Insurance options for gig workers and part-time workers differ significantly due to the nature of their employment status and income stability. Gig worker insurance typically offers flexible coverage tailored to independent contractors and freelancers, often including liability and health benefits designed for irregular earnings. Explore comprehensive insights to determine which insurance plan best safeguards your unique work situation.
Why it is important
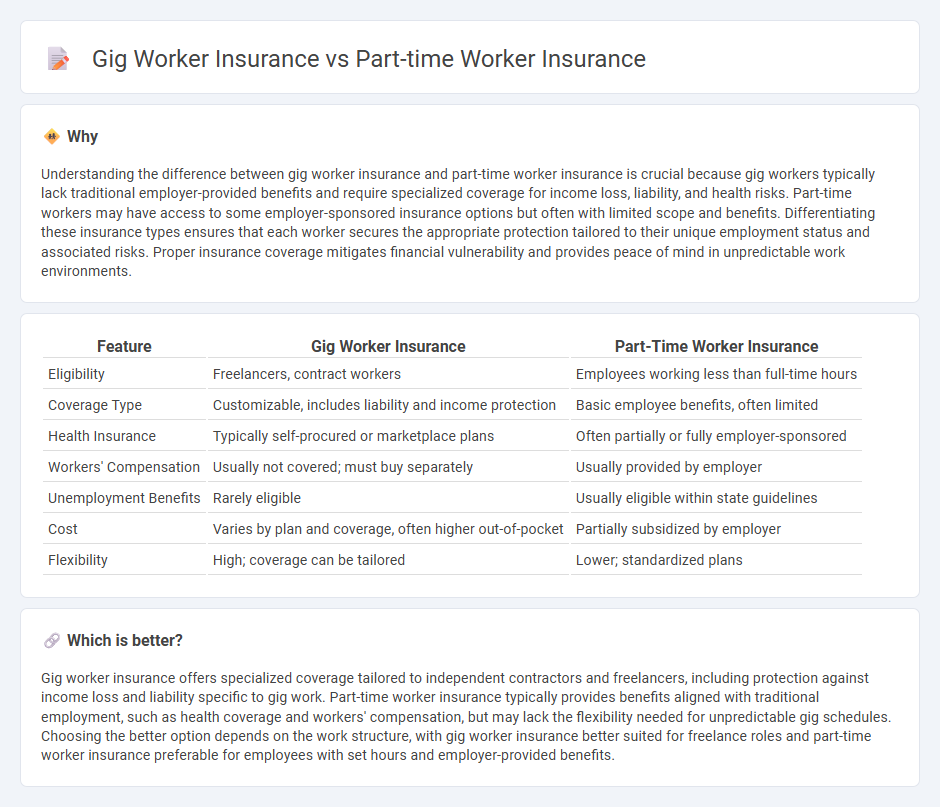
Understanding the difference between gig worker insurance and part-time worker insurance is crucial because gig workers typically lack traditional employer-provided benefits and require specialized coverage for income loss, liability, and health risks. Part-time workers may have access to some employer-sponsored insurance options but often with limited scope and benefits. Differentiating these insurance types ensures that each worker secures the appropriate protection tailored to their unique employment status and associated risks. Proper insurance coverage mitigates financial vulnerability and provides peace of mind in unpredictable work environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Gig Worker Insurance | Part-Time Worker Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | Freelancers, contract workers | Employees working less than full-time hours |
| Coverage Type | Customizable, includes liability and income protection | Basic employee benefits, often limited |
| Health Insurance | Typically self-procured or marketplace plans | Often partially or fully employer-sponsored |
| Workers' Compensation | Usually not covered; must buy separately | Usually provided by employer |
| Unemployment Benefits | Rarely eligible | Usually eligible within state guidelines |
| Cost | Varies by plan and coverage, often higher out-of-pocket | Partially subsidized by employer |
| Flexibility | High; coverage can be tailored | Lower; standardized plans |
Which is better?
Gig worker insurance offers specialized coverage tailored to independent contractors and freelancers, including protection against income loss and liability specific to gig work. Part-time worker insurance typically provides benefits aligned with traditional employment, such as health coverage and workers' compensation, but may lack the flexibility needed for unpredictable gig schedules. Choosing the better option depends on the work structure, with gig worker insurance better suited for freelance roles and part-time worker insurance preferable for employees with set hours and employer-provided benefits.
Connection
Gig worker insurance and part-time worker insurance both address the coverage gaps often left by traditional employer-sponsored plans. These insurance options provide tailored solutions such as liability, health, and income protection policies specifically designed for non-permanent employment structures. By focusing on flexible, affordable coverage, they protect workers who lack consistent benefits, ensuring financial security despite irregular work hours or contract-based roles.
Key Terms
Eligibility Criteria
Part-time worker insurance typically requires a minimum number of hours worked per week, often between 20 and 30, to qualify for benefits such as health, dental, or retirement plans offered by employers. Gig worker insurance eligibility centers on self-employment status, with individuals needing to provide proof of income and work contracts rather than traditional hours, often relying on specialized policies tailored to freelance or contract work. Explore detailed eligibility requirements for both to select the insurance plan that best suits your employment status and coverage needs.
Coverage Scope
Part-time worker insurance generally offers comprehensive coverage including health benefits, workers' compensation, and unemployment insurance, tailored to the predictable hours and employer-based structure of part-time jobs. Gig worker insurance focuses on flexible, indemnity-based plans that cover liability, income loss, and accident insurance, reflecting the irregular income and independent contractor status typical in gig economy roles. Explore the nuanced differences in coverage scope to ensure optimal protection tailored to your work arrangement.
Premium Structure
Part-time worker insurance premiums are generally calculated based on fixed hours worked and consistent income, resulting in more predictable and often lower costs. Gig worker insurance premiums fluctuate according to variable earnings and job frequency, requiring adaptable payment plans that reflect the irregular income typical of gig economy roles. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which insurance premium structure best suits your employment style and financial needs.
Source and External Links
Do Employers Have To Offer Health Insurance To Part-Time Workers? - Employers are not required by federal law to offer health insurance to part-time workers (typically those working less than 30 hours per week), though they may choose to, provided eligibility criteria are clear and consistently applied.
Marketplace Health Care Coverage for Part-Time Employees - If your employer does not offer health insurance to part-time employees, you may be eligible to purchase coverage through the Health Insurance Marketplace and could qualify for savings based on your income.
Are Part-Time Employees Eligible for Health Insurance? - Part-time employees can be eligible for employer-sponsored health insurance if the employer chooses to offer it, but there is no federal requirement for employers to do so.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com