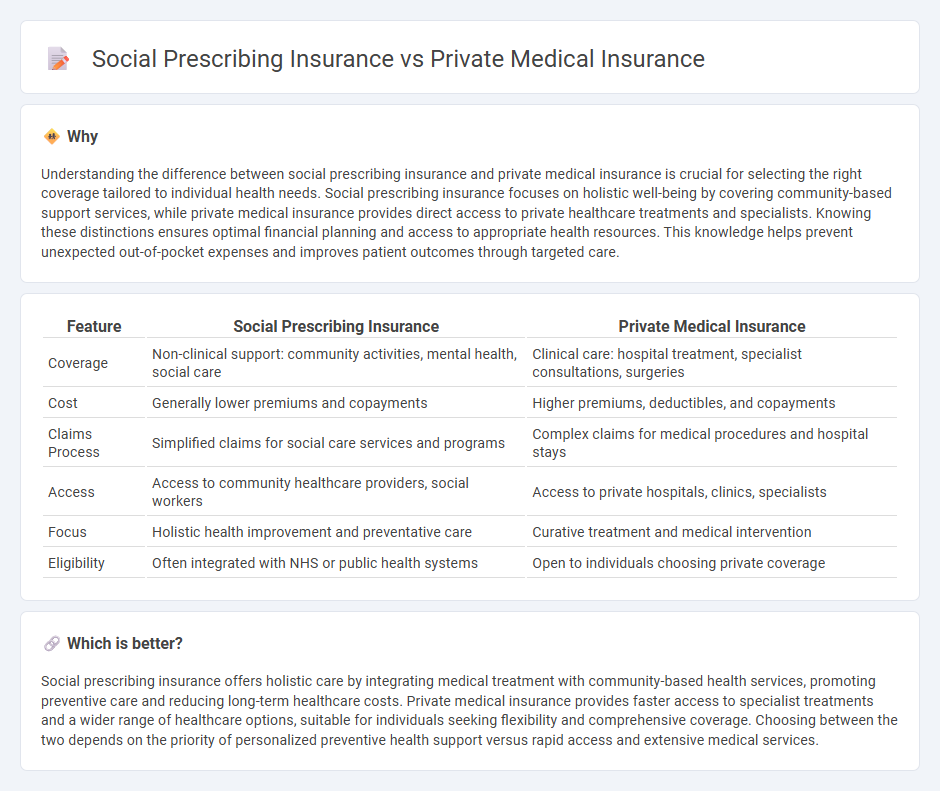
Understanding the difference between social prescribing insurance and private medical insurance is crucial for selecting the right coverage tailored to individual health needs. Social prescribing insurance focuses on holistic well-being by covering community-based support services, while private medical insurance provides direct access to private healthcare treatments and specialists. Knowing these distinctions ensures optimal financial planning and access to appropriate health resources. This knowledge helps prevent unexpected out-of-pocket expenses and improves patient outcomes through targeted care.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Social Prescribing Insurance | Private Medical Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Non-clinical support: community activities, mental health, social care | Clinical care: hospital treatment, specialist consultations, surgeries |
| Cost | Generally lower premiums and copayments | Higher premiums, deductibles, and copayments |
| Claims Process | Simplified claims for social care services and programs | Complex claims for medical procedures and hospital stays |
| Access | Access to community healthcare providers, social workers | Access to private hospitals, clinics, specialists |
| Focus | Holistic health improvement and preventative care | Curative treatment and medical intervention |
| Eligibility | Often integrated with NHS or public health systems | Open to individuals choosing private coverage |
Which is better?
Social prescribing insurance offers holistic care by integrating medical treatment with community-based health services, promoting preventive care and reducing long-term healthcare costs. Private medical insurance provides faster access to specialist treatments and a wider range of healthcare options, suitable for individuals seeking flexibility and comprehensive coverage. Choosing between the two depends on the priority of personalized preventive health support versus rapid access and extensive medical services.
Connection
Social prescribing insurance and private medical insurance intersect by facilitating comprehensive healthcare coverage that includes both medical treatments and holistic well-being services. Social prescribing enables access to community-based support, which private medical insurance increasingly incorporates to enhance patient outcomes and reduce clinical interventions. Integrating these insurance models promotes preventive care, lowers healthcare costs, and improves quality of life through personalized, non-clinical interventions.
Key Terms
Coverage Scope
Private medical insurance typically offers extensive coverage for elective procedures, specialist consultations, and hospital stays, emphasizing personalized healthcare options. Social prescribing insurance focuses on non-clinical interventions such as community activities, mental health support, and lifestyle improvements, enhancing overall well-being beyond traditional medical treatments. Discover how these differing coverage scopes can impact your healthcare choices and financial planning.
Funding Source
Private medical insurance is primarily funded through individual or employer-paid premiums, offering personalized coverage and faster access to specialist treatments. Social prescribing insurance, often funded by public health budgets or community grants, emphasizes holistic care by linking patients to non-clinical services for improved well-being. Explore how funding sources shape the benefits and accessibility of each insurance model.
Eligibility Criteria
Private medical insurance typically requires applicants to meet specific health and financial eligibility criteria, often involving medical underwriting and income verification to assess risk and affordability. Social prescribing insurance focuses on eligibility based on social determinants of health, such as community needs, mental well-being, and access to non-clinical interventions, often prioritizing vulnerable populations. Explore detailed eligibility requirements and benefits to determine the best fit for your healthcare needs.
Source and External Links
What is Private Health Insurance? | Anthem - Private medical insurance is coverage provided through an employer or purchased individually to cover medical care and related expenses, typically involving monthly premiums, copays, and deductibles, and offering more choices and broader provider networks compared to public insurance programs.
Washington health insurance plans - eHealth - Private health insurance in Washington is sold through the state marketplace Washington Healthplanfinder, offering ACA-compliant plans with comprehensive benefits and coverage for essential health services for individuals and families statewide.
Health insurance plans | UnitedHealthcare - Private medical insurance plans vary widely and can include employer-sponsored, ACA marketplace, and short-term plans, with coverage options that depend on the plan type, provider network, member age, and location, including preventive care, prescription drugs, and mental health services.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com