Cyber risk underwriting focuses on assessing threats related to data breaches, hacking, and digital asset vulnerabilities, while product liability underwriting evaluates potential damages from defective or harmful products. Both require specialized expertise to analyze risk exposure and determine appropriate coverage limits tailored to distinct industries. Explore further to understand how these underwriting approaches protect businesses against evolving risks.
Why it is important
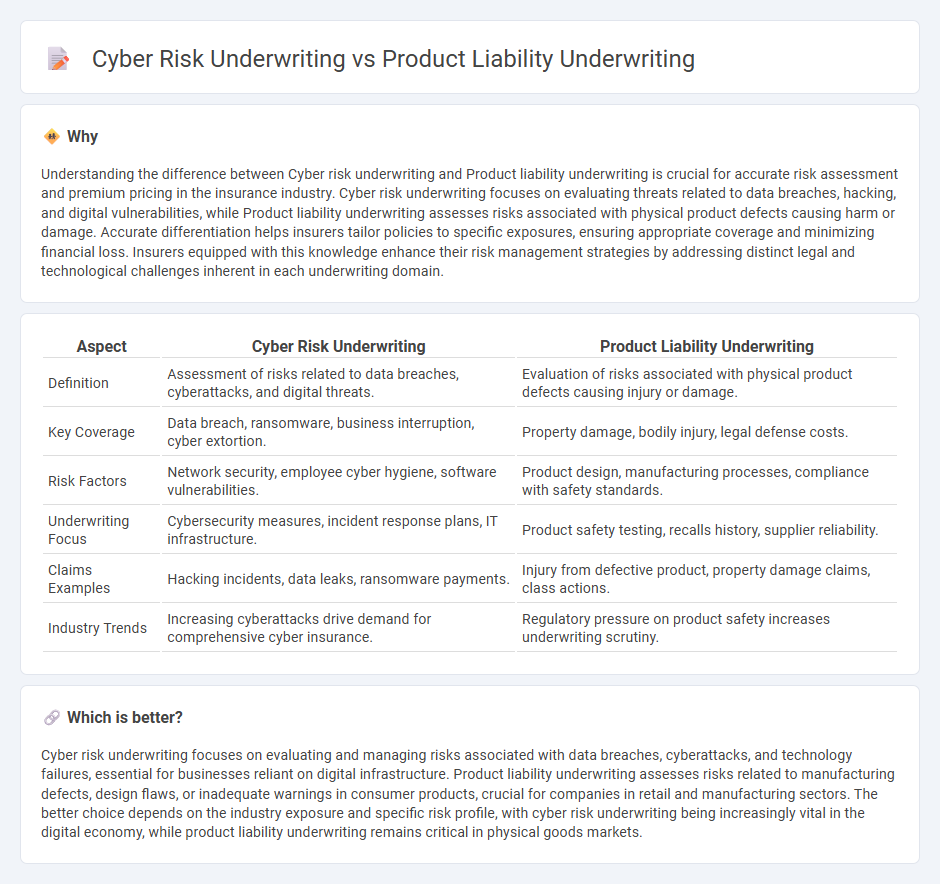
Understanding the difference between Cyber risk underwriting and Product liability underwriting is crucial for accurate risk assessment and premium pricing in the insurance industry. Cyber risk underwriting focuses on evaluating threats related to data breaches, hacking, and digital vulnerabilities, while Product liability underwriting assesses risks associated with physical product defects causing harm or damage. Accurate differentiation helps insurers tailor policies to specific exposures, ensuring appropriate coverage and minimizing financial loss. Insurers equipped with this knowledge enhance their risk management strategies by addressing distinct legal and technological challenges inherent in each underwriting domain.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cyber Risk Underwriting | Product Liability Underwriting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assessment of risks related to data breaches, cyberattacks, and digital threats. | Evaluation of risks associated with physical product defects causing injury or damage. |
| Key Coverage | Data breach, ransomware, business interruption, cyber extortion. | Property damage, bodily injury, legal defense costs. |
| Risk Factors | Network security, employee cyber hygiene, software vulnerabilities. | Product design, manufacturing processes, compliance with safety standards. |
| Underwriting Focus | Cybersecurity measures, incident response plans, IT infrastructure. | Product safety testing, recalls history, supplier reliability. |
| Claims Examples | Hacking incidents, data leaks, ransomware payments. | Injury from defective product, property damage claims, class actions. |
| Industry Trends | Increasing cyberattacks drive demand for comprehensive cyber insurance. | Regulatory pressure on product safety increases underwriting scrutiny. |
Which is better?
Cyber risk underwriting focuses on evaluating and managing risks associated with data breaches, cyberattacks, and technology failures, essential for businesses reliant on digital infrastructure. Product liability underwriting assesses risks related to manufacturing defects, design flaws, or inadequate warnings in consumer products, crucial for companies in retail and manufacturing sectors. The better choice depends on the industry exposure and specific risk profile, with cyber risk underwriting being increasingly vital in the digital economy, while product liability underwriting remains critical in physical goods markets.
Connection
Cyber risk underwriting and product liability underwriting intersect through the assessment of technological risks associated with digital products and services. Both underwriting processes analyze potential financial losses from failures or breaches, with cyber risk underwriting focusing on data breaches and cyberattacks, while product liability underwriting addresses harm caused by defective digital or IoT-enabled products. Effective risk management in these domains requires integrating cybersecurity measures and product safety standards to mitigate liabilities in technology-driven markets.
Key Terms
**Product liability underwriting:**
Product liability underwriting involves assessing risks related to manufacturing defects, design flaws, or insufficient warnings that could cause harm to consumers, emphasizing product safety standards and regulatory compliance. Underwriters evaluate historical claims data, product lifecycle, and recall potential to determine appropriate coverage terms and premiums. Explore more about the critical factors driving effective product liability risk management and underwriting strategies.
Bodily Injury
Product liability underwriting emphasizes assessing risks related to bodily injury caused by defective products, involving deep analysis of manufacturing processes, product design, and safety standards. Cyber risk underwriting, while primarily centered on data breaches and financial loss, increasingly considers potential bodily injury claims arising from cyber-attacks on critical infrastructure or medical devices. Explore our comprehensive guide to understand how these underwriting approaches address bodily injury exposures in their respective domains.
Defective Product
Product liability underwriting centers on assessing risks related to defective products that cause harm or injury, emphasizing factors such as manufacturing defects, design flaws, and failure to provide adequate warnings. Cyber risk underwriting involves evaluating exposures tied to digital threats, data breaches, and system vulnerabilities, but it rarely intersects directly with defective product claims unless products include embedded software causing malfunctions. Explore further distinctions and nuanced risk factors between these underwriting specialties to enhance your risk management strategy.
Source and External Links
Product Liability Insurance Explained - This document explains how product liability insurance protects businesses from claims related to manufacturing or selling defective products, covering manufacturing flaws, design defects, and inadequate warnings.
What is Product Liability? - This webpage explores the legal aspects of product liability, including strict liability, negligence, and breach of warranty, which are key elements in product liability claims.
Products Liability Risk Is Constantly Evolving - This article discusses the evolving nature of products liability risks and the need for underwriters to have deep expertise in understanding client exposures and managing risk effectively.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com