Peer-to-peer insurance leverages decentralized networks where individuals pool resources to cover risks collectively, reducing reliance on traditional insurers and often lowering costs. Cooperative insurance operates as a member-owned entity, emphasizing shared responsibility and mutual benefits among policyholders with aligned interests. Explore the key differences between these models to determine which suits your insurance needs best.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between peer-to-peer insurance and cooperative insurance is crucial for selecting the best risk-sharing model aligned with your financial goals and trust preferences. Peer-to-peer insurance pools premiums among a group with similar risk profiles, aiming to reduce costs and fraud through mutual accountability. Cooperative insurance, governed by its members, focuses on collective ownership and decision-making, enhancing control and transparency. Understanding these distinctions helps consumers optimize coverage, cost-efficiency, and governance participation.
Comparison Table
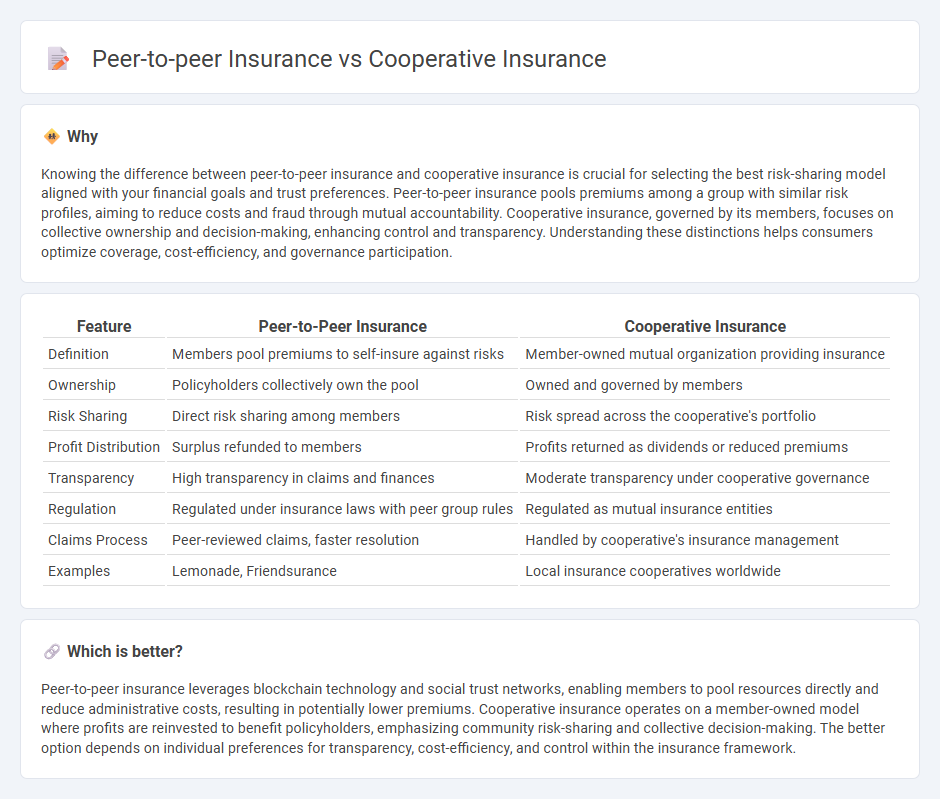
| Feature | Peer-to-Peer Insurance | Cooperative Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Members pool premiums to self-insure against risks | Member-owned mutual organization providing insurance |
| Ownership | Policyholders collectively own the pool | Owned and governed by members |
| Risk Sharing | Direct risk sharing among members | Risk spread across the cooperative's portfolio |
| Profit Distribution | Surplus refunded to members | Profits returned as dividends or reduced premiums |
| Transparency | High transparency in claims and finances | Moderate transparency under cooperative governance |
| Regulation | Regulated under insurance laws with peer group rules | Regulated as mutual insurance entities |
| Claims Process | Peer-reviewed claims, faster resolution | Handled by cooperative's insurance management |
| Examples | Lemonade, Friendsurance | Local insurance cooperatives worldwide |
Which is better?
Peer-to-peer insurance leverages blockchain technology and social trust networks, enabling members to pool resources directly and reduce administrative costs, resulting in potentially lower premiums. Cooperative insurance operates on a member-owned model where profits are reinvested to benefit policyholders, emphasizing community risk-sharing and collective decision-making. The better option depends on individual preferences for transparency, cost-efficiency, and control within the insurance framework.
Connection
Peer-to-peer insurance and cooperative insurance both emphasize collective risk sharing and member-driven governance models to reduce costs and increase transparency. In peer-to-peer insurance, groups of individuals pool premiums and collaboratively manage claims, mirroring the cooperative insurance structure where policyholders are also stakeholders who influence decision-making. Both approaches aim to disrupt traditional insurance by fostering trust, lowering overhead, and aligning interests between insured parties.
Key Terms
Risk Sharing
Cooperative insurance pools resources among members to collectively manage risk, ensuring financial protection through shared responsibility. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages smaller, decentralized groups to minimize conflicts of interest and reduce costs by directly sharing claims and premiums among members. Explore the nuances of risk sharing and financial benefits in cooperative versus peer-to-peer insurance models for deeper insights.
Mutual Ownership
Cooperative insurance and peer-to-peer insurance both emphasize mutual ownership, where policyholders collectively share risks and benefits, promoting transparency and equitable outcomes. Cooperative insurance operates through formally structured entities owned by members, while peer-to-peer insurance often utilizes decentralized platforms allowing direct interaction and claims sharing among participants. Explore further to understand how mutual ownership shapes the efficiencies and trust in these innovative insurance models.
Decentralization
Cooperative insurance operates on a member-owned model where policyholders share risks and benefits through a centralized organization, fostering community trust and mutual support. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages blockchain technology to distribute risk directly among participants without a central authority, enhancing transparency and reducing administrative costs. Explore the differences in decentralization to understand which model better suits your insurance needs.
Source and External Links
Insurance Co-ops - NCBA CLUSA - Cooperative insurance involves policies that protect individual co-op members (such as housing co-ops) by covering their personal belongings and unit interiors, while insurance co-ops like mutual insurance companies serve policyholders with member-ownership and focus on reasonable costs rather than profits.
Co-operatives and Group Property/Casualty Insurance - In New York, unrelated cooperative organizations and their for-profit management companies cannot be insured together under a single group property/casualty insurance policy due to regulatory restrictions.
Best Co-Op Insurance in NYC (2025) - Insurify - Co-op insurance typically covers personal belongings, interior upgrades, liability protection, and additional living expenses, but generally excludes loss assessment charges for common areas, flood or earthquake damage, water backup, and maintenance issues.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com