Invisible insurance integrates coverage seamlessly into everyday purchases, offering protection without separate policies, while microinsurance provides affordable, tailored insurance solutions for low-income individuals or specific risks. Both innovations address accessibility gaps in traditional insurance markets, enhancing financial security for underserved populations. Explore how these insurance models transform risk management and financial inclusion.
Why it is important
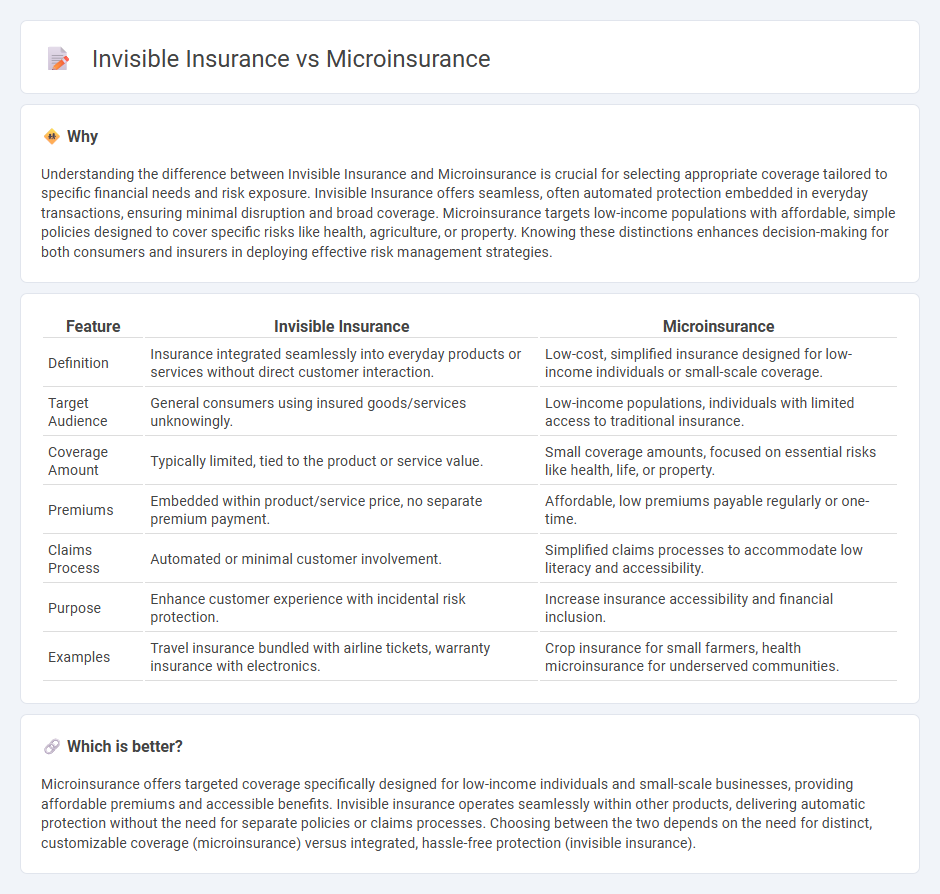
Understanding the difference between Invisible Insurance and Microinsurance is crucial for selecting appropriate coverage tailored to specific financial needs and risk exposure. Invisible Insurance offers seamless, often automated protection embedded in everyday transactions, ensuring minimal disruption and broad coverage. Microinsurance targets low-income populations with affordable, simple policies designed to cover specific risks like health, agriculture, or property. Knowing these distinctions enhances decision-making for both consumers and insurers in deploying effective risk management strategies.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Invisible Insurance | Microinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insurance integrated seamlessly into everyday products or services without direct customer interaction. | Low-cost, simplified insurance designed for low-income individuals or small-scale coverage. |
| Target Audience | General consumers using insured goods/services unknowingly. | Low-income populations, individuals with limited access to traditional insurance. |
| Coverage Amount | Typically limited, tied to the product or service value. | Small coverage amounts, focused on essential risks like health, life, or property. |
| Premiums | Embedded within product/service price, no separate premium payment. | Affordable, low premiums payable regularly or one-time. |
| Claims Process | Automated or minimal customer involvement. | Simplified claims processes to accommodate low literacy and accessibility. |
| Purpose | Enhance customer experience with incidental risk protection. | Increase insurance accessibility and financial inclusion. |
| Examples | Travel insurance bundled with airline tickets, warranty insurance with electronics. | Crop insurance for small farmers, health microinsurance for underserved communities. |
Which is better?
Microinsurance offers targeted coverage specifically designed for low-income individuals and small-scale businesses, providing affordable premiums and accessible benefits. Invisible insurance operates seamlessly within other products, delivering automatic protection without the need for separate policies or claims processes. Choosing between the two depends on the need for distinct, customizable coverage (microinsurance) versus integrated, hassle-free protection (invisible insurance).
Connection
Invisible insurance and microinsurance both aim to increase insurance accessibility by embedding coverage into everyday transactions or offering low-cost, targeted policies. Invisible insurance integrates protection seamlessly into products or services, while microinsurance provides affordable, small-scale coverage for low-income populations. Together, they address insurance gaps by simplifying enrollment and reducing financial barriers.
Key Terms
Accessibility
Microinsurance targets low-income populations by offering affordable, simplified policies that cover essential risks like health, agriculture, and property, enhancing financial accessibility. Invisible insurance integrates coverage seamlessly into everyday transactions or products, removing the need for direct customer involvement and increasing access for underserved groups. Explore the differences and benefits of these innovative insurance models to understand their impact on expanding financial inclusion.
Coverage Transparency
Microinsurance provides low-cost, accessible coverage targeting low-income populations with clear policy terms, while invisible insurance integrates protection seamlessly into everyday products and services, often lacking explicit coverage disclosure. Coverage transparency in microinsurance enhances trust and understanding among policyholders, whereas invisible insurance raises concerns about hidden terms and potential consumer confusion. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how each approach impacts policyholder awareness and protection.
Premium Structure
Microinsurance features low-premium structures designed to cater to low-income individuals, typically offering basic coverage with affordable payments made weekly or monthly. Invisible insurance often integrates premiums into everyday transactions or services, making payments seamless and unobtrusive without requiring explicit budgeting from the insured. Explore the nuances of premium strategies to understand which insurance model best fits your financial needs.
Source and External Links
Microinsurance - Microinsurance is a type of insurance designed for low-income individuals, offering low premiums and coverage against specific risks.
Background on Microinsurance and Emerging Markets - This article discusses how microinsurance projects provide low-cost insurance to individuals in developing countries, often through partnerships with microfinance organizations.
Microinsurance Network - The Microinsurance Network is an international platform that brings together experts to advance inclusive insurance for low-income populations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com