Parametric insurance offers predefined payouts based on specific event triggers such as weather conditions or natural disasters, bypassing traditional claim adjustments. Reinsurance provides insurance to insurance companies, allowing them to manage risk exposure and maintain financial stability after substantial claims. Explore how these innovative risk management solutions can enhance coverage strategies and financial resilience.
Why it is important
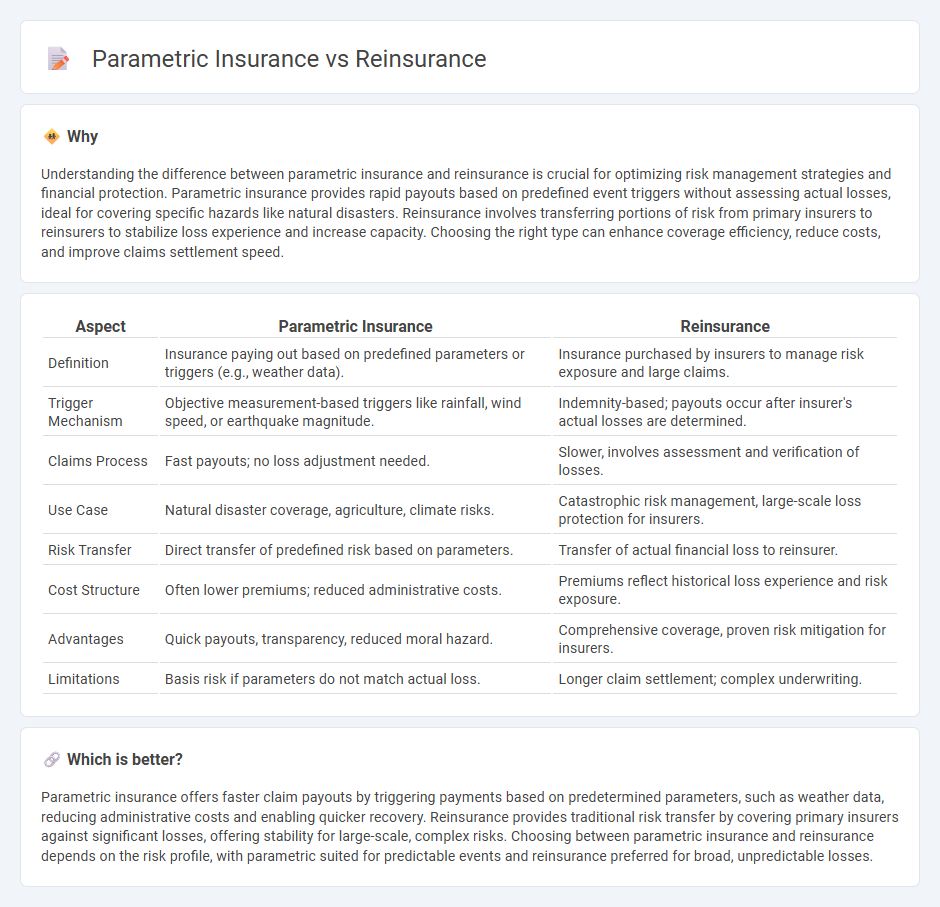
Understanding the difference between parametric insurance and reinsurance is crucial for optimizing risk management strategies and financial protection. Parametric insurance provides rapid payouts based on predefined event triggers without assessing actual losses, ideal for covering specific hazards like natural disasters. Reinsurance involves transferring portions of risk from primary insurers to reinsurers to stabilize loss experience and increase capacity. Choosing the right type can enhance coverage efficiency, reduce costs, and improve claims settlement speed.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Parametric Insurance | Reinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insurance paying out based on predefined parameters or triggers (e.g., weather data). | Insurance purchased by insurers to manage risk exposure and large claims. |
| Trigger Mechanism | Objective measurement-based triggers like rainfall, wind speed, or earthquake magnitude. | Indemnity-based; payouts occur after insurer's actual losses are determined. |
| Claims Process | Fast payouts; no loss adjustment needed. | Slower, involves assessment and verification of losses. |
| Use Case | Natural disaster coverage, agriculture, climate risks. | Catastrophic risk management, large-scale loss protection for insurers. |
| Risk Transfer | Direct transfer of predefined risk based on parameters. | Transfer of actual financial loss to reinsurer. |
| Cost Structure | Often lower premiums; reduced administrative costs. | Premiums reflect historical loss experience and risk exposure. |
| Advantages | Quick payouts, transparency, reduced moral hazard. | Comprehensive coverage, proven risk mitigation for insurers. |
| Limitations | Basis risk if parameters do not match actual loss. | Longer claim settlement; complex underwriting. |
Which is better?
Parametric insurance offers faster claim payouts by triggering payments based on predetermined parameters, such as weather data, reducing administrative costs and enabling quicker recovery. Reinsurance provides traditional risk transfer by covering primary insurers against significant losses, offering stability for large-scale, complex risks. Choosing between parametric insurance and reinsurance depends on the risk profile, with parametric suited for predictable events and reinsurance preferred for broad, unpredictable losses.
Connection
Parametric insurance and reinsurance are interconnected through their reliance on predefined triggers based on measurable parameters, such as weather data or seismic activity, to expedite claims payments without traditional loss assessments. Reinsurers support parametric insurance providers by pooling risks and offering capital to cover large-scale or catastrophic events, enhancing financial stability and risk mitigation. This synergy improves efficiency and liquidity in managing extreme risks across insurance markets.
Key Terms
Risk Transfer
Reinsurance provides risk transfer by allowing insurers to cede portions of their risk portfolios to reinsurers, mitigating losses from large-scale claims. Parametric insurance transfers risk based on predefined triggers such as weather events or natural disasters, offering faster payouts without the need for traditional claims assessments. Explore the distinct advantages of each to optimize your risk management strategy.
Indemnity vs. Trigger
Reinsurance provides indemnity coverage by compensating insurers for actual losses incurred, based on detailed loss assessments and adjustments. Parametric insurance relies on predefined triggers, such as earthquake magnitude or rainfall levels, to activate payouts without evaluating the actual loss. Explore the distinct benefits and applications of indemnity and parametric insurance for a comprehensive understanding.
Coverage Basis
Reinsurance provides traditional indemnity-based coverage by compensating insurers for actual losses incurred, while parametric insurance offers pre-agreed payouts triggered by specific parameters or indices such as weather events without requiring loss assessment. This fundamental difference allows parametric insurance to deliver faster claims settlements and reduce moral hazard but may lead to basis risk if the trigger does not perfectly correlate with the insured loss. Explore the nuances of coverage basis in reinsurance versus parametric insurance to optimize risk management strategies.
Source and External Links
REINSURANCE - The American Council of Life Insurers - Reinsurance is a risk management tool where insurers transfer some or all of their insurance risk to another insurer, called a reinsurer, to spread risk and manage capital.
Insurance Topics | Reinsurance - NAIC - Reinsurance is an essential contract between an insurer and a reinsurer that allows the insurer to transfer risk and reduce the capital it must hold, helping to stabilize underwriting results and expand insurance capacity.
Background on: Reinsurance | III - Reinsurance is insurance for insurance companies, enabling primary insurers to transfer financial risk to reinsurers, who assume all or part of the liability from the original insurance policies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com