Insurance as a service offers comprehensive risk management by transferring potential financial losses to an insurer, providing peace of mind through coverage for events like accidents, health issues, or property damage. Self-insurance involves setting aside funds internally to cover risks, requiring robust financial planning and risk assessment to manage unexpected costs effectively. Explore how these strategies can impact your financial security and risk tolerance in detail.
Why it is important
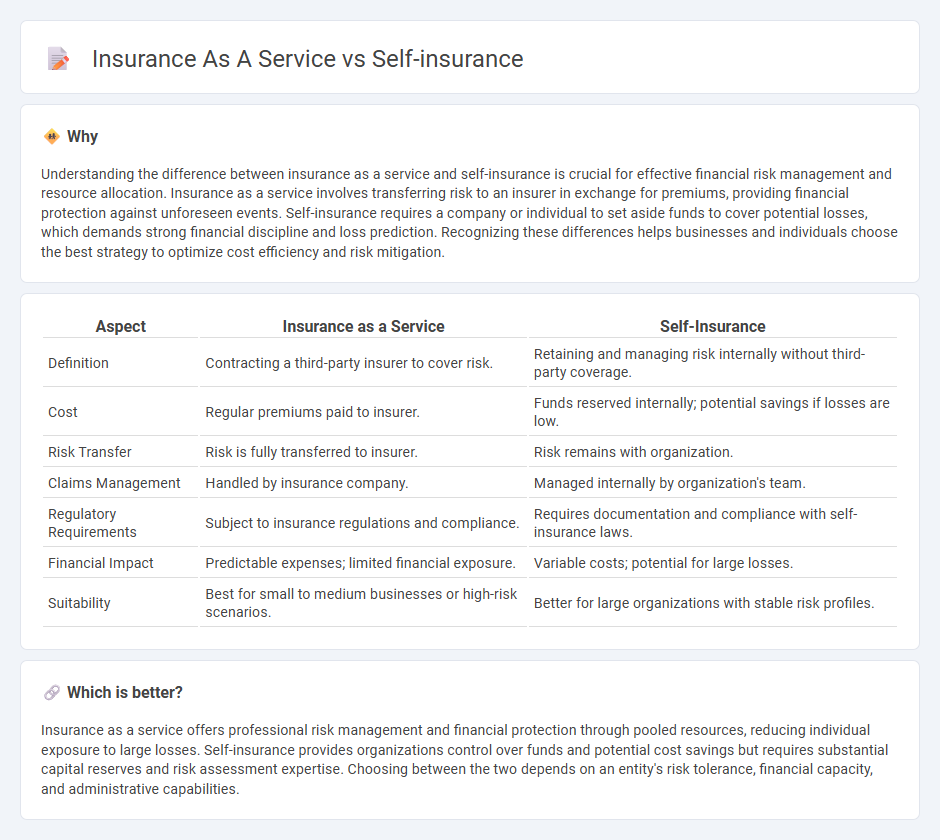
Understanding the difference between insurance as a service and self-insurance is crucial for effective financial risk management and resource allocation. Insurance as a service involves transferring risk to an insurer in exchange for premiums, providing financial protection against unforeseen events. Self-insurance requires a company or individual to set aside funds to cover potential losses, which demands strong financial discipline and loss prediction. Recognizing these differences helps businesses and individuals choose the best strategy to optimize cost efficiency and risk mitigation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Insurance as a Service | Self-Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contracting a third-party insurer to cover risk. | Retaining and managing risk internally without third-party coverage. |
| Cost | Regular premiums paid to insurer. | Funds reserved internally; potential savings if losses are low. |
| Risk Transfer | Risk is fully transferred to insurer. | Risk remains with organization. |
| Claims Management | Handled by insurance company. | Managed internally by organization's team. |
| Regulatory Requirements | Subject to insurance regulations and compliance. | Requires documentation and compliance with self-insurance laws. |
| Financial Impact | Predictable expenses; limited financial exposure. | Variable costs; potential for large losses. |
| Suitability | Best for small to medium businesses or high-risk scenarios. | Better for large organizations with stable risk profiles. |
Which is better?
Insurance as a service offers professional risk management and financial protection through pooled resources, reducing individual exposure to large losses. Self-insurance provides organizations control over funds and potential cost savings but requires substantial capital reserves and risk assessment expertise. Choosing between the two depends on an entity's risk tolerance, financial capacity, and administrative capabilities.
Connection
Insurance as a service provides risk management solutions and financial protection through third-party coverage, while self-insurance involves an organization setting aside its own funds to cover potential losses internally. Both approaches aim to mitigate financial risk but differ in execution; insurance services transfer risk externally, whereas self-insurance retains risk within the entity. Companies often analyze cost-benefit models and risk tolerance to choose between outsourcing coverage and adopting self-insurance strategies.
Key Terms
Risk Retention
Self-insurance involves a company retaining the financial risk of potential losses internally, managing claims and reserves independently, whereas insurance as a service transfers that risk to an external provider through premium payments. Risk retention in self-insurance requires robust financial planning and risk assessment to ensure sufficient capital buffers and claims administration capabilities. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how different risk retention strategies impact financial stability and operational control.
Premium
Self-insurance eliminates premium payments by allowing businesses to retain risk and cover losses internally, reducing upfront costs but increasing exposure to large claims. Insurance as a service requires regular premium payments that provide risk transfer, financial predictability, and access to risk management resources from the insurer. Discover how premium structures impact your cost-efficiency and risk strategy by exploring self-insurance versus insurance as a service in depth.
Third-party Administration
Third-party Administration (TPA) plays a critical role in self-insurance by managing claims, benefits, and compliance without the insurer's direct involvement, allowing businesses to maintain control over their risk management and reduce costs. Unlike traditional insurance services that transfer risk to an insurer, TPA enables a company to retain risk while outsourcing administrative tasks, improving efficiency and customization of health or liability plans. Explore how leveraging TPAs can optimize your self-insurance strategy and enhance operational control.
Source and External Links
Self-insurance - Wikipedia - Self-insurance is a risk management method where an organization bears the risk itself without third-party insurance, setting aside funds to cover future losses and often saving costs by eliminating commercial premiums.
Self-Insured Vs. Fully Insured Health Plans - Aetna - Self-insurance, or self-funded plans, let employers directly pay benefit claims while often offering greater flexibility, potential cost savings, and access to provider networks compared to fully insured plans.
SIP - Overview and Requirements for Becoming Self-Insured - Employers seeking to self-insure workers' compensation must apply to a regulatory office, meeting criteria such as financial strength, credit rating, and business experience to be approved for self-insurance status.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com