Peer-to-peer insurance leverages group collaboration to share risks among members, reducing reliance on traditional insurance providers and often lowering costs. Microinsurance targets low-income individuals by offering affordable, tailored coverage for specific risks such as health, agriculture, or property. Discover the key differences and benefits of Peer-to-peer insurance versus Microinsurance to find the best fit for your protection needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between peer-to-peer insurance and microinsurance is crucial because peer-to-peer insurance involves group-based risk sharing that can lower costs and increase transparency, while microinsurance targets low-income individuals with affordable, tailored coverage for specific risks. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages social networks to pool resources among similar-risk participants, reducing claims fraud and enhancing trust. Microinsurance typically addresses gaps in traditional insurance markets by offering small-scale policies that protect vulnerable populations from financial hardship due to health, agriculture, or disaster-related losses. Knowing these distinctions helps consumers and providers choose appropriate insurance models that best meet financial needs and risk profiles.
Comparison Table
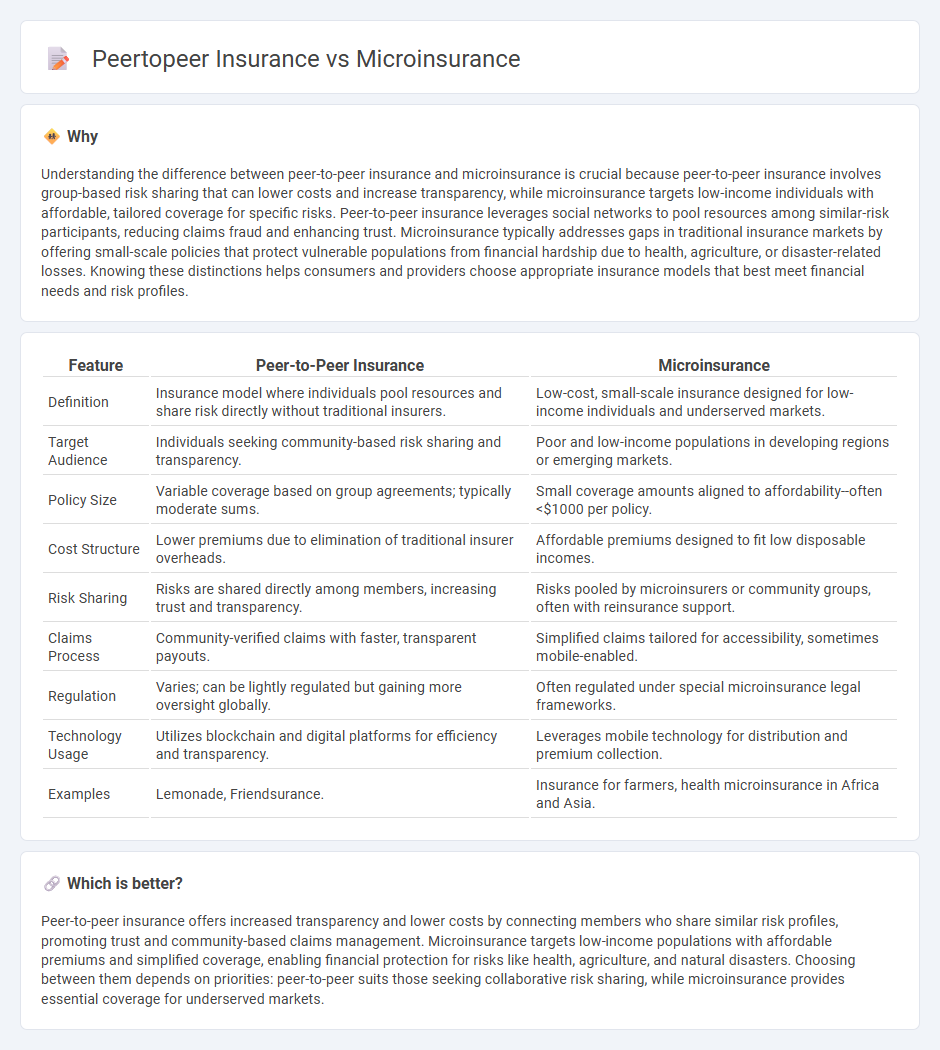
| Feature | Peer-to-Peer Insurance | Microinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insurance model where individuals pool resources and share risk directly without traditional insurers. | Low-cost, small-scale insurance designed for low-income individuals and underserved markets. |
| Target Audience | Individuals seeking community-based risk sharing and transparency. | Poor and low-income populations in developing regions or emerging markets. |
| Policy Size | Variable coverage based on group agreements; typically moderate sums. | Small coverage amounts aligned to affordability--often <$1000 per policy. |
| Cost Structure | Lower premiums due to elimination of traditional insurer overheads. | Affordable premiums designed to fit low disposable incomes. |
| Risk Sharing | Risks are shared directly among members, increasing trust and transparency. | Risks pooled by microinsurers or community groups, often with reinsurance support. |
| Claims Process | Community-verified claims with faster, transparent payouts. | Simplified claims tailored for accessibility, sometimes mobile-enabled. |
| Regulation | Varies; can be lightly regulated but gaining more oversight globally. | Often regulated under special microinsurance legal frameworks. |
| Technology Usage | Utilizes blockchain and digital platforms for efficiency and transparency. | Leverages mobile technology for distribution and premium collection. |
| Examples | Lemonade, Friendsurance. | Insurance for farmers, health microinsurance in Africa and Asia. |
Which is better?
Peer-to-peer insurance offers increased transparency and lower costs by connecting members who share similar risk profiles, promoting trust and community-based claims management. Microinsurance targets low-income populations with affordable premiums and simplified coverage, enabling financial protection for risks like health, agriculture, and natural disasters. Choosing between them depends on priorities: peer-to-peer suits those seeking collaborative risk sharing, while microinsurance provides essential coverage for underserved markets.
