Credit life insurance protects borrowers by paying off outstanding debts if they pass away, ensuring creditors receive payment without burdening heirs. Mortgage life insurance specifically covers the remaining mortgage balance, preventing foreclosure and protecting the family home. Explore the differences and benefits to determine which insurance suits your financial security needs.
Why it is important
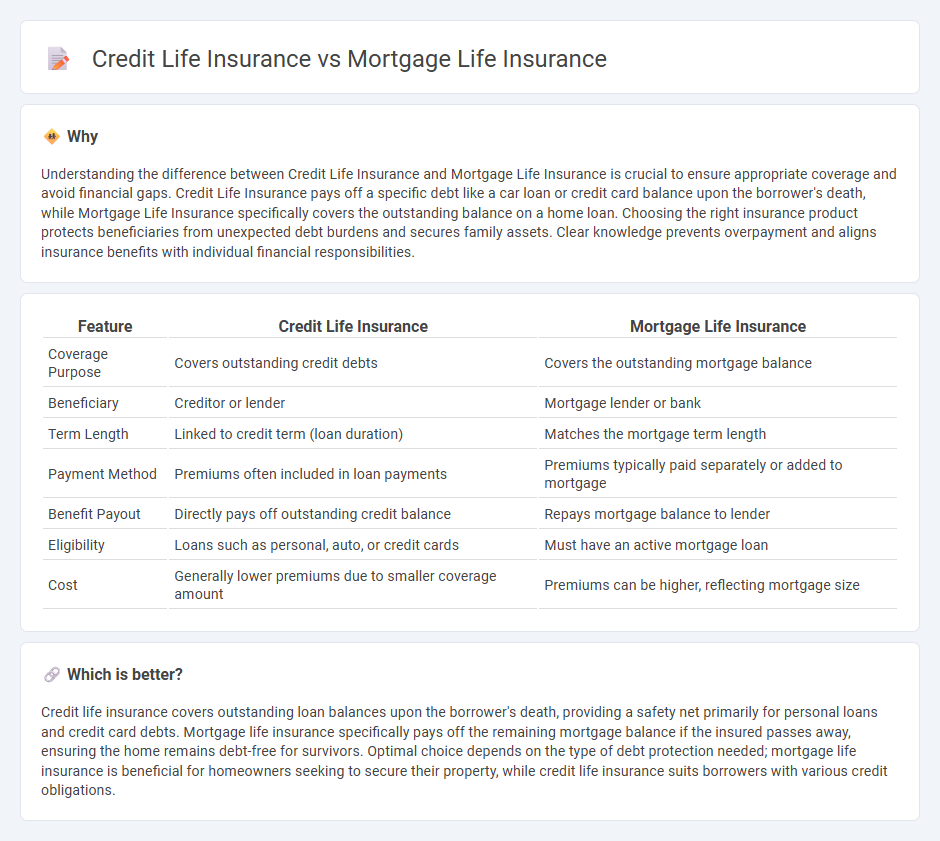
Understanding the difference between Credit Life Insurance and Mortgage Life Insurance is crucial to ensure appropriate coverage and avoid financial gaps. Credit Life Insurance pays off a specific debt like a car loan or credit card balance upon the borrower's death, while Mortgage Life Insurance specifically covers the outstanding balance on a home loan. Choosing the right insurance product protects beneficiaries from unexpected debt burdens and secures family assets. Clear knowledge prevents overpayment and aligns insurance benefits with individual financial responsibilities.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Credit Life Insurance | Mortgage Life Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Purpose | Covers outstanding credit debts | Covers the outstanding mortgage balance |
| Beneficiary | Creditor or lender | Mortgage lender or bank |
| Term Length | Linked to credit term (loan duration) | Matches the mortgage term length |
| Payment Method | Premiums often included in loan payments | Premiums typically paid separately or added to mortgage |
| Benefit Payout | Directly pays off outstanding credit balance | Repays mortgage balance to lender |
| Eligibility | Loans such as personal, auto, or credit cards | Must have an active mortgage loan |
| Cost | Generally lower premiums due to smaller coverage amount | Premiums can be higher, reflecting mortgage size |
Which is better?
Credit life insurance covers outstanding loan balances upon the borrower's death, providing a safety net primarily for personal loans and credit card debts. Mortgage life insurance specifically pays off the remaining mortgage balance if the insured passes away, ensuring the home remains debt-free for survivors. Optimal choice depends on the type of debt protection needed; mortgage life insurance is beneficial for homeowners seeking to secure their property, while credit life insurance suits borrowers with various credit obligations.
Connection
Credit life insurance and mortgage life insurance both provide financial protection by paying off outstanding debts in the event of the policyholder's death. Credit life insurance typically covers personal loans or credit card balances, while mortgage life insurance specifically targets the remaining mortgage balance. Both policies help safeguard families from financial hardship by ensuring debts do not become a burden after the borrower's passing.
Key Terms
Beneficiary
Mortgage life insurance specifically designates the lender as the beneficiary to cover the outstanding mortgage balance in case of the borrower's death, ensuring the home is paid off. Credit life insurance names the creditor as the beneficiary but covers a variety of loans, such as personal loans or credit cards, with payoffs decreasing as the debt is repaid. Explore our detailed guide to understand which insurance aligns better with your financial protection needs.
Policyholder
Mortgage life insurance specifically covers the outstanding mortgage balance if the policyholder passes away, ensuring the home can be paid off without burdening the family. Credit life insurance pays off various types of debt, including credit cards or personal loans, on behalf of the policyholder's creditors upon death. Compare these options to find the best protection tailored to your financial responsibilities.
Outstanding Debt
Mortgage life insurance specifically covers the outstanding mortgage balance, ensuring the loan is paid off if the borrower passes away, which protects the family home. Credit life insurance, however, insures various types of outstanding debts such as personal loans, credit cards, or car loans, often with coverage amounts that decrease as the debt reduces. Explore the key differences and benefits of each policy to choose the best fit for your outstanding debt protection needs.
Source and External Links
Mortgage life insurance - Mortgage life insurance is designed to specifically cover the repayment mortgage; if the insured dies during the policy term, it pays out enough to repay the outstanding mortgage balance, protecting the borrower's ability to repay the mortgage over its lifetime, unlike private mortgage insurance which protects the lender.
What Is Mortgage Protection Insurance? - Mortgage protection insurance (MPI) is a type of life insurance that pays off your mortgage balance in the event of death, with decreasing coverage aligned to your mortgage payoff, but typically costs more than term life insurance and pays the benefit directly to the lender rather than your beneficiaries.
Veterans' Mortgage Life Insurance (VMLI) - VMLI provides mortgage protection insurance specifically for veterans with severe service-connected disabilities who have specialized adapted homes, offering coverage up to $200,000 paid directly to the mortgage lender to help their families maintain the home.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com