Ghost broking involves fraudsters selling fake or altered insurance policies, deceiving customers and leaving them unprotected when claims arise. Bad faith occurs when an insurance company refuses to pay legitimate claims or delays settlements without reasonable cause, violating policyholder rights. Discover how to identify risks and protect yourself from these insurance pitfalls.
Why it is important
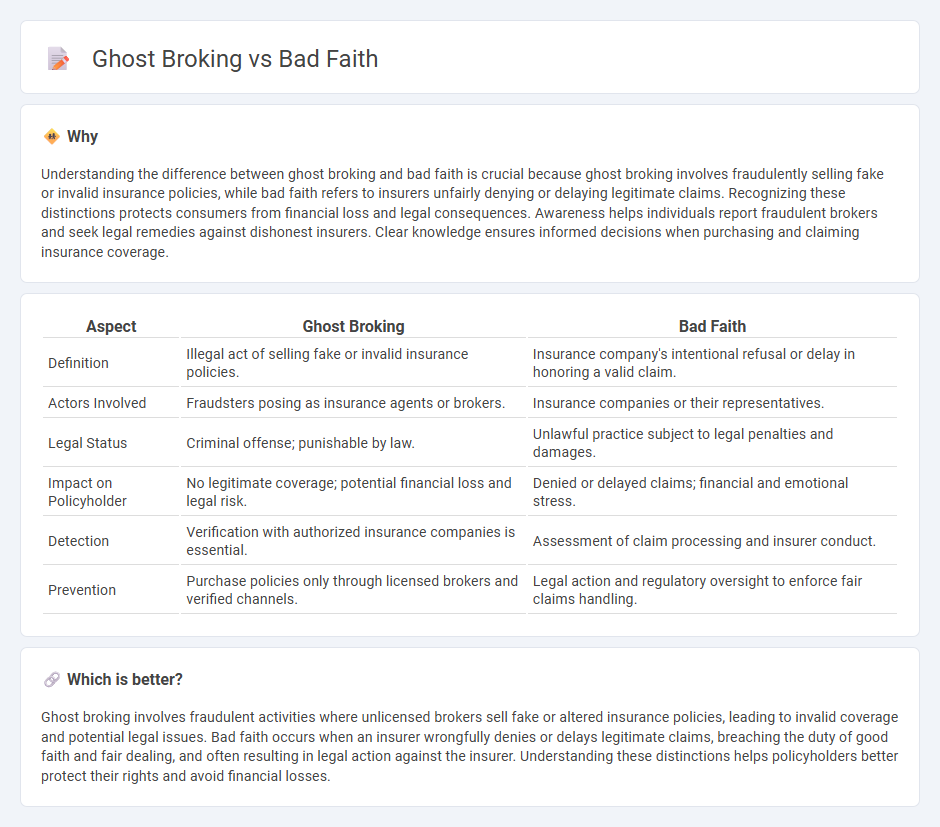
Understanding the difference between ghost broking and bad faith is crucial because ghost broking involves fraudulently selling fake or invalid insurance policies, while bad faith refers to insurers unfairly denying or delaying legitimate claims. Recognizing these distinctions protects consumers from financial loss and legal consequences. Awareness helps individuals report fraudulent brokers and seek legal remedies against dishonest insurers. Clear knowledge ensures informed decisions when purchasing and claiming insurance coverage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Broking | Bad Faith |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Illegal act of selling fake or invalid insurance policies. | Insurance company's intentional refusal or delay in honoring a valid claim. |
| Actors Involved | Fraudsters posing as insurance agents or brokers. | Insurance companies or their representatives. |
| Legal Status | Criminal offense; punishable by law. | Unlawful practice subject to legal penalties and damages. |
| Impact on Policyholder | No legitimate coverage; potential financial loss and legal risk. | Denied or delayed claims; financial and emotional stress. |
| Detection | Verification with authorized insurance companies is essential. | Assessment of claim processing and insurer conduct. |
| Prevention | Purchase policies only through licensed brokers and verified channels. | Legal action and regulatory oversight to enforce fair claims handling. |
Which is better?
Ghost broking involves fraudulent activities where unlicensed brokers sell fake or altered insurance policies, leading to invalid coverage and potential legal issues. Bad faith occurs when an insurer wrongfully denies or delays legitimate claims, breaching the duty of good faith and fair dealing, and often resulting in legal action against the insurer. Understanding these distinctions helps policyholders better protect their rights and avoid financial losses.
Connection
Ghost broking involves fraudsters using counterfeit insurance documents to illegally sell policies, which often leads to claims denial due to invalid coverage. Bad faith occurs when insurers unjustly refuse or delay legitimate claims, exacerbating financial harm to policyholders already victimized by ghost broking schemes. Both practices undermine consumer trust in the insurance industry and highlight the need for stringent verification processes and regulatory enforcement.
Key Terms
Misrepresentation
Bad faith insurance practices involve deliberate misrepresentation to deceive policyholders and evade claims, while ghost broking entails fraudulent agents selling fake or invalid insurance policies by misrepresenting their legitimacy. Misrepresentation in bad faith often occurs within insurer actions, undermining trust and contractual obligations, whereas ghost broking targets unsuspecting consumers through false promises and forged documents. Explore more to understand how these deceptive tactics impact insurance fraud and consumer protection strategies.
Claim denial
Bad faith in insurance involves deliberate claim denial or underpayment by insurers to avoid payouts, often exploiting policy ambiguities or misrepresenting terms. Ghost broking refers to fraudulent intermediaries selling fake or invalid insurance policies, leading to claim denials due to non-existent or insufficient coverage. Learn more about how to identify and protect yourself from these deceptive practices affecting insurance claims.
Fraud
Bad faith insurance claims involve intentional dishonesty by policyholders to receive unwarranted benefits, resulting in significant financial losses for insurers. Ghost broking refers to fraudulent activities where criminals impersonate licensed insurance brokers to sell fake or invalid insurance policies, often leaving customers uninsured and exposed to legal risks. Explore how to identify and protect yourself from these types of insurance fraud to safeguard your financial security.
Source and External Links
Bad faith - Wikipedia - Bad faith (Latin: mala fides) is a sustained form of deception involving pretending to have one set of feelings while acting under another, associated with hypocrisy, breach of contract, and deceit in various contexts including philosophy, legal, and social settings.
Bad faith | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - Bad faith in law refers to dishonesty, fraud, or neglect of fair dealing in transactions, including acting with a dishonest purpose or breaching the duty to deal fairly in contracts.
Bad Faith (film) - Wikipedia - "Bad Faith: Christian Nationalism's Unholy War on Democracy" is a 2024 American documentary analyzing the rise of Christian nationalism in the U.S. and its opposition to democracy, illustrating political manipulation and ideological deception.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com