Connection
Peer-to-peer insurance and microinsurance both focus on affordable, community-based risk sharing, targeting underinsured or low-income populations. They leverage collective pooling of resources to provide tailored, low-cost coverage options that traditional insurance companies often overlook. This connection enhances financial inclusion by increasing access to insurance products in underserved markets.
Key Terms
Risk Pooling
Microinsurance and peer-to-peer insurance both leverage risk pooling to distribute risk among participants, yet microinsurance typically pools risks across a broader, often underserved population to provide affordable coverage. Peer-to-peer insurance creates smaller, more personalized risk pools where members share premiums and claims directly, enhancing transparency and trust within the group. Explore the differences in risk pooling dynamics between these models to understand which better fits specific insurance needs.
Premium Structure
Microinsurance typically features low, fixed premiums designed to be affordable for low-income individuals, ensuring broad accessibility and risk pooling within defined parameters. Peer-to-peer insurance organizes premiums based on group risk profiles, often pooling member contributions to cover claims collectively, which can lead to more personalized and potentially lower costs. Explore how these distinct premium structures impact affordability and coverage options in modern insurance models.
Claims Management
Microinsurance streamlines claims management by leveraging simplified processes and mobile technology to serve low-income clients efficiently, minimizing paperwork and reducing claim settlement time. Peer-to-peer insurance enhances transparency and trust in claims handling by enabling members to collectively review and approve claims, often facilitated through blockchain or digital platforms that reduce fraud and conflicts of interest. Explore the latest strategies in claims management for microinsurance and peer-to-peer insurance models to optimize customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
Background on: microinsurance and emerging markets | III - Microinsurance provides low-cost insurance to low-income individuals typically not covered by traditional insurance, offering high volume, low cost, and efficient administration, often distributed through microfinance organizations and humanitarian groups.
Microinsurance | Insurance | Milliman | Worldwide - Microinsurance is designed specifically for low-income people with affordable premiums, suitable terms, and accessible delivery, helping vulnerable populations manage risks that can lead to poverty, such as health issues or crop loss.
Unlocking the Global Potential of Microinsurance and Life Insurance - Microinsurance is expanding rapidly due to low insurance penetration and mobile technology enabling distribution to remote and low-income populations, showing potential for both social impact and profitability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com