Embedded insurance integrates coverage directly into the purchase of products or services, streamlining protection seamlessly for consumers. Microinsurance offers affordable, low-premium policies designed to safeguard low-income individuals against specific risks like health emergencies or natural disasters. Explore more to understand which insurance solution best fits your needs and circumstances.
Why it is important
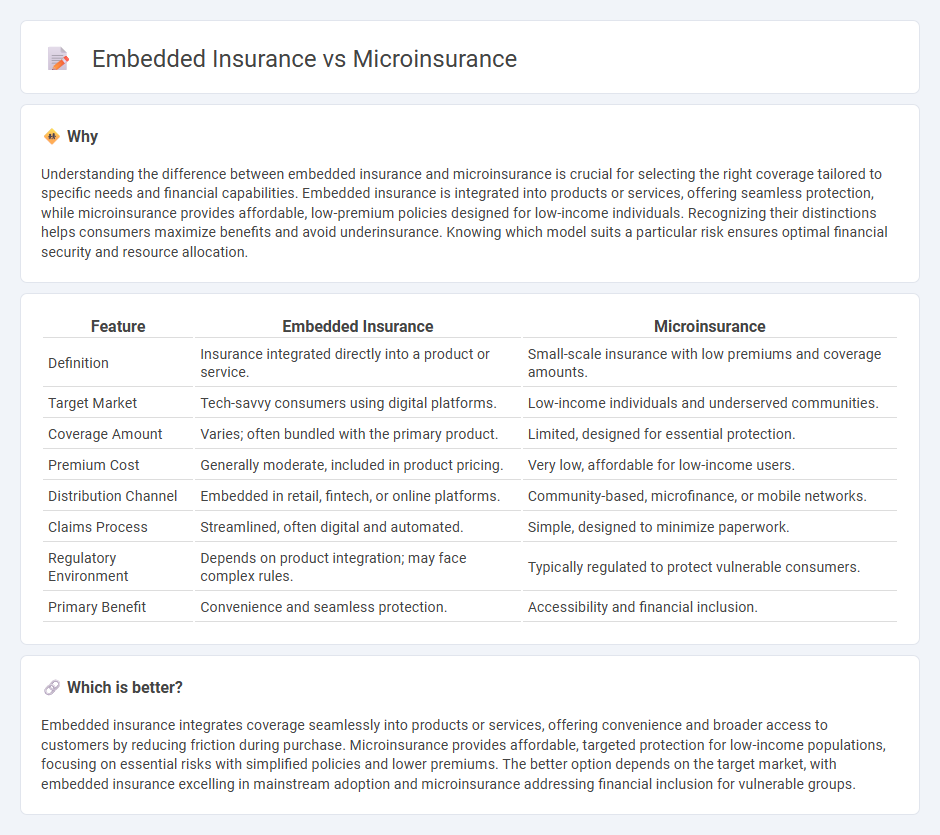
Understanding the difference between embedded insurance and microinsurance is crucial for selecting the right coverage tailored to specific needs and financial capabilities. Embedded insurance is integrated into products or services, offering seamless protection, while microinsurance provides affordable, low-premium policies designed for low-income individuals. Recognizing their distinctions helps consumers maximize benefits and avoid underinsurance. Knowing which model suits a particular risk ensures optimal financial security and resource allocation.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Embedded Insurance | Microinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insurance integrated directly into a product or service. | Small-scale insurance with low premiums and coverage amounts. |
| Target Market | Tech-savvy consumers using digital platforms. | Low-income individuals and underserved communities. |
| Coverage Amount | Varies; often bundled with the primary product. | Limited, designed for essential protection. |
| Premium Cost | Generally moderate, included in product pricing. | Very low, affordable for low-income users. |
| Distribution Channel | Embedded in retail, fintech, or online platforms. | Community-based, microfinance, or mobile networks. |
| Claims Process | Streamlined, often digital and automated. | Simple, designed to minimize paperwork. |
| Regulatory Environment | Depends on product integration; may face complex rules. | Typically regulated to protect vulnerable consumers. |
| Primary Benefit | Convenience and seamless protection. | Accessibility and financial inclusion. |
Which is better?
Embedded insurance integrates coverage seamlessly into products or services, offering convenience and broader access to customers by reducing friction during purchase. Microinsurance provides affordable, targeted protection for low-income populations, focusing on essential risks with simplified policies and lower premiums. The better option depends on the target market, with embedded insurance excelling in mainstream adoption and microinsurance addressing financial inclusion for vulnerable groups.
Connection
Embedded insurance integrates seamlessly into the purchase of products or services, providing convenient and instant coverage, often leveraging digital platforms. Microinsurance targets low-income populations with affordable, tailored policies to cover specific risks, promoting financial inclusion. The connection lies in embedded insurance's capability to distribute microinsurance products efficiently, expanding access to underserved markets through everyday transactions.
Key Terms
Microinsurance:
Microinsurance offers affordable, low-premium insurance products designed to protect low-income individuals from specific risks such as health emergencies, crop failure, or natural disasters. It addresses accessibility barriers by leveraging mobile technology and simplified underwriting processes to reach underserved populations in developing regions. Discover how microinsurance creates financial resilience and empowers vulnerable communities by learning more about its impact and implementation.
Low premiums
Microinsurance offers low premiums tailored for low-income individuals, providing essential coverage with minimal financial burden. Embedded insurance integrates low-cost coverage seamlessly within products or services, enhancing affordability and convenience for users. Explore more to understand how these affordable insurance models can protect diverse needs effectively.
Financial inclusion
Microinsurance provides affordable, tailored coverage for low-income individuals often excluded from traditional insurance markets, promoting financial inclusion by mitigating risks like health expenses and crop failures. Embedded insurance integrates coverage directly into products or services, making insurance more accessible and seamless for underserved populations, thus enhancing financial inclusion through convenience and widespread distribution. Explore how these innovative insurance models drive financial inclusion and empower vulnerable communities with essential protection.
Source and External Links
Microinsurance - Microinsurance is a form of protection for low-income people against specific risks via low premiums and low coverage limits, designed to be affordable and proportional to the likelihood and cost of the risk, and can be delivered by various channels including community schemes or large insurers.
Background on: microinsurance and emerging markets | III - Microinsurance provides low-cost insurance to individuals in developing countries who are generally not covered by traditional insurance, typically characterized by high volumes, low costs, and efficient administration often linked with microloans or other financial products.
Microinsurance | Insurance | Milliman | Worldwide - Microinsurance is tailored to be affordable and appropriate for low-income individuals by balancing price, coverage, and delivery, helping protect vulnerable populations against risks related to health, agriculture, disasters, and mortality that could trap them in poverty.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com