Catastrophe bonds transfer disaster-related financial risks from insurers to investors by issuing securities that pay out when specified catastrophic events occur, providing rapid liquidity. Parametric insurance offers predefined payouts based on measured event parameters, such as hurricane wind speeds or earthquake magnitudes, eliminating lengthy claims processes. Explore further to understand which risk management solution best suits your insurance needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between catastrophe bonds and parametric insurance is crucial for effective risk management in the insurance industry. Catastrophe bonds transfer risk to investors by paying out based on the occurrence of specific catastrophic events, helping insurers manage large-scale disaster losses. Parametric insurance provides predefined payouts triggered by measurable parameters like earthquake magnitude or hurricane wind speed, allowing quicker claims settlements. Knowing these differences helps insurers and businesses choose the most suitable financial protection for natural disaster risks.
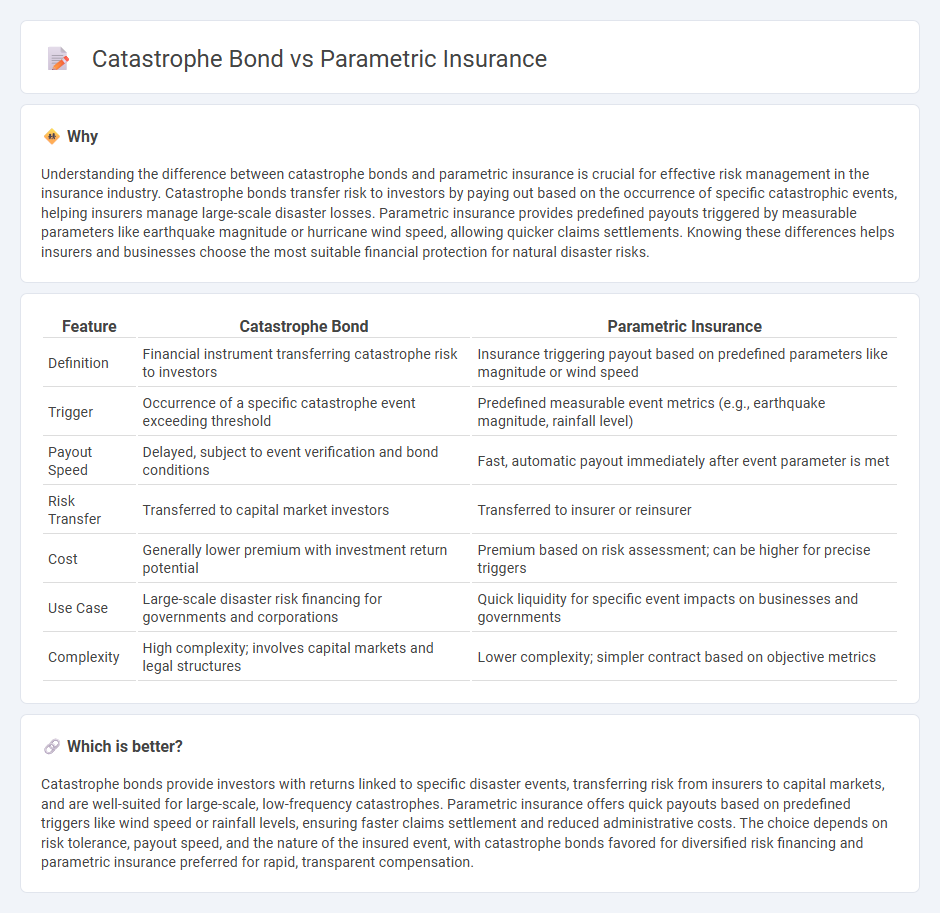
Comparison Table
| Feature | Catastrophe Bond | Parametric Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial instrument transferring catastrophe risk to investors | Insurance triggering payout based on predefined parameters like magnitude or wind speed |
| Trigger | Occurrence of a specific catastrophe event exceeding threshold | Predefined measurable event metrics (e.g., earthquake magnitude, rainfall level) |
| Payout Speed | Delayed, subject to event verification and bond conditions | Fast, automatic payout immediately after event parameter is met |
| Risk Transfer | Transferred to capital market investors | Transferred to insurer or reinsurer |
| Cost | Generally lower premium with investment return potential | Premium based on risk assessment; can be higher for precise triggers |
| Use Case | Large-scale disaster risk financing for governments and corporations | Quick liquidity for specific event impacts on businesses and governments |
| Complexity | High complexity; involves capital markets and legal structures | Lower complexity; simpler contract based on objective metrics |
Which is better?
Catastrophe bonds provide investors with returns linked to specific disaster events, transferring risk from insurers to capital markets, and are well-suited for large-scale, low-frequency catastrophes. Parametric insurance offers quick payouts based on predefined triggers like wind speed or rainfall levels, ensuring faster claims settlement and reduced administrative costs. The choice depends on risk tolerance, payout speed, and the nature of the insured event, with catastrophe bonds favored for diversified risk financing and parametric insurance preferred for rapid, transparent compensation.
Connection
Catastrophe bonds and parametric insurance both provide financial protection against natural disasters by offering quick payouts based on predefined triggers rather than actual losses. Parametric insurance relies on measurable parameters like wind speed or earthquake magnitude to activate claims, which aligns with catastrophe bonds that transfer disaster risks to capital markets using similar trigger events. This connection enhances risk management strategies for insurers and investors seeking efficient recovery solutions after catastrophic events.
Key Terms
Trigger Event
Parametric insurance pays out based on predefined trigger events such as specific levels of rainfall, wind speed, or earthquake magnitude, allowing for rapid claims processing without loss assessment. Catastrophe bonds activate when an independent trigger event, often an index surpassing a threshold, causes principal loss for the investor and transfers risk to the capital markets. Explore further to understand how trigger events shape risk transfer mechanisms in parametric insurance and catastrophe bonds.
Payout Structure
Parametric insurance provides predefined payouts based on specific parameters or indices, such as wind speed or earthquake magnitude, triggering compensation immediately after data thresholds are met. Catastrophe bonds involve investors bearing risks, and payouts occur only when actual catastrophic events cause losses exceeding predefined layers, ensuring funds are available for disaster recovery. Explore the nuances of payout structures to understand which risk transfer solution better matches your financial protection needs.
Risk Transfer
Parametric insurance provides rapid risk transfer through predefined triggers based on measurable parameters such as wind speed or earthquake magnitude, enabling quick claims payouts without loss adjustments. Catastrophe bonds transfer risk to investors by issuing securities that pay principal and interest unless a specified disaster event occurs, shifting large-scale catastrophe risks away from insurers to the capital markets. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how these risk transfer mechanisms can optimize financial resilience in disaster management.
Source and External Links
What is parametric insurance? - Parametric insurance pays out when a predefined, objectively measurable event (like an earthquake of a certain magnitude) occurs, regardless of the actual loss suffered, based on triggers such as magnitude, wind speed, or rainfall.
Parametric insurance - Unlike traditional indemnity insurance, parametric insurance provides quick, pre-specified payouts when a trigger event (e.g., a specific wind speed or earthquake intensity) is met or exceeded, without the need for loss assessment, though it may not cover the full extent of actual damage.
Parametric Insurance Solutions - Parametric insurance uses clear, predefined triggers and payout structures, enabling fast claims payments (often within weeks) based on real-time, objective data, with the insured free to use the payout as needed for recovery.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com