Crop microinsurance protects small-scale farmers against losses caused by adverse weather, pests, or diseases, securing their livelihoods and ensuring financial stability. In contrast, microloan insurance safeguards borrowers by covering loan repayments in case of unforeseen events such as illness, unemployment, or death. Explore how tailored insurance solutions can enhance financial resilience for vulnerable agricultural communities.
Why it is important
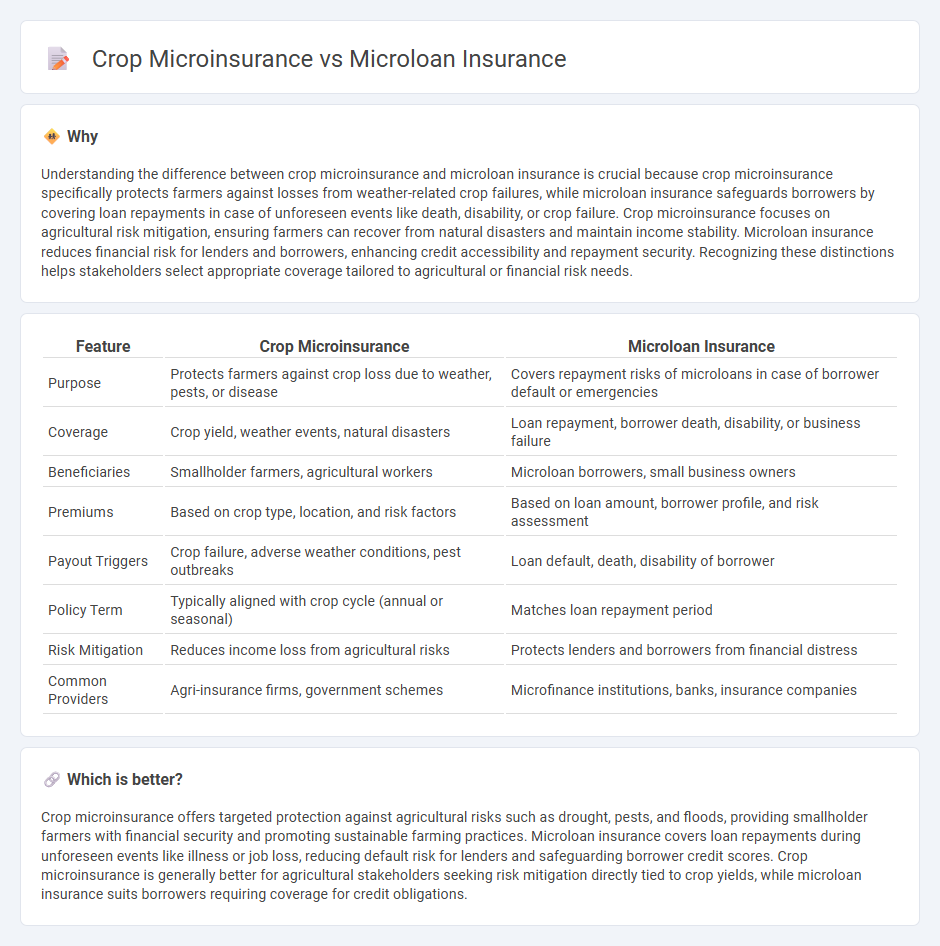
Understanding the difference between crop microinsurance and microloan insurance is crucial because crop microinsurance specifically protects farmers against losses from weather-related crop failures, while microloan insurance safeguards borrowers by covering loan repayments in case of unforeseen events like death, disability, or crop failure. Crop microinsurance focuses on agricultural risk mitigation, ensuring farmers can recover from natural disasters and maintain income stability. Microloan insurance reduces financial risk for lenders and borrowers, enhancing credit accessibility and repayment security. Recognizing these distinctions helps stakeholders select appropriate coverage tailored to agricultural or financial risk needs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Crop Microinsurance | Microloan Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects farmers against crop loss due to weather, pests, or disease | Covers repayment risks of microloans in case of borrower default or emergencies |
| Coverage | Crop yield, weather events, natural disasters | Loan repayment, borrower death, disability, or business failure |
| Beneficiaries | Smallholder farmers, agricultural workers | Microloan borrowers, small business owners |
| Premiums | Based on crop type, location, and risk factors | Based on loan amount, borrower profile, and risk assessment |
| Payout Triggers | Crop failure, adverse weather conditions, pest outbreaks | Loan default, death, disability of borrower |
| Policy Term | Typically aligned with crop cycle (annual or seasonal) | Matches loan repayment period |
| Risk Mitigation | Reduces income loss from agricultural risks | Protects lenders and borrowers from financial distress |
| Common Providers | Agri-insurance firms, government schemes | Microfinance institutions, banks, insurance companies |
Which is better?
Crop microinsurance offers targeted protection against agricultural risks such as drought, pests, and floods, providing smallholder farmers with financial security and promoting sustainable farming practices. Microloan insurance covers loan repayments during unforeseen events like illness or job loss, reducing default risk for lenders and safeguarding borrower credit scores. Crop microinsurance is generally better for agricultural stakeholders seeking risk mitigation directly tied to crop yields, while microloan insurance suits borrowers requiring coverage for credit obligations.
Connection
Crop microinsurance and microloan insurance are interconnected financial products aimed at supporting small-scale farmers and low-income borrowers by mitigating risks related to agriculture and credit repayment. Crop microinsurance protects farmers against losses from adverse weather or pests, improving their ability to repay microloans by stabilizing income streams. This risk-sharing mechanism enhances credit access by reducing the default risk for microloan providers, thereby fostering financial inclusion and agricultural resilience.
Key Terms
Microloan insurance:
Microloan insurance provides financial protection to microfinance borrowers by covering loan repayments in case of unforeseen events like illness, job loss, or death, ensuring loan recovery and minimizing default risks for lenders. Unlike crop microinsurance, which specifically addresses agricultural risks such as weather damage or pest infestation, microloan insurance applies broadly to various microloans across different sectors. Explore more about how microloan insurance secures microfinance ecosystems and enhances borrower resilience.
Credit risk
Microloan insurance primarily mitigates credit risk by protecting lenders against borrower default by covering outstanding loan balances in cases of non-payment. Crop microinsurance targets farmers, managing credit risk through coverage against crop failure caused by weather events, pests, or diseases, which directly affect the farmer's ability to repay loans. Explore the distinctions and benefits of these insurance types for effective risk management strategies.
Borrower default
Microloan insurance primarily covers lender losses from borrower default, providing financial protection against unpaid loans in microfinance. Crop microinsurance, while including borrower default risk, mainly protects farmers against agricultural losses due to weather, pests, or natural disasters affecting crop yield. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how these insurance types mitigate risks in agricultural lending and borrower defaults.
Source and External Links
Microfinance and Microinsurance Tools for Poverty - Microinsurance, often bundled with microloans, provides financial protection against specific risks for low-income individuals.
Providing Health Insurance through Microfinance Networks in Rural Karnataka, India - Bundling health insurance with microloans can help mitigate financial shocks but may reduce loan renewal rates due to increased costs.
Microloans | U.S. Small Business Administration - While focused on small business loans, there is no specific mention of insurance directly linked to these microloans, but they can be used for various business purposes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com