Usage-based insurance calculates premiums based on individual driving behavior, using data such as mileage, speed, and braking patterns to tailor coverage and costs accurately. Telematics insurance employs advanced technology like GPS and onboard sensors to monitor real-time driving habits and vehicle diagnostics for risk assessment. Explore how these innovative insurance models can optimize your policy and savings.
Why it is important
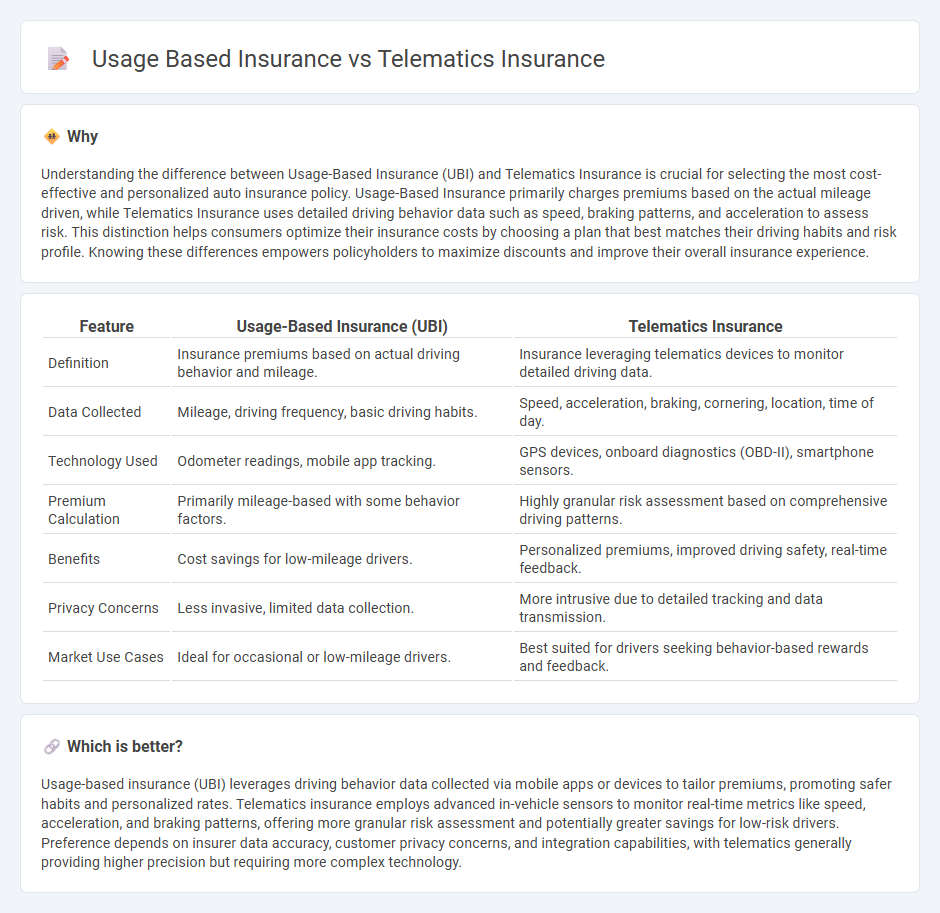
Understanding the difference between Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) and Telematics Insurance is crucial for selecting the most cost-effective and personalized auto insurance policy. Usage-Based Insurance primarily charges premiums based on the actual mileage driven, while Telematics Insurance uses detailed driving behavior data such as speed, braking patterns, and acceleration to assess risk. This distinction helps consumers optimize their insurance costs by choosing a plan that best matches their driving habits and risk profile. Knowing these differences empowers policyholders to maximize discounts and improve their overall insurance experience.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) | Telematics Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insurance premiums based on actual driving behavior and mileage. | Insurance leveraging telematics devices to monitor detailed driving data. |
| Data Collected | Mileage, driving frequency, basic driving habits. | Speed, acceleration, braking, cornering, location, time of day. |
| Technology Used | Odometer readings, mobile app tracking. | GPS devices, onboard diagnostics (OBD-II), smartphone sensors. |
| Premium Calculation | Primarily mileage-based with some behavior factors. | Highly granular risk assessment based on comprehensive driving patterns. |
| Benefits | Cost savings for low-mileage drivers. | Personalized premiums, improved driving safety, real-time feedback. |
| Privacy Concerns | Less invasive, limited data collection. | More intrusive due to detailed tracking and data transmission. |
| Market Use Cases | Ideal for occasional or low-mileage drivers. | Best suited for drivers seeking behavior-based rewards and feedback. |
Which is better?
Usage-based insurance (UBI) leverages driving behavior data collected via mobile apps or devices to tailor premiums, promoting safer habits and personalized rates. Telematics insurance employs advanced in-vehicle sensors to monitor real-time metrics like speed, acceleration, and braking patterns, offering more granular risk assessment and potentially greater savings for low-risk drivers. Preference depends on insurer data accuracy, customer privacy concerns, and integration capabilities, with telematics generally providing higher precision but requiring more complex technology.
Connection
Usage-based insurance (UBI) relies on telematics technology to collect real-time data on driving behavior, including speed, acceleration, braking, and mileage. Telematics devices transmit this information to insurers, enabling personalized premiums based on actual usage patterns rather than traditional risk factors. The integration of telematics in UBI enhances risk assessment accuracy, promotes safer driving habits, and reduces costs for both insurers and policyholders.
Key Terms
Data Collection
Telematics insurance collects detailed driver data through installed devices or smartphone apps, capturing metrics like speed, acceleration, braking patterns, and location, which enable personalized risk assessment and pricing. Usage-based insurance (UBI) primarily uses mileage and driving behavior to calculate premiums, focusing on actual usage rather than fixed rates. Explore how data collection methods impact insurance costs and driver benefits.
Premium Calculation
Telematics insurance calculates premiums based on real-time driving data such as speed, braking patterns, and mileage, allowing for personalized risk assessment. Usage-based insurance (UBI) also relies on driving behavior but emphasizes the amount of vehicle usage, factoring in miles driven and time on the road to determine rates. Discover the nuances between these models and how they impact your insurance costs by exploring detailed comparisons.
Driving Behavior
Telematics insurance uses real-time data collected from a vehicle's onboard device to monitor driving behavior such as speed, braking, and acceleration, which allows insurers to tailor premiums based on individual risk profiles. Usage-based insurance (UBI) often incorporates telematics but emphasizes mileage and driving patterns to determine rates, rewarding safer driving habits with lower costs. Explore how these approaches revolutionize risk assessment and personalize auto insurance pricing.
Source and External Links
Telematics Insurance: How it Works, Benefits + Providers - Telematics insurance uses real-time vehicle data to assess risk and set premiums based on driving behavior, offering potential cost savings through usage-based insurance programs.
Car Insurance Telematics Pros and Cons - This report outlines the benefits and drawbacks of telematics insurance, including discounts offered by major insurers and the factors that influence these discounts.
Telematics Devices for Car Insurance - Telematics devices, such as smartphone apps or plug-in devices, monitor driving habits to potentially lower insurance premiums by rewarding safe driving behaviors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com